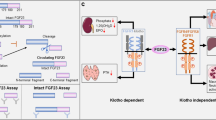
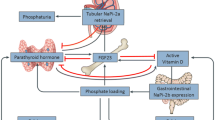
Abstract
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), which is produced in bone, participates in the maintenance of phosphate metabolism and can serve as a biomarker for adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Circulating FGF23 rapidly increases after acute kidney injury (AKI), preceding other known markers such as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and serum creatinine. The increase in FGF23 in AKI appears to be independent of parathyroid hormone, vitamin D signaling pathways, and dietary phosphate. The potential mechanisms include: (1) increased production of FGF23 in the bone by yet-to-be-identified factors; (2) ectopic production of FGF23 by injured renal tubules; and (3) decreased renal clearance of circulating FGF23. Circulating FGF23 determined by intact FGF23 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a more reliable biomarker of AKI than FGF23 C-terminal ELISA (a mixed readout of C-terminal fragment and intact FGF23). Given that FGF23 can be ectopically expressed in differentiated renal tubules and iron modulates FGF23 metabolism, an effect of iron on FGF23 expression in renal tubules is conceivable but remains to be confirmed. More clinical and experimental studies are required to validate the use of circulating FGF23 as a biomarker for the early identification of AKI and prediction of short- and long-term adverse outcomes post-AKI. More importantly, the biologic effect of increased FGF23 in AKI needs to be defined.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu MC, Shiizaki K, Kuro-o M, Moe OW (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and Klotho: physiology and pathophysiology of an endocrine network of mineral metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 75:503–533
Itoh N, Ornitz DM (2008) Functional evolutionary history of the mouse Fgf gene family. Dev Dyn 237:18–27
Kurosu H, Choi M, Ogawa Y, Dickson AS, Goetz R, Eliseenkova AV, Mohammadi M, Rosenblatt KP, Kliewer SA, Kuro-o M (2007) Tissue-specific expression of betaKlotho and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor isoforms determines metabolic activity of FGF19 and FGF21. J Biol Chem 282:26687–26695
Suzuki M, Uehara Y, Motomura-Matsuzaka K, Oki J, Koyama Y, Kimura M, Asada M, Komi-Kuramochi A, Oka S, Imamura T (2008) betaKlotho is required for fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21 signaling through FGF receptor (FGFR) 1c and FGFR3c. Mol Endocrinol 22:1006–1014
Wu X, Lemon B, Li X, Gupte J, Weiszmann J, Stevens J, Hawkins N, Shen W, Lindberg R, Chen JL, Tian H, Li Y (2008) C-terminal tail of FGF19 determines its specificity toward Klotho co-receptors. J Biol Chem 283:33304–33309
ADHR Consortium (2000) Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23. Nat Genet 26:345–348
Gattineni J, Baum M (2010) Regulation of phosphate transport by fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23): implications for disorders of phosphate metabolism. Pediatr Nephrol 25:591–601
Gattineni J, Bates C, Twombley K, Dwarakanath V, Robinson ML, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Baum M (2009) FGF23 decreases renal NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c expression and induces hypophosphatemia in vivo predominantly via FGF receptor 1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F282–F291
Krajisnik T, Bjorklund P, Marsell R, Ljunggren O, Akerstrom G, Jonsson KB, Westin G, Larsson TE (2007) Fibroblast growth factor-23 regulates parathyroid hormone and 1alpha-hydroxylase expression in cultured bovine parathyroid cells. J Endocrinol 195:125–131
