Abstract
Key message
As the estimated parameters differed across samples, even from the same site, sample-based calibration is the recommended procedure. A trait-based approach (i.e., the use of structural parameters of the trees) would be an alternative procedure.
Abstract
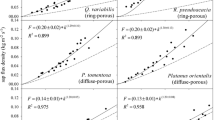
The thermal dissipation method (TDM) is widely used for estimating transpiration by individual trees or stands. Although the importance of TDM calibration experiments is widely recognized, there is still no consensus on whether the calibration should be undertaken in practice for each species, site, or tree sample. The primary reason is that intraspecific variations in the fitting parameters have not been well examined in multiple sites. To address this, we performed TDM calibration experiments using 24 Cryptomeria japonica and Chamaecyparis obtusa samples collected from six regions in Japan and Taiwan. The sap flux density (Fd) based on the original TDM parameters was underestimated for most samples. Using a common set of parameters for 21 samples reduced the systematic underestimation. In addition, root mean square error (RMSE) was reduced by 44%. Site- and sample-based calibration reduced the RMSE by 69% and 75%, respectively. The estimated parameters for the samples varied, even among samples obtained from the same site. The recommended procedure is to obtain sample-specific parameters by performing a calibration experiment after measuring Fd under the target conditions. An alternative procedure is to use the parameters for other trees of the same species at the same site. Further, we discovered that one of the two parameters determined for each sample significantly correlated with the diameter/age ratio and height of the corresponding tree. A trait-based approach for predicting calibration parameters based on associated tree features allows the parameters to be determined without the need for calibration experiments.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Asbjornsen H, Goldsmith GR, Alvarado-Barrientos MS, Rebel K, Van Osch FP, Rietkerk M, Chen J, Gotsch S, Tobón C, Geissert DR, Gómez-Tagle A, Vache K, Dawson TE (2011) Ecohydrological advances and applications in plant-water relations research: a review. J Plant Ecol 4:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rtr005
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67:1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Bréda N, Huc R, Granier A, Dreyer E (2006) Temperate forest trees and stands under severe drought: a review of ecophysiological responses, adaptation processes and long-term consequences. Ann for Sci 63:625–644. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:2006042
Bush SE, Hultine KR, Sperry JS, Ehleringer JR, Phillips N (2010) Calibration of thermal dissipation sap flow probes for ring- and diffuse-porous trees. Tree Physiol 30:1545–1554. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpq096
Čermák J, Kučera J, Nadezhdina N (2004) Sap flow measurements with some thermodynamic methods, flow integration within trees and scaling up from sample trees to entire forest stands. Trees 18:529–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-004-0339-6
Chandrathilake GGT, Tanaka N, Kamata N (2017) Whole-tree sap flux in Quercus serrata trees after three levels of partial sapwood removal to simulate Japanese oak wilt. Ecohydrology 10:e1797. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.1797
Clearwater MJ, Meinzer FC, Andrade JL, Goldstein G, Holbrook NM (1999) Potential errors in measurement of nonuniform sap flow using heat dissipation probes. Tree Physiol 19:681–687. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/19.10.681
Delzon S, Sartore M, Granier A, Loustau D (2004) Radial profiles of sap flow with increasing tree size in maritime pine. Tree Physiol 24:1285–1293. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/24.11.1285
Fan J, Guyot A, Ostergaard KT, Lockington DA (2018) Effects of earlywood and latewood on sap flux density-based transpiration estimates in conifers. Agric for Meteorol 249:264–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.11.006
Fuchs S, Leuschner C, Link R, Coners H, Schuldt B (2017) Calibration and comparison of thermal dissipation, heat ratio and heat field deformation sap flow probes for diffuse-porous trees. Agric for Meteorol 244–245:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.04.003
Fujiwara T, Yamashita L, Hirakawa Y (2004) Mean basic density and density variation within individual trees in major plantation species. Bull FFPRI 393:341–348 (in Japanese with English summary)
Granier A (1985) Une nouvelle méthode pour la mesure du flux de sève brute dans le tronc des arbres. Ann Sci for 42:193–200
Hölttä T, Linkosalo T, Riikonen A, Sevanto S, Nikinmaa E (2015) An analysis of Granier sap flow method, its sensitivity to heat storage and a new approach to improve its time dynamics. Agric for Meteorol 211–212:2–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.05.005
Iida S, Shimizu T, Shinohara Y, Takeuchi S, Kumagai T (2020a) The necessity of sensor calibration for the precise measurement of water fluxes in forest ecosystems. In: Levia DF, Carlyle-Moses DE, Iida S, Michalzik B, Nanko K, Tischer A (eds) Forest–water interactions. Ecological studies series, No. 240. Springer Nature, Cham, pp 29–54
Iida S, Shimizu T, Tamai K, Kabeya N, Shimizu A, Ito E, Ohnuki Y, Chann S, Levia DF (2020b) Evapotranspiration from the understory of a tropical dry deciduous forest in Cambodia. Agric for Meteorol 295:108170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2020.108170
Japan Forestry Agency (2021) Data for Japanese cedar and Japanese cypress. https://www.rinya.maff.go.jp/j/sin_riyou/kafun/data.html (in Japanese). Accessed 2 Feb 2021
