Abstract
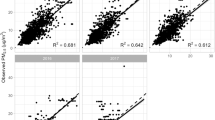
This study estimates intra-daily PM10 concentrations at 213 inland and coastal monitoring sites in Türkiye from 2008 to 2019 using satellite-based aerosol optical depth (AOD) from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). An estimation model based on the random forest (RF) approach was developed using the AOD data from the Terra satellite, the meteorological data, and aerosol diagnostics from the Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, version 2 (MERRA-2), and other auxiliary variables. First, the correlation between the matched PM10 concentrations and MODIS AOD was investigated simply with the quadrant regression (QR) approach. Next, the feature selection procedure was applied to obtain the most significant predictive variables for the estimation model. Then, the spatial and temporal performances of the developed RF model were intensely discussed. Finally, a bias analysis based on the most influential input parameters was also performed to examine the potential errors in the estimated PM10 concentrations. As a result, the RF model showed moderately good performance, with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.72 and low root mean square error (RMSE) over the entire country, which was better than the results of previous studies in the region. Moreover, the model better estimated PM10 concentrations at individual monitoring sites (with R up to 0.90), particularly in coastal regions. However, overfitting occurred in areas with low populations and few monitoring stations. Additionally, the RF model’s performance varied slightly across different seasons, such as autumn (R ≅ 0.69), spring (R ≅ 0.65), winter (R ≅ 0.64), and summer (R ≅ 0.60), and it did not adequately estimate intra-daily PM10 concentrations at the seasonal scale. Furthermore, the bias analyses indicated that higher PM10 and dust mass concentrations, u and v wind components were significant parameters that caused bias in the estimations. Finally, this study provides valuable information for further applications in PM10 patterns and represents the first step toward constructing a high-resolution satellite-based air quality monitoring network in Türkiye.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Alam K, Tariq S et al (2019) Estimating fine particulate concentration using a combined approach of linear regression and artificial neural network. Atmos Environ 219:117050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.117050
Banerjee T, Kumar M, Mall RK, Singh RS (2017) Airing ‘clean air’ in clean India mission. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:6399–6413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8264-y
Barnes MJ, Brade TK, Mackenzie AR et al (2014) Spatially-varying surface roughness and ground-level air quality in an operational dispersion model. Environ Pollut 185:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.039
Biau G, Scornet E (2016) A random forest guided tour. TEST 25:197–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-016-0481-7
Bilal M, Nazeer M, Qiu Z et al (2018) Global validation of MODIS C6 and C6.1 merged aerosol products over diverse vegetated surfaces. Remote Sens 10:475. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030475
Boloorani AD, Nabavi SO, Bahrami HA et al (2014) Investigation of dust storms entering Western Iran using remotely sensed data and synoptic analysis. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:124. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-014-0124-4
Breiman L (2001) Statistical modeling: the two cultures. Stat Sci 16:199–215. https://doi.org/10.1214/ss/1009213726
Che H, Yang L, Liu C et al (2019) Long-term validation of MODIS C6 and C6.1 dark target aerosol products over China using CARSNET and AERONET. Chemosphere 236:124268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.238
Chen G, Wang Y, Li S et al (2018) Spatiotemporal patterns of PM10 concentrations over China during 2005–2016: a satellite-based estimation using the random forests approach. Environ Pollut 242:605–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.012
Chen ZY, Zhang TH, Zhang R et al (2019) Extreme gradient boosting model to estimate PM2.5 concentrations with missing-filled satellite data in China. Atmos Environ 202:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.01.027
Chen G, Li Y, Zhou Y, Shi C, Guo Y, Liu Y (2021) The comparison of AOD-based and non-AOD prediction models for daily PM2.5 estimation in Guangdong province, China with poor AOD coverage. Environ Res 195:110735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110735
Chu DA, Kaufman YJ, Zibordi G et al (2003) Global monitoring of air pollution over land from the earth observing system-terra moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). J Geophys Res Atmos 108:4661. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002jd003179
Di Q, Kloog I, Koutrakis P et al (2016) Assessing PM2.5 exposures with high spatiotemporal resolution across the continental United States. Environ Sci Technol 50:4712–4721. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b06121
