Abstract
Key message
Using hypocotyls as explants, an in vitro adventitious shoot regeneration system of Manchurian ash was established, and it has been successfully applied in Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation.
Abstract
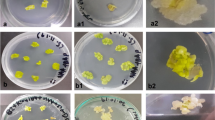
Manchurian ash, Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr., is an important tree species for landscaping, timber, and afforestation. However, a genetic transformation system of this tree species has not been reported thus far, which impedes its breeding and investigation (e.g., functional gene assays). In this study, we present an ultrasound-aided Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation system for this tree species using hypocotyls as explants. The optimum medium for bud induction was WPM (Woody Plant Medium) + 1.0 mg L−1 TDZ (thidiazuron) + 30 g L−1 sucrose. Sonication for 90 s and vacuum treatment for 10 min doubled the number of adventitious buds from 33.23 to 77.67 buds per hypocotyl. The optimum medium for shoot elongation was WPM supplemented with 0.025 mg L−1 TDZ and 1.0 mg L−1 gibberellic acid (GA3), which resulted in a survival rate of 70.97%. Our results also showed that lower light intensity culture can prevent tissue browning, which is of vital concern for the in vitro propagation of this tree species. Using this regeneration system, precultured hypocotyl explants were transformed with the aid of 90 s sonication plus 10 min vacuum infiltration. After performing a screening culture at 30 mg L−1 kanamycin, 16 transgenic plant lines were obtained, for a transformation rate of 7.31%.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmad A, Ahmad N, Anis M, Alatar AA, Abdel-Salam EM, Qahtan AA, Faisal M (2021) Gibberellic acid and thidiazuron promote micropropagation of an endangered woody tree (Pterocarpus marsupium Roxb.) using in vitro seedlings. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 144:449–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01969-1
Buyukalaca S, Mavituna F (1996) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of pepper in liquid media. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 46:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02307099
Chen SQ (2019) Induction of embryogenic callus and suspension culture of tissue culture seedlings of Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr. Dissertation, Northeast Forestry University
de Oliveira MLP, Febres VJ, Costa MGC, Moore GA, Otoni WC (2009) High-efficiency Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of citrus via sonication and vacuum infiltration. Plant Cell Rep 28:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0646-2
Du N, Pijut PM (2009) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Fraxinus pennsylvanica hypocotyls and plant regeneration. Plant Cell Rep 28:915–923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0697-z
Eva C, Valdés AE, Fernández B, Moysset L, Trillas MI (2004) Levels and immunolocalization of endogenous cytokinins in thidiazuron-induced shoot organogenesis in carnation. J Plant Physiol 161:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00957
Feyissa T, Welander M, Negash L (2005) In vitro regeneration of Hagenia abyssinica (Bruce) J.F. Gmel. (Rosaceae) from leaf explants. Plant Cell Rep 24:392–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0949-5
Gallois P, Marinho P (1995) Leaf disk transformation using Agrobacterium tumefaciens-Expression of heterologous genes in tobacco. Methods Mol Biol 49:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1385/0-89603-321-x:39
Gao Y (2014) Diseases and insect pests of Fraxinus mandshuica and their control methods. J Changchun Univ 24:1385–1388
He L, Xu Y, Zeng F, Tian H, Xiao Y, Liu H, Yu L, Zhan Y (2021) Establishment of a micropropagation supporting technology for the Fraxinus mandshurica × Fraxinus sogdiana. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 57:307–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-021-10157-5
Hebda A, Liszka A, ZhBobicki P, Nawrot-Chorabik K, Lyczakowski JJ (2021) Transformation of European ash (Fraxinus excelsior L.) callus as a starting point for understanding the molecular basis of ash dieback. Plants 10:2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10112524
Hu LJ, Uchiyama K, Shen HL, Ide Y (2010) Multiple-scaled spatial genetic structures of Fraxinus mandshurica over a riparian–mountain landscape in Northeast China. Conserv Genet 11:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-009-0004-0
Ikeuchi M, Sugimoto K, Iwase A (2013) Plant callus: mechanisms of induction and repression. Plant Cell 25:3159–3173
Ikeuchi M, Ogawa Y, Iwase A, Sugimoto K (2016) Plant regeneration: cellular origins and molecular mechanisms. Dev 143:1442–1451. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.134668
Ikeuchi M, Shibata M, Rymen B, Iwase A, Bågman A-M, Watt L, Coleman D, Favero DS, Takahashi T, Ahnert SE, Brady SM, Sugimoto K (2018) A gene regulatory network for cellular reprogramming in plant regeneration. Plant Cell Physiol 59:770–782. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy013
Jain P, Rashid A (2001) Stimulation of shoot regeneration on linum hypocotyl segments by thidiazuron and its response to light and calcium. Biol Plant 44:611–613. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1013767426219
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the gus gene fusion system. Plant Mol Bio Rep 5:387–405
Kim SW, Oh SC, In DS, Liu JR (2003) Plant regeneration of rose (Rosa hybridia) from embryogenic cell-derived protoplasts. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 73:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022693605436
Kong DM, Preece JE, Shen H-L (2012) Somatic embryogenesis in immature cotyledons of Manchurian ash (Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 108:485–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-0062-0
Kou Y, Yuan C, Zhao Q, Liu G, Nie J, Ma Z, Cheng C, Teixeira da Silva JA, Zhao L (2016) Thidiazuron triggers morphogenesis in Rosa canina L. protocorm-like bodies by changing incipient cell fate. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00557
Lee JH, Pijut PM (2018) Optimization of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Fraxinus nigra and development of black ash for possible emerald ash borer resistance. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 134:217–229
