Abstract
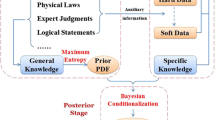
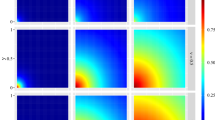
This paper is concerned with a computational formulation of the Bayesian maximum entropy (BME) mapping method, which can handle rigorously and efficiently spatiotemporal applications of considerable practical importance. BME is a method of modern geostatistics that can integrate and process physical knowledge that belongs to two major bases: general knowledge (i.e., obtained from general principles and laws, summary statistics and background information), and specificatory knowledge (i.e., obtained through experience with the specific situation). BME allows considerable flexibility regarding the choice of an appropriate spatiotemporal map, offers a complete assessment of the mapping uncertainty and contributes to the scientific understanding of the underlying natural phenomenon. Valuable insight is gained by studying a spatiotemporal data set representing water-level elevations at the Equus Beds aquifer (Kansas). Numerical results show that, as was expected in theory, classical geostatistics analysis is obtained as a special case of the considerably more general BME approach. Moreover, modern geostatistical analysis in terms of BME offers more accurate and informative results in practice, by incorporating various sources of physical knowledge that cannot be processed by the classical methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serre, M., Christakos, G. Modern geostatistics: computational BME analysis in the light of uncertain physical knowledge – the Equus Beds study. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment 13, 1–26 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004770050029
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004770050029