Abstract
Background
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is one of the most common genetic renal diseases and may be inherited in an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive pattern. Pathogenic variants in two major genes, PKD1 and PKD2, and two rarer genes, GANAB and DNAJB11, cause autosomal dominant PKD (ADPKD). Early onset and severe PKD can occur with PKD1 and PKD2 pathogenic variants and such phenotypes may be modified by second alleles inherited in trans. Homozygous or compound heterozygous hypomorphic PKD1 variants may also cause a moderate to severe disease PKD phenotype.
Methods
Targeted renal gene panel followed by Sanger sequencing of PKD1 gene were employed to investigate molecular causes in early onset PKD patients.
Results
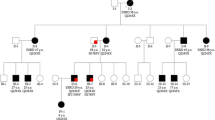
In this study, we report four consanguineous Saudi Arabian families with early onset PKD which were associated with biallelic variants in PKD1 gene.
Conclusions
Our findings confirm that PKD1 alleles may combine to produce severe paediatric onset PKD mimicking the more severe autosomal recessive ciliopathy syndromes associated with PKD. Screening of parents of such children may also reveal subclinical PKD phenotypes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y (2007) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 369:1287–1301
Hildebrandt F, Otto E (2005) Cilia and centrosomes: a unifying pathogenic concept for cystic kidney disease? Nat Rev Genet 6:928–940
Igarashi P, Somlo S (2002) Genetics and pathogenesis of polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2384–2398
Hulten M (1988) Linkage heterogeneity in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 2:451–452
Kimberling WJ, Fain PR, Kenyon JB, Goldgar D, Sujansky E, Gabow PA (1988) Linkage heterogeneity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 319:913–918
Mochizuki T, Wu G, Hayashi T, Xenophontos SL, Veldhuisen B, Saris JJ, Reynolds DM, Cai Y, Gabow PA, Pierides A, Kimberling WJ, Breuning MH, Deltas CC, Peters DJ, Somlo S (1996) PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes an integral membrane protein. Science 272:1339–1342
Porath B, Gainullin VG, Cornec-Le Gall E, Dillinger EK, Heyer CM, Hopp K, Edwards ME, Madsen CD, Mauritz SR, Banks CJ, Baheti S, Reddy B, Herrero JI, Banales JM, Hogan MC, Tasic V, Watnick TJ, Chapman AB, Vigneau C, Lavainne F, Audrezet MP, Ferec C, Le Meur Y, Torres VE, Genkyst Study Group HPoPKDG, Consortium for Radiologic Imaging Studies of Polycystic Kidney D, Harris PC (2016) Mutations in GANAB, encoding the glucosidase IIalpha subunit, cause autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney and liver disease. Am J Hum Genet 98:1193–1207
Cornec-Le Gall E, Olson RJ, Besse W, Heyer CM, Gainullin VG, Smith JM, Audrezet MP, Hopp K, Porath B, Shi B, Baheti S, Senum SR, Arroyo J, Madsen CD, Ferec C, Joly D, Jouret F, Fikri-Benbrahim O, Charasse C, Coulibaly JM, Yu AS, Khalili K, Pei Y, Somlo S, Le Meur Y, Torres VE, Harris PC (2018) Monoallelic mutations to DNAJB11 cause atypical autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Hum Genet 102:832–844
The International Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium (1995) Polycystic kidney disease: the complete structure of the PKD1 gene and its protein. Cell 81:289–298
Harris PC, Torres VE (2009) Polycystic kidney disease. Annu Rev Med 60:321–337
Schneider MC, Rodriguez AM, Nomura H, Zhou J, Morton CC, Reeders ST, Weremowicz S (1996) A gene similar to PKD1 maps to chromosome 4q22: a candidate gene for PKD2. Genomics 38:1–4
Steinman TI (2012) Polycystic kidney disease: a 2011 update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 21:189–194