Gattineni J, Twombley K, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Baum M (2011) Regulation of serum 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 levels by fibroblast growth factor 23 is mediated by FGF receptors 3 and 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 301:F371–F377
Larsson T, Marsell R, Schipani E, Ohlsson C, Ljunggren O, Tenenhouse HS, Juppner H, Jonsson KB (2004) Transgenic mice expressing fibroblast growth factor 23 under the control of the alpha1(I) collagen promoter exhibit growth retardation, osteomalacia, and disturbed phosphate homeostasis. Endocrinology 145:3087–3094
Bai X, Miao D, Li J, Goltzman D, Karaplis AC (2004) Transgenic mice overexpressing human fibroblast growth factor 23 (R176Q) delineate a putative role for parathyroid hormone in renal phosphate wasting disorders. Endocrinology 145:5269–5279
Finer G, Price HE, Shore RM, White KE, Langman CB (2014) Hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis: response to acetazolamide and postulated mechanisms. Am J Med Genet A 164A:1545–1549
Faul C, Amaral AP, Oskouei B, Hu MC, Sloan A, Isakova T, Gutierrez OM, Aguillon-Prada R, Lincoln J, Hare JM, Mundel P, Morales A, Scialla J, Fischer M, Soliman EZ, Chen J, Go AS, Rosas SE, Nessel L, Townsend RR, Feldman HI, St John Sutton M, Ojo A, Gadegbeku C, Di Marco GS, Reuter S, Kentrup D, Tiemann K, Brand M, Hill JA, Moe OW, Kuro OM, Kusek JW, Keane MG, Wolf M (2011) FGF23 induces left ventricular hypertrophy. J Clin Invest 121:4393–4408
Wolf M (2010) Forging forward with 10 burning questions on FGF23 in kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1427–1435
Gutierrez OM (2010) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and disordered vitamin D metabolism in chronic kidney disease: updating the “trade-off” hypothesis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1710–1716
Portale AA, Wolf M, Juppner H, Messinger S, Kumar J, Wesseling-Perry K, Schwartz GJ, Furth SL, Warady BA, Salusky IB (2014) Disordered FGF23 and mineral metabolism in children with CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:344–353
Pavik I, Jaeger P, Ebner L, Wagner CA, Petzold K, Spichtig D, Poster D, Wuthrich RP, Russmann S, Serra AL (2013) Secreted Klotho and FGF23 in chronic kidney disease Stage 1 to 5: a sequence suggested from a cross-sectional study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:352–359
Jonsson KB, Zahradnik R, Larsson T, White KE, Sugimoto T, Imanishi Y, Yamamoto T, Hampson G, Koshiyama H, Ljunggren O, Oba K, Yang IM, Miyauchi A, Econs MJ, Lavigne J, Juppner H (2003) Fibroblast growth factor 23 in oncogenic osteomalacia and X-linked hypophosphatemia. N Engl J Med 348:1656–1663
Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, Iijima K, Hasegawa H, Okawa K, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2006) Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature 444:770–774
Kurosu H, Ogawa Y, Miyoshi M, Yamamoto M, Nandi A, Rosenblatt KP, Baum MG, Schiavi S, Hu MC, Moe OW, Kuro-o M (2006) Regulation of fibroblast growth factor-23 signaling by Klotho. J Biol Chem 281:6120–6123
Di Marco GS, Reuter S, Kentrup D, Grabner A, Amaral AP, Fobker M, Stypmann J, Pavenstadt H, Wolf M, Faul C, Brand M (2014) Treatment of established left ventricular hypertrophy with fibroblast growth factor receptor blockade in an animal model of CKD. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29:2028–2035
Smith ER, McMahon LP, Holt SG (2014) Fibroblast growth factor 23. Ann Clin Biochem 51:203–227
Wan M, Smith C, Shah V, Gullet A, Wells D, Rees L, Shroff R (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and soluble Klotho in children with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:153–161
