Abstract
Background
Both IgA nephropathy (IgAN) and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephropathy (HSPN) are characterized by glomerular mesangial IgA deposition. Several large studies on adults have suggested that glomerular C4d deposition has prognostic value in IgAN. However, there are few relevant studies on the clinical value of C4d deposition in children with IgAN or HSPN.
Methods
We performed a retrospective cohort study in pediatric patients with IgAN or HSPN. Clinicopathological data were collected at the time of kidney biopsy. Kidney C4d deposition was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. The end point was defined as a ≥ 20% decrease in estimated glomerular filtration from baseline.
Results
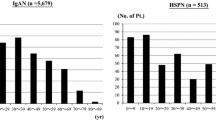
We enrolled 75 children, including 36 children with IgAN and 39 with HSPN. The prevalence of C4d deposition was 36% (27/75). C4d deposition was more abundant in children with proteinuria ≥ 50 mg/kg/day (51.9% versus 20.8%, P = 0.006) or nephrotic syndrome (37.0% versus 10.4%, P = 0.006). Mesangial hypercellularity (hazard ratio [HR], 5.745, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.670–19.761, P = 0.006) and IgM deposition (HR, 4.522, 95% CI, 1.321–15.478, P = 0.016) were associated with C4d deposition. After a median follow-up of 22 months, seven (19.4%) IgAN patients and one (2.6%) HSPN patient had decreased kidney function. In children with IgAN, positive C4d was associated with decreased kidney function (P = 0.047).
Conclusion
Glomerular C4d deposition was associated with mesangial hypercellularity and glomerular IgM deposition in IgAN and HSPN. Glomerular C4d deposition may be a risk factor for eGFR decline in children with IgAN.
Graphical abstract
A higher resolution version of the Graphical abstract is available as Supplementary information.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waldos FB (1988) Is Henoch-Schönlein purpura the systemic form of IgA nephropathy? Am J Kidney Dis 12:373–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-6386(88)80028-3
Davin JC, Ten Berge IJ, Weening JJ (2001) What is the difference between IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis? Kidney Int 59:823–834. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.059003823.x
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, Flores-Suarez LF, Gross WL, Guillevin L, Hagen EC, Hoffman GS, Jayne DR, Kallenberg CGM, Lamprecht P, Langford CA, Luqmani RA, Mahr AD, Matteson EL, Merkel PA, Ozen S, Pusey CD, Rasmussen N, Rees AJ, Scott DGI, Specks U, Stone JH, Takahashi K, Watts RA (2013) 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum 65:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37715
Coppo R (2019) Pediatric IgA nephropathy in Europe. Kidney Dis (Basel) 5:182–188. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495751
Gutiérrez E, Zamora I, Ballarín JA, Arce Y, Jiménez S, Quereda C, Olea T, Martínez-Ara J, Segarra A, Bernis C, García A, Goicoechea M, García de Vinuesa S, Rojas-Rivera J, Praga M, Grupo de Estudio de Enfermedades Glomerulares de la Sociedad Española de Nefrología (GLOSEN) (2012) Long-term outcomes of IgA nephropathy presenting with minimal or no proteinuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1753–1760. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2012010063
Maixnerova D, Reily C, Bian Q, Neprasova M, Novak J, Tesar V (2016) Markers for the progression of IgA nephropathy. J Nephrol 29:535–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-016-0299-0
Xie J, Kiryluk K, Wang W, Wang Z, Guo S, Shen P, Ren H, Pan X, Chen X, Zhang W, Li X, Shi H, Li Y, Gharavi AG, Chen N (2012) Predicting progression of IgA nephropathy: new clinical progression risk score. PLoS One 7:e38904. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038904
Reich HN, Troyanov S, Scholey JW, Cattran DC, Toronto Glomerulonephritis Registry (2007) Remission of proteinuria improves prognosis in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:3177–3183. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2007050526