Didan K, Munoz AB (2019) MODIS vegetation index user’s guide (MOD13 Series). University of Arizona: vegetation index and phenology lab. Retrieved December, 30 2020 from: https://vip.arizona.edu/MODIS_UsersGuide.php
Dündar C, Oğuz K, Güllü G (2013) Evaluation of sand and dust storms (SDS) over eastern mediterranean Basin. In: 10th national environmental engineering congress, September, pp 12–14, HacettepeUniversity, Ankara
Elbir T (2004) A GIS based decision support system for estimation, visualization and analysis of air pollution for large Turkish cities. Atmos Environ 38:4509–4517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.05.033
Elbir T, Müezzinoǧlu A, Bayram A (2000) Evaluation of some air pollution indicators in Turkey. Environ Int 26:5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(00)00071-4
Elbir T, Mangir N, Kara M et al (2010) Development of a GIS-based decision support system for urban air quality management in the city of Istanbul. Atmos Environ 44:441–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.11.008
Engel-Cox JA, Hoff RM, Haymet ADJ (2004) Recommendations on the use of satellite remote-sensing data for urban air quality. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 54:1360–1371. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2004.10471005
Erdun H, Öztürk A, Çapraz Ö, Toros H, Dursun S, Deniz A (2015) Spatial variation of PM10 in Turkey. In: 7th atmospheric science symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, pp 311–323
European Environment Agency (EEA) (2019). Air quality in Europe—2019 report. EEA Report No 10/2019, Copenhagen, Denmark, https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-quality-in-europe-2019
Feng L, Li Y, Wang Y, Du Q (2020) Estimating hourly and continuous ground-level PM2.5 concentrations using an ensemble learning algorithm: the ST-stacking model. Atmos Environ 223:117242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.117242
Gelaro R, McCarty W, Suárez MJ et al (2017) The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J Clim 30:5419–5454. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0758.1
Georgoulias AK, Alexandri G, Kourtidis KA et al (2016) Spatiotemporal variability and contribution of different aerosol types to the aerosol optical depth over the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos Chem Phys 16:13853–13884. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-13853-2016
Ghahremanloo M, Choi Y, Sayeed A et al (2021) Estimating daily high-resolution PM2.5 concentrations over Texas: machine learning approach. Atmos Environ 247:118209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118209
Gündoğdu S, Tuna Tuygun G, Li Z, Wei J, Elbir T (2022) Estimating daily PM2.5 concentrations using an extreme gradient boosting model based on VIIRS aerosol products over southeastern Europe. Air Qual Atmos Health 15:2185–2198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-022-01245-5
Gupta P, Christopher SA (2009) Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: multiple regression approach. J Geophys Res Atmos 114:D14205. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD011496
He Q, Zhang M, Huang B, Tong X (2017) MODIS 3 km and 10 km aerosol optical depth for China: evaluation and comparison. Atmos Environ 153:150–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.01.023
Hengl T, Nussbaum M, Wright MN et al (2018) Random forest as a generic framework for predictive modeling of spatial and spatio-temporal variables. PeerJ 6:e5518. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5518
Hu X, Belle JH, Meng X et al (2017) Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in the conterminous United States using the random forest approach. Environ Sci Technol 51:6936–6944. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b01210
Huang Y, Zhu B, Zhou X et al (2019) Evaluation and comparison of MODIS collection 6.1 and collection 6 dark target aerosol optical depth over mainland China under various conditions including spatiotemporal distribution, haze effects, and the underlying surface. Earth Space Sci 6(12):2575–2592
Ichoku C, Allen Chu D, Mattoo S et al (2002) A spatio-temporal approach for global validation and analysis of MODIS aerosol products. Geophys Res Lett 29:MOD1-1-MOD1-4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001GL013206
Jiang T, Chen B, Nie Z et al (2021) Estimation of hourly full-coverage PM2.5 concentrations at 1-km resolution in China using a two-stage random forest model. Atmos Res 248:105146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105146
Jin Q, Crippa P, Pryor SC (2020) Spatial characteristics and temporal evolution of the relationship between PM2.5 and aerosol optical depth over the eastern USA during 2003–2017. Atmos Environ 239:117718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117718