Isakova T, Wahl P, Vargas GS, Gutierrez OM, Scialla J, Xie H, Appleby D, Nessel L, Bellovich K, Chen J, Hamm L, Gadegbeku C, Horwitz E, Townsend RR, Anderson CA, Lash JP, Hsu CY, Leonard MB, Wolf M (2011) Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 79:1370–1378
Wolf M, Molnar MZ, Amaral AP, Czira ME, Rudas A, Ujszaszi A, Kiss I, Rosivall L, Kosa J, Lakatos P, Kovesdy CP, Mucsi I (2011) Elevated fibroblast growth factor 23 is a risk factor for kidney transplant loss and mortality. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:956–966
Six I, Okazaki H, Gross P, Cagnard J, Boudot C, Maizel J, Drueke TB, Massy ZA (2014) Direct, acute effects of Klotho and FGF23 on vascular smooth muscle and endothelium. PLoS One 9:e93423
Silswal N, Touchberry CD, Daniel DR, McCarthy DL, Zhang S, Andresen J, Stubbs JR, Wacker MJ (2014) FGF23 directly impairs endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation by increasing superoxide levels and reducing nitric oxide bioavailability. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 307:E426–E436
Nakano C, Hamano T, Fujii N, Matsui I, Tomida K, Mikami S, Inoue K, Obi Y, Okada N, Tsubakihara Y, Isaka Y, Rakugi H (2012) Combined use of vitamin D status and FGF23 for risk stratification of renal outcome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:810–819
Zhang M, Hsu R, Hsu CY, Kordesch K, Nicasio E, Cortez A, McAlpine I, Brady S, Zhuo H, Kangelaris KN, Stein J, Calfee CS, Liu KD (2011) FGF-23 and PTH levels in patients with acute kidney injury: a cross-sectional case series study. Ann Intensive Care 1:21
Leaf DE, Wolf M, Waikar SS, Chase H, Christov M, Cremers S, Stern L (2012) FGF-23 levels in patients with AKI and risk of adverse outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:1217–1223
Leaf DE, Waikar SS, Wolf M, Cremers S, Bhan I, Stern L (2013) Dysregulated mineral metabolism in patients with acute kidney injury and risk of adverse outcomes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 79:491–498
Ali FN, Hassinger A, Price H, Langman CB (2013) Preoperative plasma FGF23 levels predict acute kidney injury in children: results of a pilot study. Pediatr Nephrol 28:959–962
Christov M, Waikar SS, Pereira RC, Havasi A, Leaf DE, Goltzman D, Pajevic PD, Wolf M, Juppner H (2013) Plasma FGF23 levels increase rapidly after acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 84:776–785
Brown JR, Katz R, Ix JH, de Boer IH, Siscovick DS, Grams ME, Shlipak M, Sarnak MJ (2014) Fibroblast growth factor-23 and the long-term risk of hospital-associated AKI among community-dwelling older individuals. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:239–246
Leaf DE, Wolf M, Stern L (2010) Elevated FGF-23 in a patient with rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:1335–1337
Kellum JA, Lameire N (2013) Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: a KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit Care 17:204
Zanchi C, Locatelli M, Benigni A, Corna D, Tomasoni S, Rottoli D, Gaspari F, Remuzzi G, Zoja C (2013) Renal expression of FGF23 in progressive renal disease of diabetes and the effect of ACE inhibitor. PLoS One 8:e70775
Pavik I, Jaeger P, Ebner L, Poster D, Krauer F, Kistler AD, Rentsch K, Andreisek G, Wagner CA, Devuyst O, Wuthrich RP, Schmid C, Serra AL (2012) Soluble Klotho and autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:248–257
Pavik I, Jaeger P, Kistler AD, Poster D, Krauer F, Cavelti-Weder C, Rentsch KM, Wuthrich RP, Serra AL (2011) Patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease have elevated fibroblast growth factor 23 levels and a renal leak of phosphate. Kidney Int 79:234–240
Spichtig D, Zhang H, Mohebbi N, Pavik I, Petzold K, Stange G, Saleh L, Edenhofer I, Segerer S, Biber J, Jaeger P, Serra AL, Wagner CA (2014) Renal expression of FGF23 and peripheral resistance to elevated FGF23 in rodent models of polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 85:1340–1350