Bergmann C, von Bothmer J, Ortiz Bruchle N, Venghaus A, Frank V, Fehrenbach H, Hampel T, Pape L, Buske A, Jonsson J, Sarioglu N, Santos A, Ferreira JC, Becker JU, Cremer R, Hoefele J, Benz MR, Weber LT, Buettner R, Zerres K (2011) Mutations in multiple PKD genes may explain early and severe polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:2047–2056
Oatley P, Talukder MM, Stewart AP, Sandford R, Edwardson JM (2013) Polycystin-2 induces a conformational change in polycystin-1. Biochemistry 52:5280–5287
Hateboer N, v Dijk MA, Bogdanova N, Coto E, Saggar-Malik AK, San Millan JL, Torra R, Breuning M, Ravine D (1999) Comparison of phenotypes of polycystic kidney disease types 1 and 2. European PKD1-PKD2 study group. Lancet 353:103–107
Cornec-Le Gall E, Audrezet MP, Chen JM, Hourmant M, Morin MP, Perrichot R, Charasse C, Whebe B, Renaudineau E, Jousset P, Guillodo MP, Grall-Jezequel A, Saliou P, Ferec C, Le Meur Y (2013) Type of PKD1 mutation influences renal outcome in ADPKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1006–1013
Rossetti S, Harris PC (2007) Genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1374–1380
Vujic M, Heyer CM, Ars E, Hopp K, Markoff A, Orndal C, Rudenhed B, Nasr SH, Torres VE, Torra R, Bogdanova N, Harris PC (2010) Incompletely penetrant PKD1 alleles mimic the renal manifestations of ARPKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1097–1102
Rossetti S, Kubly VJ, Consugar MB, Hopp K, Roy S, Horsley SW, Chauveau D, Rees L, Barratt TM, van't Hoff WG, Niaudet P, Torres VE, Harris PC (2009) Incompletely penetrant PKD1 alleles suggest a role for gene dosage in cyst initiation in polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 75:848–855
Halvorson CR, Bremmer MS, Jacobs SC (2010) Polycystic kidney disease: inheritance, pathophysiology, prognosis, and treatment. Int J Nephrol Renov Dis 3:69–83
Bergmann C (2015) ARPKD and early manifestations of ADPKD: the original polycystic kidney disease and phenocopies. Pediatr Nephrol 30:15–30
Audrezet MP, Corbiere C, Lebbah S, Moriniere V, Broux F, Louillet F, Fischbach M, Zaloszyc A, Cloarec S, Merieau E, Baudouin V, Deschenes G, Roussey G, Maestri S, Visconti C, Boyer O, Abel C, Lahoche A, Randrianaivo H, Bessenay L, Mekahli D, Ouertani I, Decramer S, Ryckenwaert A, Cornec-Le Gall E, Salomon R, Ferec C, Heidet L (2016) Comprehensive PKD1 and PKD2 mutation analysis in prenatal autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:722–729
Dias T, Sairam S, Kumarasiri S (2014) Ultrasound diagnosis of fetal renal abnormalities. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 28:403–415
Al-Hamed MH, Kurdi W, Alsahan N, Alabdullah Z, Abudraz R, Tulbah M, Alnemer M, Khan R, Al-Jurayb H, Alahmed A, Tahir AI, Khalil D, Edwards N, Al Abdulaziz B, Binhumaid FS, Majid S, Faquih T, El-Kalioby M, Abouelhoda M, Altassan N, Monies D, Meyer B, Sayer JA, Albaqumi M (2016) Genetic spectrum of Saudi Arabian patients with antenatal cystic kidney disease and ciliopathy phenotypes using a targeted renal gene panel. J Med Genet 53:338–347
el-Hazmi MA, al-Swailem AR, Warsy AS, al-Swailem AM, Sulaimani R, al-Meshari AA (1995) Consanguinity among the Saudi Arabian population. J Med Genet 32:623–626
Yu C, Chang C, Chang F, Ko H, Chen H (2000) Fetal renal volume in normal gestation: a three-dimensional ultrasound study. Ultrasound Med Biol 26:1253–1256
Tan YC, Blumenfeld JD, Anghel R, Donahue S, Belenkaya R, Balina M, Parker T, Levine D, Leonard DG, Rennert H (2009) Novel method for genomic analysis of PKD1 and PKD2 mutations in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Hum Mutat 30:264–273