Just AC, Arfer KB, Rush J et al (2020) Advancing methodologies for applying machine learning and evaluating spatiotemporal models of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) using satellite data over large regions. Atmos Environ 239:117649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117649
Kamarul Zaman NAF, Kanniah KD, Kaskaoutis DG (2017) Estimating particulate matter using satellite based aerosol optical depth and meteorological variables in Malaysia. Atmos Res 193:142–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.04.019
Kara M, Mangir N, Bayram A, Elbir T (2014) A spatially high resolution and activity based emissions inventory for the metropolitan area of Istanbul, Turkey. Aerosol Air Qual Res 14:10–20. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2013.04.0124
Kara M, Hopke PK, Dumanoglu Y et al (2015) Characterization of PM using multiple site data in a heavily industrialized region of Turkey. Aerosol Air Qual Res 15:11–27. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2014.02.0039
Karaca F (2012) Determination of air quality zones in Turkey. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 62:408–419. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2012.655883
Kloog I, Sorek-Hamer M, Lyapustin A et al (2015) Estimating daily PM2.5 and PM10 across the complex geo-climate region of Israel using MAIAC satellite-based AOD data. Atmos Environ 122:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.10.004
Lanzaco BL, Olcese LE, Palancar GG, Toselli BM (2016) A method to improve MODIS AOD values: application to South America. Aerosol Air Qual Res 16:1509–1522. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2015.05.0375
Lelieveld J, Berresheim H, Borrmann S et al (2002) Global air pollution crossroads over the Mediterranean. Science 298:794–799. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1075457
Levy RC, Mattoo S, Munchak LA et al (2013) The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos Meas Tech 6:2989–3034. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-6-2989-2013
Li L (2020) A robust deep learning approach for spatiotemporal estimation of satellite AOD and PM2.5. Remote Sens 12:264. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020264
Liu, Y. (2015). Particulate matter air quality from space–advanced statistical modeling. https://appliedsciences.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/2020-11/ParticulateMatter_Part3.pdf. Accessed January 1, 2020
Loría-Salazar SM, Panorska A, Arnott WP et al (2017) Toward understanding atmospheric physics impacting the relationship between columnar aerosol optical depth and near-surface PM2.5 mass concentrations in Nevada and California, U.S.A., during 2013. Atmos Environ 171:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.10.023
Lu J, Zhang Y, Chen M et al (2021) Estimation of monthly 1 km resolution PM2.5 concentrations using a random forest model over “2 + 26” cities, China. Urban Clim 35:100734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2020.100734
Ma Z, Hu X, Sayer AM et al (2016) Satellite-based spatiotemporal trends in PM2.5 concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ Health Perspect 124:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1409481
Meng X, Fu Q, Ma Z et al (2016) Estimating ground-level PM10 in a Chinese city by combining satellite data, meteorological information and a land use regression model. Environ Pollut 208:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.09.042
Meng X, Liu C, Zhang L et al (2021) Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in Northeastern China with full spatiotemporal coverage, 2005–2016. Remote Sens Environ 253:112203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.112203
Nabavi SO, Haimberger L, Samimi C (2016) Climatology of dust distribution over West Asia from homogenized remote sensing data. Aeolian Res 21:93–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeolia.2016.04.002
Nabavi SO, Haimberger L, Abbasi E (2019) Assessing PM2.5 concentrations in Tehran, Iran, from space using MAIAC, deep blue, and dark target AOD and machine learning algorithms. Atmos Pollut Res 19:889–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2018.12.017
Ozdemir E, Tuna Tuygun G, Elbir T (2020) Application of aerosol classification methods based on AERONET version 3 product over eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea. Atmos Pollut Res 11:2226–2243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.06.008
Park S, Shin M, Im J et al (2019) Estimation of ground-level particulate matter concentrations through the synergistic use of satellite observations and process-based models over South Korea. Atmos Chem Phys 19:1097–1113. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-19-1097-2019
Park S, Lee J, Im J et al (2020) Estimation of spatially continuous daytime particulate matter concentrations under all sky conditions through the synergistic use of satellite-based AOD and numerical models. Sci Total Environ 713:136516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136516