Coppo R, Lofaro D, Camilla RR, Bellur S, Cattran D, Cook HT, Roberts IS, Peruzzi L, Amore A, Emma F, Fuiano L, Berg U, Topaloglu R, Bilginer Y, Gesualdo L, Polci R, Mizerska-Wasiak M, Caliskan Y, Lundberg S, Cancarini G, Geddes C, Wetzels J, Wiecek A, Durlik M, Cusinato S, Rollino C, Maggio M, Praga M, K Smerud H, Tesar V, Maixnerova D, Barratt J, Papalia T, Bonofiglio R, Mazzucco G, Giannakakis C, Soderberg M, Orhan D, Di Palma AM, Maldyk J, Ozluk Y, Sudelin B, Tardanico R, Kipgen D, Steenbergen E, Karkoszka H, Perkowska-Ptasinska A, Ferrario F, Gutierrez E, Honsova E (2017) Risk factors for progression in children and young adults with IgA nephropathy: an analysis of 261 cases from the VALIGA European cohort. Pediatr Nephrol 32:139-150.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-016-3469-3
Barbour SJ, Coppo R, Er L, Russo ML, Liu ZH, Ding J, Katafuchi R, Yoshikawa N, Xu H, Kagami S, Yuzawa Y, Emma F, Cambier A, Peruzzi L, Wyatt RJ, Cattran DC, International IgA Nephropathy Network (2021) Updating the International IgA Nephropathy Prediction Tool for use in children. Kidney Int 99:1439-1450.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2020.10.033
Fabiano RCG, de Almeida AS, Bambirra EA, Oliveira EA, Silva SE, AC, Pinheiro SVB (2017) Mesangial C4d deposition may predict progression of kidney disease in pediatric patients with IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1211–1220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3610-y
Wyatt RJ, Julian BA (2013) IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med 368:2402–2414. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.07420716
Roos A, Rastaldi MP, Calvaresi N, Oortwijn BD, Schlagwein N, van Gijlswijk-Janssen DJ, Stahl GL, Matsushita M, Fujita T, van Kooten C, Daha MR (2006) Glomerular activation of the lectin pathway of complement in IgA nephropathy is associated with more severe renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1724–1734. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2005090923
Medjeral-Thomas NR, Lomax-Browne HJ, Beckwith H, Willicombe M, McLean AG, Brookes P, Pusey CD, Falchi M, Cook HT, Pickering MC (2017) Circulating complement factor H-related proteins 1 and 5 correlate with disease activity in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 92:942–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2017.03.043
Daha MR, van Kooten C (2016) Role of complement in IgA nephropathy. J Nephrol 29:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-015-0245-6
Espinosa M, Ortega R, Sánchez M, Segarra A, Salcedo MT, González F, Camacho R, Valdivia MA, Cabrera R, López K, Pinedo F, Gutierrez E, Valera A, Leon M, Cobo MA, Rodriguez R, Ballarín J, Arce Y, García B, Muñoz MD, Praga M; Spanish Group for Study of Glomerular Diseases (GLOSEN) (2014) Association of C4d deposition with clinical outcomes in IgA nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:897–904.https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.09710913
Sahin OZ, Yavas H, Taslı F, Gibyeli DG, Ersoy R, Uzum A, Cirit M (2014) Prognostic value of glomerular C4d staining in patients with IgA nephritis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:3299–3304
Faria B, Henriques C, Matos AC, Daha MR, Pestana M, Seelen M (2015) Combined C4d and CD3 immunostaining predicts immunoglobulin (Ig)A nephropathy progression. Clin Exp Immunol 179:354–361. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12461
Espinosa M, Ortega R, Gómez-Carrasco JM, López-Rubio F, López-Andreu M, López-Oliva MO, Aljama P (2009) Mesangial C4d deposition: a new prognostic factor in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:886–891. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfn563
Benz K, Ferrazzi F, Galiano M, Sauerstein K, Vonbrunn E, Daniel C, Büttner-Herold M, Amann K (2020) Relevance of glomerular C4d deposition in pediatric patients with Henoch-Schönlein purpura compared to IgA nephritis. J Nephropathol 10:e16. https://doi.org/10.34172/jnp.2021.16
Schwartz GJ, Work DF (2009) Measurement and estimation of GFR in children and adolescents. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1832–1843. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.01640309
(1987) Report of the second task force on blood pressure control in children--1987. Pediatrics 79:1–25
Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, Blowey D, Carroll AE, Daniels SR, de Ferranti SD, Dionne JM, Falkner B, Flinn SK, Gidding SS, Goodwin C, Leu MG, Powers ME, Rea C, Samuels J, Simasek M, Thaker VV, Urbina EM; Subcommittee on screening and management of high blood pressure in children (2017) Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 140:e20171904. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-1904
Trimarchi H, Barratt J, Cattran DC, Cook HT, Coppo R, Haas M, Liu ZH, Roberts IS, Yuzawa Y, Zhang H, Feehally J; IgAN Classification working group of the international IgA nephropathy network and the renal pathology society; Conference Participants (2016) Oxford Classification of IgA nephropathy 2016: an update from the IgA Nephropathy Classification Working Group. Kidney Int 91:1014-1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2017.02.003
Heybeli C, Unlu M, Yildiz S, Cavdar C, Sarioglu S, Camsari T (2015) IgA nephropathy: association of C4d with clinical and histopathological findings and possible role of IgM. Ren Fail 37:1464–1469. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2015.1077319
Haas M, Verhave JC, Liu ZH, Liu ZH, Alpers CE, Barratt J, Becker JU, Cattran D, Cook HT, Coppo R, Feehally J, Pani A, Perkowska-Ptasinska A, Roberts IS, Soares MF, Trimarchi H, Wang S, Yuzawa Y, Zhang H, Troyanov S, Katafuchi R (2017) A multicenter study of the predictive value of crescents in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 28:691–701. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2016040433
Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society; Coppo R, Troyanov S, Camilla R, Hogg RJ, Cattran DC, Cook HT, Feehally J, Roberts IS, Amore A, Alpers CE, Barratt J, Berthoux F, Bonsib S, Bruijn JA, D’ Agati V, D’ Amico G, Emancipator SN, Emma F, Ferrario F, Fervenza FC, Florquin S, Fogo AB, Geddes CC, Groene HJ, Haas M, Herzenberg AM, Hill PA, Hsu SI, Jennette JC, Joh K, Julian BA, Kawamura T, Lai FM, Li LS, Li PK, Liu ZH, Mezzano S, Schena FP, Tomino Y, Walker PD, Wang H, Weening JJ, Yoshikawa N, Zhang H (2010) The Oxford IgA nephropathy clinicopathological classification is valid for children as well as adults. Kidney Int 77:921-927. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2010.43
Edström Halling S, Söderberg MP, Berg UB (2012) Predictors of outcome in paediatric IgA nephropathy with regard to clinical and histopathological variables (Oxford classification). Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:715–722. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr339
Xu K, Zhang L, Ding J, Wang S, Su B, Xiao H, Wang F, Zhong X, Li Y (2018) Value of the Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy in children with Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis. J Nephrol 31:279–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-017-0457-z
McMullen ME, Hart ML, Walsh MC, Buras J, Takahashi K, Stahl GL (2006) Mannose-binding lectin binds IgM to activate the lectin complement pathway in vitro and in vivo. Immunobiology 211:759–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2006.06.011
Acknowledgements
The Capital Health Research and Development Special Grant (No. 2016-2-2094), the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission’s Research on the Application of Capital Clinical Characteristics Program (No. Z161100000516106), and the Beijing Science and Technology Commission’s Project (No. D181100000118006) all contributed to this research. We appreciate all of our colleagues from Beijing Children’s Hospital, Department of Nephrology for providing information on the pediatric patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The Ethics Committee of Beijing Children’s Hospital in China approved this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, D., Lei, L., Zhang, H. et al. Clinical relevance of glomerular C4d deposition in children with early IgA nephropathy or Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 38, 431–438 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-022-05585-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-022-05585-3