Su Q, Hu F, Ge X, Lei J, Yu S, Wang T, Zhou Q, Mei C, Shi Y (2018) Structure of the human PKD1-PKD2 complex. Science 361, Issue 6406
Rossetti S, Hopp K, Sikkink RA, Sundsbak JL, Lee YK, Kubly V, Eckloff BW, Ward CJ, Winearls CG, Torres VE, Harris PC (2012) Identification of gene mutations in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease through targeted resequencing. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:915–933
Hopp K, Ward CJ, Hommerding CJ, Nasr SH, Tuan HF, Gainullin VG, Rossetti S, Torres VE, Harris PC (2012) Functional polycystin-1 dosage governs autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease severity. J Clin Invest 122:4257–4273
Sattar S, Gleeson JG (2011) The ciliopathies in neuronal development: a clinical approach to investigation of Joubert syndrome and Joubert syndrome-related disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol 53:793–798
Tsai J, Taylor R, Chothia C, Gerstein M (1999) The packing density in proteins: standard radii and volumes. J Mol Biol 290:253–266
Carrera P, Calzavara S, Magistroni R, den Dunnen JT, Rigo F, Stenirri S, Testa F, Messa P, Cerutti R, Scolari F, Izzi C, Edefonti A, Negrisolo S, Benetti E, Alibrandi MT, Manunta P, Boletta A, Ferrari M (2016) Deciphering variability of PKD1 and PKD2 in an Italian cohort of 643 patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Sci Rep 6:30850
Wilkes M, Madej MG, Kreuter L, Rhinow D, Heinz V, De Sanctis S, Ruppel S, Richter RM, Joos F, Grieben M, Pike AC, Huiskonen JT, Carpenter EP, Kuhlbrandt W, Witzgall R, Ziegler C (2017) Molecular insights into lipid-assisted ca(2+) regulation of the TRP channel Polycystin-2. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24:123–130
Shen PS, Yang X, DeCaen PG, Liu X, Bulkley D, Clapham DE, Cao E (2016) The structure of the polycystic kidney Disease Channel PKD2 in lipid Nanodiscs. Cell 167:763–773 e711
Grieben M, Pike AC, Shintre CA, Venturi E, El-Ajouz S, Tessitore A, Shrestha L, Mukhopadhyay S, Mahajan P, Chalk R, Burgess-Brown NA, Sitsapesan R, Huiskonen JT, Carpenter EP (2017) Structure of the polycystic kidney disease TRP channel Polycystin-2 (PC2). Nat Struct Mol Biol 24:114–122
Arthur LL, Chung JJ, Jankirama P, Keefer KM, Kolotilin I, Pavlovic-Djuranovic S, Chalker DL, Grbic V, Green R, Menassa R, True HL, Skeath JB, Djuranovic S (2017) Rapid generation of hypomorphic mutations. Nat Commun 8:14112
Acknowledgements
We thank all the families for participating in the study. We also thank all team members at Saudi Human Genome project for help in conducting the study. In addition, we thank sequencing and genotyping core facilities at Genetics Department at the Research Centre, King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre for performing sequencing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MHA-H, FI and JAS conceived of the study and participated in its design and coordination, and drafted and revised the manuscript. NA-S, WK, EN, MA-O and MA-N participated in the clinical diagnosis of the cases. SJR, NE and NO-N performed in silico analysis and protein modelling. WA, NA-T and NA-M carried out all technical aspects of molecular diagnosis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 5267 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Hamed, M.H., Alsahan, N., Rice, S.J. et al. Bialleleic PKD1 mutations underlie early-onset autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in Saudi Arabian families. Pediatr Nephrol 34, 1615–1623 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04267-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04267-x