Komatsu H, Shinohara Y, Kumagai T, Kume T, Tsuruta K, Xiang Y, Ichihashi R, Tateishi M, Shimizu T, Miyazawa Y, Nogata M, Laplace S, Han T, Chiu C-W, Ogura A, Saito T, Otsuki K (2014) A model relating transpiration for Japanese cedar and cypress plantations with stand structure. For Ecol Manag 334:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-017-0638-x
Komatsu H, Shinohara Y, Kume T, Tsuruta K, Otsuki K (2016) Does measuring azimuthal variations in sap flux lead to more reliable stand transpiration estimates? Hydrol Process 30:2129–2137. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10780
Komatsu H, Kume T, Shinohara Y (2017) Optimal sap-flux sensor allocation for stand transpiration estimates: a non-dimensional analysis. Ann for Sci 74:38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-017-0638-x
Kumagai T, Aoki S, Nagasawa H, Mabuchi T, Kubota K, Inoue S, Utsumi Y, Otsuki K (2005) Effects of tree-to-tree and radial variations on sap flow estimates of transpiration in Japanese cedar. Agric for Meteorol 135:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.11.007
Kumagai T, Aoki S, Shimizu T, Otsuki K (2007) Sap flow estimates of stand transpiration at two slope positions in a Japanese cedar forest watershed. Tree Physiol 27:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/27.2.161
Kume T, Tsuruta K, Komatsu H, Kumagai T, Higashi N, Shinohara Y, Otsuki K (2010) Effects of sample size on sap flux-based stand-scale transpiration estimates. Tree Physiol 30:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpp074
Kume T, Otsuki K, Du S, Yamanaka N, Wang YL, Liu GB (2012) Spatial variation in sap flow velocity in semiarid region trees: its impact on stand-scale transpiration estimates. Hydrol Process 26:1161–1168. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8205
Kume T, Tsuruta K, Komatsu H, Shinohara Y, Katayama A, Ide J, Otsuki K (2016) Differences in sap flux based stand transpiration between upper and lower slope positions in a Japanese cypress plantation watershed. Ecohydrology 9:1105–1116. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.1709
Laplace S, Komatsu H, Tseng H, Kume T (2017) Difference between the transpiration rates of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) and Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) forests in a subtropical climate in Taiwan. Ecol Res 32:835–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-017-1512-x
Menditto A, Patriarca M, Magnusson B (2006) Understanding the meaning of accuracy, trueness and precision. Accreditation Qual Assur 12:45–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-006-0191-z
Merlin M, Solarik KA, Landhäusser SM (2020) Quantification of uncertainties introduced by data-processing procedures of sap flow measurements using the cut-tree method on a large mature tree. Agric for Meteorol 287:107926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2020.107926
Oda T, Asano Y, Suzuki M (2009) Transit time evaluation using a chloride concentration input step shift after forest cutting in a Japanese headwater catchment. Hydrol Process 23:2705–2713. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7361
Peters RL, Fonti P, Frank DC, Poyatos R, Pappas C, Kahmen A, Carraro V, Prendin AL, Schneider L, Baltzer JL, Baron-Gafford GA, Dietrich L, Heinrich I, Minor RL, Sonnentag O, Matheny AM, Wightman MG, Steppe K (2018) Quantification of uncertainties in conifer sap flow measured with the thermal dissipation method. New Phytol 219:1283–1299. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15241
Piermattei A, von Arx G, Avanzi C, Fonti P, Gärtner H, Piotti A, Urbinati C, Vendramin GG, Büntgen U, Crivellaro A (2020) Functional relationships of wood anatomical traits in Norway spruce. Front Plant Sci 11:683. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00683
Poyatos R, Granda V, Molowny-Horas R, Mencuccini M, Steppe K, Martínez-Vilalta J (2016) SAPFLUXNET: towards a global database of sap flow measurements. Tree Physiol 36:1449–1455. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpw110
R Development Core Team (2021) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 28 Oct 2021
Rana G, De Lorenzi F, Palatella L, Martinelli N, Ferrara RM (2019) Field scale recalibration of the sap flow thermal dissipation method in a Mediterranean vineyard. Agric for Meteorol 269:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.02.018
Saito T, Kumagai T, Tateishi M, Kobayashi N, Otsuki K, Giambelluca TW (2017) Differences in seasonality and temperature-dependency of stand transpiration and canopy conductance between Japanese cypress (Hinoki) and Japanese cedar (Sugi) in a plantation. Hydrol Process 31:1952–1965. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11162
Seneviratne SI, Corti T, Davin EL, Hirschi M, Jaeger EB, Lehner I, Orlowsky B, Teuling AJ (2010) Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: a review. Earth Sci Rev 99:125–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.02.004
Shinohara Y, Tsuruta K, Kume T, Otsuki K (2013a) An overview of stand-scale transpiration measurements using the sap flow technique for evaluating the effects of forest management practices on transpiration. J Jpn for Sci 95:321–331. https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.95.321(inJapanesewithEnglishsummary)
Shinohara Y, Tsuruta K, Ogura A, Noto F, Komatsu H, Otsuki K, Maruyama T (2013b) Azimuthal and radial variations in sap flux density and effects on stand-scale transpiration estimates in a Japanese cedar forest. Tree Physiol 33:550–558. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpt029