Li L (2014) Advances in genetics and breeding of Fraxinus mandshuric in China. Liaoning Sci Tec 2:52–54
Li X, Krasnyanski SF, Korban SS (2002) Somatic embryogenesis, secondary somatic embryogenesis, and shoot organogenesis in Rosa. J Plant Physiol 159:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00688
Liu Y, Wei C, Wang H, Ma X, Shen H, Yang L (2020) Indirect somatic embryogenesis and regeneration of Fraxinus mandshurica plants via callus tissue. J for Res 32:1613–1625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-020-01199-3
Lloyd G, McCown BH (1980) Commercially-feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kalmia latifolia, by use of shoot-tip culture. Combined Proc Int Plant Propagator’s Soc 30:421–427
Murthy BNS, Murch SJ, Saxena PK (1998) Thidiazuron: a potent regulator ofin vitro plant morphogenesis. In Vit Cell Dev Bi Plant 34:267. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02822732
Palla KJ, Pijut PM (2015) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Fraxinus americana hypocotyls. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120:631–641
Rokhina EV, Lens P, Virkutyte J (2009) Low-frequency ultrasound in biotechnology: state of the art. Trends Biotechnol 27:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.02.001
Safari M, Ghanati F, Behmanesh M, Hajnorouzi A, Nahidian B, Mina G (2013) Enhancement of antioxidant enzymes activity and expression of CAT and PAL genes in hazel (Corylus avellana L.) cells in response to low-intensity ultrasound. Acta Physiol Plant 35:2847–2855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1318-6
Santarém ER, Trick HN, Essig JS, Finer JJ (1998) Sonication-assisted Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of soybean immature cotyledons: optimization of transient expression. Plant Cell Rep 17(10):752–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050478
Shen H, Wang QS, Liu Y, Liu CP, Yang L (2020) Effects of BA and NAA on explant browning and SE from immature zygotic cotyledon of Fraxinus mandshurica. Mol Plant Breed 18:1266–1273
Stevens ME, Pijut PM (2014) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation and plant regeneration of the hardwood tree species Fraxinus profunda. Plant Cell Rep 33:861–870
Subramanyam K, Subramanyam K, Sailaja KV, Srinivasulu M, Lakshmidevi K (2011) Highly efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of banana cv. Rasthali (AAB) via sonication and vacuum infiltration. Plant Cell Rep 30:425–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0996-4
Sun GJ (2009) Maturation and germination promotion for somatic embryos of Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr. Dissertation, Northeast Forestry University
Tabrett AM, Hammatt N (1992) Regeneration of shoots from embryo hypocotyls of common ash (Fraxinus excelsior). Plant Cell Rep 11:514–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00236267
Thomas JC, Katterman FR (1986) Cytokinin activity induced by thidiazuron. Plant Physiol 81:681–683. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.81.2.681
Trick HN, Finer JJ (1997) SAAT: sonication-assisted Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Transgenic Res 6:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1018470930944
Trick HN, Finer JJ (1998) Sonication-assisted Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] embryogenic suspension culture tissue. Plant Cell Rep 17:482–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050429
Wei M, Yang C-y, Wei S-h (2012) Enhancement of the differentiation of protocorm-like bodies of Dendrobium officinale to shoots by ultrasound treatment. J Plant Physiol 169:770–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.01.018
Yang L, Bian L, Shen H-l, Li Y-h (2013) Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from mature zygotic embryos of Manchurian ash (Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 115:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0345-8
Ye R, Lv X, Li XL, Tian HL, Ji N, Zhang MS (2018) Effects of five browning inhibitors on protocorms proliferation culture of Cremastra appendiculata. Plant Physiol J 54(6):1103–1110
Yu L, Li X, Tian H, Liu H, Xiao Y, Liang N, Zhao X, Zhan Y (2020) Effects of hormones and epigenetic regulation on the callus and adventitious bud induction of Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr. Forests 11:590. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11050590
Zeng FS, Zhou S, Zhan YG, Dong J (2014) Drought resistance and DNA methylation of interspecific hybrids between Fraxinus mandshurica and Fraxinus americana. Trees 28:1679–1692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-014-1077-z
Zeng Q, Han Z, Kang X (2019) Adventitious shoot regeneration from leaf, petiole and root explants in triploid (Populus alba × P. glandulosa)× P. tomentosa. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 138:121–130
Zhang LJ, Zhang LW, Feng DD (2007) In Vitro culture of axillary bud sprouting of Fraxinus mandshurica. Bull Bot Res 27:319–324
Zhang LJ, Zhao LM, Lu XJ, Shen HL, University SA (2015) callus induction and somatic embryogenesis from zygotic cotyledons and hypocotyls of Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr. Mol Plant Breed 13:1645–1652
Zhou H, Li M, Zhao X, Fan X, Guo A (2010) Plant regeneration from in vitro leaves of the peach rootstock ‘Nemaguard’ (Prunus persica × P. davidiana). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 101:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9666-z
Zhu Z, Qi F, Yan C, Zhan Y (2016) Sexually different morphological, physiological and molecular responses of Fraxinus mandshurica flowers to floral development and chilling stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 99:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.12.006
Funding
This study was co-funded by the China National Key R&D Program during the 14th Five-year Plan Period (2021YFD220030301), Heilongjiang Provincial R&D Project on Provincial Applied Technology (GA19B201), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2572020DR09). The funders had no role in the study design, analysis, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, F., Tang, M., Wang, W. et al. In vitro adventitious shoot regeneration system for Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr.. Trees 36, 1387–1399 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-022-02302-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-022-02302-3