Préndez MM, Egido M, Tomas C et al (1995) Correlation between solar radiation and total syspended particulate matter in Santiago, Chile-Preliminary results. Atmos Environ 29:1543–1551. https://doi.org/10.1016/1352-2310(94)00349-P
Price DJ, Kacarab M, Cocker DR et al (2016) Effects of temperature on the formation of secondary organic aerosol from amine precursors. Aerosol Sci Technol 50:1216–1226. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2016.1236182
Randles CA, da Silva AM, Buchard V et al (2017) The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part I: system description and data assimilation evaluation. J Clim 30:6823–6850. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0609.1
Ranjan AK, Patra AK, Gorai AK (2021) A review on estimation of particulate matter from satellite-based aerosol optical depth: data, methods, and challenges. Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 57:679–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00215-0
Sayer AM, Munchak LA, Hsu NC et al (2014) Modis collection 6 aerosol products: Comparison between aqua’s e-deep blue, dark target, and “merged” data sets, and usage recommendations. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:13,965-13,989. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD022453
Shaheen A, Wu R, Lelieveld J et al (2021) Winter AOD trend changes over the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East region. Int J Climatol 41:5516–5535. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7139
Shtein A, Karnieli A, Katra I et al (2018) Estimating daily and intra-daily PM10 and PM2.5 in Israel using a spatio-temporal hybrid modeling approach. Atmos Environ 191:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.08.002
Sorek-Hamer M, Just AC, Kloog I (2016) Satellite remote sensing in epidemiological studies. Curr Opin Pediatr 28:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0000000000000326
Stafoggia M, Schwartz J, Badaloni C et al (2017) Estimation of daily PM10 concentrations in Italy (2006–2012) using finely resolved satellite data, land use variables and meteorology. Environ Int 99:234–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.11.024
Stafoggia M, Bellander T, Bucci S et al (2019) Estimation of daily PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations in Italy, 2013–2015, using a spatiotemporal land-use random-forest model. Environ Int 124:170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.016
Stirnberg R, Cermak J, Andersen H (2018) An analysis of factors influencing the relationship between satellite-derived AOD and ground-level PM10. Remote Sens 10:1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091353
Stirnberg R, Cermak J, Fuchs J, Andersen H (2020) Mapping and understanding patterns of air quality using satellite data and machine learning. J Geophys Res Atmos 125:e2019JD03138. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031380
Su T, Li Z, Kahn R (2018) Relationships between the planetary boundary layer height and surface pollutants derived from lidar observations over China: regional pattern and influencing factors. Atmos Chem Phys 18:15921–15935. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-15921-2018
Tian X, Liu Q, Li X, Wei J (2018) Validation and comparison of MODIS C6.1 and C6 aerosol products over Beijing, China. Remote Sensing 10(12):2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122021
Tuna Tuygun G, Altuğ H, Elbir T, Gaga EE (2017) Modeling of air pollutant concentrations in an industrial region of Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(9):8230–8241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8492-9
Toros H, Erdun H, Çapraz Ö, Özer B, Bozyazı Daylan E, Öztürk Aİ (2013) Air pollution and quality level in metropolitan Turkey for sustainable life. Eur J Sci Technol 1(1):12–18
Triantafyllou E, Giamarelou M, Bossioli E et al (2016) Particulate pollution transport episodes from Eurasia to a remote region of northeast Mediterranean. Atmos Environ 128:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.12.054
Tuna Tuygun G (2021) Development of a regional-scale prediction method for ground level particulate matter concentrations based on AOD from different satellites in Turkey, Ph.D. thesis, Dokuz Eylul University, Izmir, Turkey, pp 211
Tuna Tuygun G, Elbir T (2021) Estimating intra-daily PM10 concentrations over the northwestern region of Turkey based on MODIS AOD using random forest approach. Proscience. https://doi.org/10.14644/dust2021.003
Tuna Tuygun G, Ozdemir E, Elbir T (2020) Evaluation of MODIS C6 and C6.1 dark target AOD products over Turkey based on NDVI and aerosol type. Atmos Pollut Res 11:2335–2349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.07.003
Tuna Tuygun G, Gündoğdu S, Elbir T (2021) Estimation of ground-level particulate matter concentrations based on synergistic use of MODIS, MERRA-2 and AERONET AODs over a coastal site in the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos Environ 261:118562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118562
