Abstract
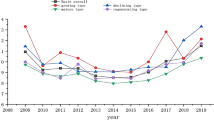
Green development is an important path to achieve sustainable development, which has attracted worldwide attention. However, the evaluation system of green development efficiency (GDE) and the spatial-temporal heterogeneity of factors affecting GDE are still critical gaps that need to be filled. Here, based on the panel data of 59 prefecture-level cities in Yellow River Basin from 2007 to 2019, we improve the evaluation system to measure GDE, and explore the influencing factors of GDE and their spatial-temporal heterogeneity. From our results, the GDE of Yellow River Basin has improved from 0.56 to 0.87, but it still needs further improvement. Industrial upgrading, technological innovation and transport infrastructure are main factors affecting GDE. More importantly, the influence of these factors has significant time-lag effect and spatial differences. Therefore, the green development of Yellow River Basin should not only restore the ecological environment, but also take account of key factors affecting regional GDE according to local conditions, ultimately achieving a win-win situation between ecological environmental conservation and social-economic development.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahi P, Searcy C (2014) A stochastic approach for sustainability analysis under the green economics paradigm. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28:1743–1753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-013-0836-5
Bao Z, Zhang J, Wang G, Chen Q, Wang J (2019) The impact of climate variability and land use/cover change on the water balance in the Middle Yellow River Basin, China. J Hydrol 577:123942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123942
Basheer M, Nechifor V, Calzadilla A, Ringler C, Hulme D, Harou J (2022) Balancing national economic policy outcomes for sustainable development. Nat Commun 13:5041. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32415-9
Cai Z, Li W, Cao S (2021) Driving factors for coordinating urbanization with conservation of the ecological environment in China. Ambio 50:1269–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-020-01458-x
Cao S, Zhong B, Yue H, Zeng H, Zeng J (2009) Development and testing of a sustainable environmental restoration policy on eradicating the poverty trap in China’s Changting County. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(26):10712–10716. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0900197106
Cao S, Xia C, Li W, Xian J (2020) Win–win path for ecological restoration. Land Degrad Dev 32(1):430–438. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3739
Chen W, Shen Y, Wang Y (2018) Evaluation of economic transformation and upgrading of resource-based cities in Shaanxi province based on an improved TOPSIS method. Sust Cities Soc 37:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2017.11.019
Chen L, Zhang X, He F, Yuan R (2019) Regional green development level and its spatial relationship under the constraints of haze in China. J Clean Prod 210:376–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.037
Ding TH, Chen JF (2022) Evaluation and obstacle factors of coordination development of regional water-energy-food-ecology system under green development: a case study of Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 36:2477–2493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-02114-w
Ding J, Liu B, Shao X (2022) Spatial effects of industrial synergistic agglomeration and regional green development efficiency: evidence from China. Energy Econ 112:106156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106156
Dong F, Li Y, Qin C, Sun J (2021) How industrial convergence affects regional green development efficiency: a spatial conditional process analysis. J Environ Manage 300:113738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113738
Fan F, Lian H, Liu X, Wang X (2021) Can environmental regulation promote urban green innovation efficiency? An empirical study based on chinese cities. J Clean Prod 287:125060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125060
Fang G, Wang Q, Tian L (2020) Green development of Yangtze River Delta in China under population-resources-environment-development-satisfaction perspective. Sci Total Environ 727:138710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138710
Fay M, Hallegatte S, Bank W (2012) Inclusive green growth: the pathway to Sustainable Development. World Bank, Washington, DC
Feng C, Wang M, Liu G, Huang J (2017) Green development performance and its influencing factors: a global perspective. J Clean Prod 144:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.005
Fukuyama H, Weber W (2009) A directional slacks-based measure of technical inefficiency. Socio-Econ Plan Sci 43(4):274–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2008.12.001
Guo Y, Tong L, Mei L (2020) The effect of industrial agglomeration on green development efficiency in Northeast China since the revitalization. J Clean Prod 258:120584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120584
Guo L, Zhu W, Wei J, Wang L (2022) Water demand forecasting and countermeasures across the Yellow River basin: analysis from the perspective of water resources carrying capacity. J Hydrol 42:101148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2022.101148
He C, Huang Z, Ye X (2014) Spatial heterogeneity of economic development and industrial pollution in urban China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28:767–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-013-0736-8
Hou D, Li G, Chen D, Zhu B, Hu S (2019) Evaluation and analysis on the green development of China’s industrial parks using the long-tail effect model. J Environ Manage 248:109288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109288