Shinohara Y, Komatsu H, Otsuki K (2015) Sapwood and intermediate wood thickness variation in Japanese cedar: impacts on sapwood area estimates. Hydrol Res Lett 9:35–40. https://doi.org/10.3178/hrl.9.35
Spicer R, Gartner BL (2001) The effects of cambial age and position within the stem on specific conductivity in Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) sapwood. Trees 15:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004680100093
Steppe K, De Pauw DJW, Doody TM, Teskey RO (2010) A comparison of sap flux density using thermal dissipation, heat pulse velocity and heat field deformation methods. Agric for Meteorol 150:1046–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.04.004
Sun H, Aubrey DP, Teskey RO (2012) A simple calibration improved the accuracy of the thermal dissipation technique for sap flow measurements in juvenile trees of six species. Trees 26:631–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-011-0631-1
Tseng H, Chiu CW, Laplace S, Kume T (2017) Can we assume insignificant temporal changes in spatial variations of sap flux for year-round individual tree transpiration estimates? A case study on Cryptomeria japonica in central Taiwan. Trees 31:1239–1251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-017-1542-6
Tsuruta K, Kume T, Komatsu H, Higashi N, Umebayashi T, Kumagai T, Otsuki K (2010) Azimuthal variations of sap flux density within Japanese cypress xylem trunks and their effects on tree transpiration estimates. J for Res 15:398–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-010-0202-0
Tsuruta K, Kume T, Komatsu H, Otsuki K (2018) Effects of soil water decline on diurnal and seasonal variations in sap flux density for differently aged Japanese cypress trees. Ann for Res 61:5–18
Tsuruta K, Komatsu H, Kume T, Otsuki K, Kosugi Y, Kosugi K (2019) Relationship between stem diameter and transpiration for Japanese cypress trees: implications for estimating canopy transpiration. Ecohydrology 12:e2097. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.2097
Tsushima S, Fujioka Y, Oda K, Matsumura J, Shiraishi S (2006a) Variations of wood properties in forests of seedlings and cutting cultivar of Hinoki (Chamaecyparis obtusa). Mokuzai Gakkaishi 52:277–284. https://doi.org/10.2488/jwrs.52.277(inJapanesewithEnglishsummary)
Tsushima S, Koga S, Oda K, Shiraishi S (2006b) Effects of initial spacing on growth and wood properties of Sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) cutting cultivars. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 52:196–205. https://doi.org/10.2488/jwrs.52.196(inJapanesewithEnglishsummary)
Wilson KB, Hason PJ, Mulholland PJ, Baldocchi DD, Wullschleger SD (2001) A comparison of methods for determining forest evapotranspiration and its components: sap-flow, soil water budget, eddy covariance and catchment water balance. Agric for Meteorol 106:153–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00199-4
Wullschleger SD, King AW (2000) Radial variation in sap velocity as a function of stem diameter and sapwood thickness in yellow-poplar trees. Tree Physiol 20:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/20.8.511
Wullschleger SD, Meinzer FC, Vertessy RA (1998) A review of whole-plant water use studies in trees. Tree Physiol 18:499–512. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/18.8-9.499
Wullschleger SD, Childs KW, King AW, Hanson PJ (2011) A model of heat transfer in sapwood and implications for sap flux density measurements using thermal dissipation probes. Tree Physiol 31:669–679. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpr051
Zhang Z, Tian F, Hu H, Yang P (2014) A comparison of methods for determining field evapotranspiration: photosynthesis system, sap flow, and eddy covariance. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 18:1053–1072. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-18-1053-2014
Zhang Z, Zhao P, Zhao X, Zhou J, Zhao P, Zeng X, Hu Y, Ouyang L (2018) The tree height-related spatial variances of tree sap flux density and its scale-up to stand transpiration in a subtropical evergreen broadleaf forest: spatial variances of tree sap flux density and its scale-up. Ecohydrology 11:e1979. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.197
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Naoya Masaoka and Mr. Yuichi Sempuku (Kyoto University) and the technical staff of Kyushu University Forest, the University of Tokyo Forests, Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute, and National Taiwan University Experimental Forest for their help in taking tree samples. Yoshinori Shinohara is also grateful to Prof. Kyoichi Otsuki of Kyushu University and Prof. Masahiro Takagi of the University of Miyazaki for providing the concept of the calibration system. This study was supported by Ichimura Foundation for New Technology and partly supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant number JP18K14492 and the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology Grant number 103-2313-B-002-009-MY3.
Funding
This study was supported by Ichimura Foundation for New Technology and partly supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number JP18K14492 and the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology Grant Number 103-2313-B-002-009-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
None declared.
Additional information
Communicated by Beck.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinohara, Y., Iida, S., Oda, T. et al. Are calibrations of sap flow measurements based on thermal dissipation needed for each sample in Japanese cedar and cypress trees?. Trees 36, 1219–1229 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-022-02283-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-022-02283-3