Tuna Tuygun G, Ozdemir E, Elbir T (2022) Calibrating MERRA-2 PM2.5 concentrations with aerosol diagnostics: testing different machine learning approaches in the Eastern Mediterranean. Air Qual Atmos Health 15:2283–2297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-022-01250-8
Ustaoglu E, Aydinoglu AC (2019) Regional variations of land-use development and land-use/cover change dynamics: a case study of Turkey. Remote Sens 11:885. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS11070885
Wei J, Sun L, Huang B et al (2018) Verification, improvement and application of aerosol optical depths in China Part 1: inter-comparison of NPP-VIIRS and Aqua-MODIS. Atmos Environ 175:221–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.11.048
Wei J, Li Z, Cribb M et al (2020) Improved 1 km resolution PM2.5 estimates across China using enhanced space-time extremely randomized trees. Atmos Chem Phys 20:3273–3289. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-20-3273-2020
Wei J, Li Z, Sun L et al (2022) Extending the EOS long-term PM2.5data records since 2013 in China: application to the VIIRS deep blue aerosol products. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3050999
Wei J, Huang W, Li Z et al (2019) Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2.5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens Environ 231:111221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111221
Wei J, Li Z, Xue W et al (2021) The ChinaHighPM10 dataset: generation, validation, and spatiotemporal variations from 2015 to 2019 across China. Environ Int 146:106290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106290
Wright MN, Ziegler A (2017) Ranger: a fast implementation of random forests for high dimensional data in C++ and R. J Stat Softw 77:1–17. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v077.i01
Xiao Q, Wang Y, Chang HH et al (2017) Full-coverage high-resolution daily PM2.5 estimation using MAIAC AOD in the Yangtze river delta of China. Remote Sens Environ 199:437–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.07.023
Xu Q, Chen X, Yang S, Tang L, Dong J (2021) Spatiotemporal relationship between Himawari-8 hourly columnar aerosol optical depth (AOD) and ground-level PM2.5 mass concentration in mainland China. Sci Total Environ 765:144241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144241
Yan X, Zang Z, Luo N et al (2020) New interpretable deep learning model to monitor real-time PM2.5 concentrations from satellite data. Environ Int 144:106060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106060
Yang Q, Yuan Q, Yue L et al (2019) The relationships between PM2.5 and aerosol optical depth (AOD) in mainland China: about and behind the Spatio-temporal variations. Environ Pollut 248:526–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.071
Yang L, Xu H, Yu S (2020) Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in Yangtze River Delta region of China using random forest model and the top-of-atmosphere reflectance. J Environ Manage 272:111061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111061
Yao F, Palmer PI (2021) A model framework to reduce bias in ground-level PM2.5 concentrations inferred from satellite-retrieved AOD. Atmos Environ 248:118217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118217
Yazdi MD, Kuang Z, Dimakopoulou K et al (2020) Predicting fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the greater london area: an ensemble approach using machine learning methods. Remote Sens 12:914. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060914
Zeydan Ö, Wang Y (2019) Using MODIS derived aerosol optical depth to estimate ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over Turkey. Atmos Pollut Res 10:1565–1576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2019.05.005
Zhang T, He W, Zheng H et al (2021) Satellite-based ground PM2.5 estimation using a gradient boosting decision tree. Chemosphere 268:128801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128801
Acknowledgements
This study is a Ph. D. thesis financially supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye (TUBITAK) 2214A International Scholarship Programme for Ph.D. Students. This study was also supported by TUBITAK (Project No: 119Y005). We want to thank TUBITAK for all its financial support. In addition, we gratefully acknowledge NASA for making the MODIS aerosol products, MERRA-2, and AERONET data publicly available. We also thank the Turkish Ministry of Environment and Urbanization for making PM10 data publicly available.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gizem Tuna Tuygun: formal analysis, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization. Tolga Elbir: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tuna Tuygun, G., Elbir, T. Estimation of particulate matter concentrations in Türkiye using a random forest model based on satellite AOD retrievals. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 37, 3469–3491 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02459-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02459-4