Khan S, Cui Y, Khan A, Ali M, Khan A, Xia X, Liu G, Zhao M (2021) Tracking sustainable development efficiency with human-environmental system relationship: an application of DPSIR and super efficiency SBM model. Sci Total Environ 783:146959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146959
Li W, Cai Z (2022) Spatiotemporal differences and influencing factors of high–quality utilization of land resources in the Yellow River Basin of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22077-x
Li X, Zhang X, Wang S (2021) Managing conflicts and equitability in hierarchical decision making for water resources planning under fuzzy uncertainty: a case study of Yellow River, China. J Hydrol 38:100963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100963
Li W, Cai X, Jin L (2022) Spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of the coupling coordinated development of production-living-ecology system in China. Ecol Indic 145:109738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109738
Liao B, Li L (2022) Urban green innovation efficiency and its influential factors: the chinese evidence. Environ Dev Sustain 25:6551–6573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02316-4
Liu Y, Dong F (2021) How technological innovation impacts urban green economy efficiency in emerging economies: a case study of 278 chinese cities. Resour Conserv Recycl 169:105534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105534
Liu L, Yang YR, Liu S, Gong XJ, Zhao YT, Jin RF, Duan HY, Jiang P (2023) A comparative study of green growth efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Belt and Yellow River Basin between 2010 and 2020. Ecol Indic 150:110214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110214
Loiseau E, Saikku L, Antikainen R, Droste N, Hansjürgens B, Pitkänen K, Leskinen P, Kuikman P, Thomsen M (2016) Green economy and related concepts: an overview. J Clean Prod 139:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.024
Long LJ, Wang X, Guo B (2017) Evaluation of urban ecological well-being performance based on revised DEA model—A case study of 35 major cities in China. J Nat Resour 32(4):69–79. https://doi.org/10.11849/zrzyxb.20160515
Long RY, Li HF, Wu MF, Li WB (2021) Dynamic evaluation of the green development level of China’s coal-resource-based cities using the TOPSIS method. Resour Policy 74:102415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102415
Lu W, Zhang G (2022) Green development efficiency of urban agglomerations in a developing country: evidence from Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei in China. Environ Dev Sustain 25:6939–6962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02341-3
National Bureau of Statistics (2021) China statistical yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Oh D (2010) A global Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index. J Prod Anal 34(3):183–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11123-010-0178-y
Pearce DW, Markandya A, Barbier EB (1989) Blueprint for a Green Economy. Earthscan, London. https://doi.org/10.9774/gleaf.978-1-907643-44-6_16
Peng YX, Chen Z, Lee J (2020) Dynamic convergence of green total factor productivity in chinese cities. Sustainability 12(12):4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124883
Qin CY, Yang CXG, Zhang M, Zhu BZ (2023) Does high-speed rail improve green development? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. J Clean Prod 407:137174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137174
Qiu M, Zuo Q, Wu Q, Yang Z, Zhang J (2022) Water ecological security assessment and spatial autocorrelation analysis of prefectural regions involved in the Yellow River Basin. Sci Rep 12:5105. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-07656-9
Ren YF, Fang CL, Lin XQ, Sun A, Li GD, Fan BL (2019) Evaluation of the eco-efciency of four major urban agglomerations in coastal eastern China. J Geogr Sci 29(8):1315–1330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-019-1661-7
Song X, Zhou Y, Jia W (2019) How do economic openness and R&D investment affect green economic growth? —Evidence from China. Resour Conserv Recycl 146:405–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.050
Su S, Zhang F (2020) Modeling the role of environmental regulations in regional green economy efficiency of China: empirical evidence from super efficiency DEA-Tobit model. J Environ Manage 261:110227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110227
Tao XP, Wang P, Zhu BZ (2016) Provincial green economic efficiency of China: a non-separable input–output SBM approach. Appl Energy 171:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.02.133
Tobin J (1958) Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econometrica 26(1):24–36. https://doi.org/10.2307/1907382
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):498–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00407-5
Tone K (2002) A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 143:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2009.12.007
United Nations (2015) Transforming our world: the 2030 agenda for sustainable development. United Nations, New York
Wang SJ, Ma HT, Zhao YB (2014) Exploring the relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment-a case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Ecol Indic 45:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.04.006
Wang M, Zhao H, Cui J, Fan D, Lv B, Wang G, Li Z, Zhou G (2018) Evaluating green development level of nine cities within the Pearl River Delta, China. J Clean Prod 174:315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.328
Wang SY, Zhang YX, Wen HW (2021) Comprehensive measurement and regional imbalance of China’s green development performance. Sustainability 13(3):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031409
Wohlfart C, Kuenzer C, Chen C, Liu G (2016) Social–ecological challenges in the Yellow River basin (China): a review. Environ Earth Sci 75:1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5864-2
Wursthom S, Poganielz WR, Schebek L (2011) Economic environmental monitoring indicators for european countries: a disaggregated sector based approach for monitoring eco-efciency. Ecol Econ 70(3):487–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2010.09.033
Xi J (2019) Speech at the symposium on ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. Water Resour Dev Manage 11:1–4. https://doi.org/10.16616/j.cnki.10-1326/TV.2019.11.01
Yang Q, Wan XZ, Ma HM (2015) Assessing green development efficiency of municipalities and provinces in China integrating models of super-efficiency DEA and Malmquist index. Sustainability 7(4):4492–4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7044492
Yang Y, Guo H, Chen L, Liu X, Gu M, Ke X (2019) Regional analysis of the green development level differences in chinese mineral resource-based cities. Resour Policy 61:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.02.003
Yang T, Zhou K, Zhang C (2022a) Spatiotemporal patterns and influencing factors of green development efficiency in China’s urban agglomerations. Sust Cities Soc 85:104069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.104069
Yang YF, Wang HR, Wang C, Yang B (2022b) Model-based temporal evolution and spatial equilibrium analysis of green development in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2009 to 2018. Ecol Indic 141:109071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109071
Yu X (2023) An assessment of the green development efficiency of industrial parks in China: based on non-desired output and non-radial DEA model. Struct Change and Econ Dyn 66:81–88
Yuan WH, Li JC, Meng L, Qin XN, Qi XX (2019) Measuring the area green efciency and the infuencing factors in urban agglomeration. J Clean Prod 241:118092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118092
Zeng SZ, Gu JX (2023) Coordination evaluation and dynamic adjustment mechanism of China’s green development at inter-provincial level. Ecol Indic 153:110419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110419
Zhang J, Chang Y, Zhang L, Li D (2018) Do technological innovations promote urban green development? A spatial econometric analysis of 105 cities in China. J Clean Prod 182:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.067
Zhang JZ, Wang S, Zhao WW, Meadows ME, Fu BJ (2022a) Finding pathways to synergistic development of Sustainable Development Goals in China. Hum Soc Sci Commun 9:21. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01036-4
Zhang JZ, Wang S, Pradhan P, Zhao WW, Fu BJ (2022b) Untangling the interactions among the sustainable development goals in China. Sci Bull 67(9):977–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2022.01.006
Zhang JZ, Wang S, Liu YS, Zhao WW, Fu BJ (2022c) Does having more sustainable communities bring better sustainability. Innovation 3(4):100267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100267
Zhao P, Zeng L, Lu H, Zhou Y, Hu H, Wei X (2020) Green economic efficiency and its influencing factors in China from 2008 to 2017: based on the super-SBM model with undesirable outputs and spatial Dubin model. Sci Total Environ 741:140026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140026
Zhou P, Ang B, Poh K (2008) Measuring environmental performance under different environmental DEA technologies. Energy Econ 30(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2006.05.001
Zhou L, Zhou C, Che L, Wang B (2020) Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban green development efficiency in China. J Geogr Sci 30(5):724–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-020-1752-5
Zhu B, Zhang M, Zhou Y, Wang P, Sheng J, He K, He K, Wei Y, Xie R (2019) Exploring the effect of industrial structure adjustment on interprovincial green development efficiency in China: a novel integrated approach. Energy policy 134:110946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.110946
Zhuo C, Deng F (2020) How does China’s western development strategy affect regional green economic efficiency? Sci Total Environ 707:135939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135939
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Program in Social Science: Research on the institutional mechanism and policy system for the coordinated promotion of eco-compensation and rural green development (No.18ZDA048). We are also grateful for the comments and criticisms of the journal’s anonymous reviewers and our colleagues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.J. designed the research, W.L. and Z.C. performed the data analysis and wrote the main manuscript text. All authors have reviewed the manuscript and approved it for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The opinions expressed here are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the position of the government of China or of any other organization. We consent to publish this article in your journal and to transfer copyright to the publisher once the paper has been accepted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Cai, Z. & Jin, L. A spatial-temporal analysis on green development in China’s Yellow River Basin: model-based efficiency evaluation and influencing factors identification. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 37, 4431–4444 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02516-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02516-y