Wang J, Pantopoulos K (2011) Regulation of cellular iron metabolism. Biochem J 434:365–381
Andrews NC (2000) Iron metabolism: iron deficiency and iron overload. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 1:75–98
Andrews NC (1999) Disorders of iron metabolism. N Engl J Med 341:1986–1995
Wolf M, White KE (2014) Coupling fibroblast growth factor 23 production and cleavage: iron deficiency, rickets, and kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 23:411–419
Imel EA, Gray AK, Padgett LR, Econs MJ (2014) Iron and fibroblast growth factor 23 in X-linked hypophosphatemia. Bone 60:87–92
Imel EA, Peacock M, Gray AK, Padgett LR, Hui SL, Econs MJ (2011) Iron modifies plasma FGF23 differently in autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets and healthy humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:3541–3549
Farrow EG, Yu X, Summers LJ, Davis SI, Fleet JC, Allen MR, Robling AG, Stayrook KR, Jideonwo V, Magers MJ, Garringer HJ, Vidal R, Chan RJ, Goodwin CB, Hui SL, Peacock M, White KE (2011) Iron deficiency drives an autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets (ADHR) phenotype in fibroblast growth factor-23 (Fgf23) knock-in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:E1146–E1155
Schouten BJ, Doogue MP, Soule SG, Hunt PJ (2009) Iron polymaltose-induced FGF23 elevation complicated by hypophosphataemic osteomalacia. Ann Clin Biochem 46:167–169
Yamamoto S, Okada Y, Mori H, Fukumoto S, Tanaka Y (2012) Fibroblast growth factor 23-related osteomalacia caused by the prolonged administration of saccharated ferric oxide. Intern Med 51:2375–2378
Schouten BJ, Hunt PJ, Livesey JH, Frampton CM, Soule SG (2009) FGF23 elevation and hypophosphatemia after intravenous iron polymaltose: a prospective study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2332–2337
Wolf M, Koch TA, Bregman DB (2013) Effects of iron deficiency anemia and its treatment on fibroblast growth factor 23 and phosphate homeostasis in women. J Bone Miner Res 28:1793–1803
Clinkenbeard EL, Farrow EG, Summers LJ, Cass TA, Roberts JL, Bayt CA, Lahm T, Albrecht M, Allen MR, Peacock M, White KE (2014) Neonatal iron deficiency causes abnormal phosphate metabolism by elevating FGF23 in normal and ADHR mice. J Bone Miner Res 29:361–369
Davis CL, Kausz AT, Zager RA, Kharasch ED, Cochran RP (1999) Acute renal failure after cardiopulmonary bypass in related to decreased serum ferritin levels. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2396–2402
Tuttle KR, Worrall NK, Dahlstrom LR, Nandagopal R, Kausz AT, Davis CL (2003) Predictors of ARF after cardiac surgical procedures. Am J Kidney Dis 41:76–83
Martines AM, Masereeuw R, Tjalsma H, Hoenderop JG, Wetzels JF, Swinkels DW (2013) Iron metabolism in the pathogenesis of iron-induced kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol 9:385–398
Shah SV, Rajapurkar MM, Baliga R (2011) The role of catalytic iron in acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:2329–2331
Johnson AC, Becker K, Zager RA (2010) Parenteral iron formulations differentially affect MCP-1, HO-1, and NGAL gene expression and renal responses to injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299:F426–F435
Goetz R, Nakada Y, Hu MC, Kurosu H, Wang L, Nakatani T, Shi M, Eliseenkova AV, Razzaque MS, Moe OW, Kuro-o M, Mohammadi M (2010) Isolated C-terminal tail of FGF23 alleviates hypophosphatemia by inhibiting FGF23-FGFR-Klotho complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:407–412
Smith ER, Cai MM, McMahon LP, Holt SG (2012) Biological variability of plasma intact and C-terminal FGF23 measurements. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:3357–3365
Shimada T, Urakawa I, Isakova T, Yamazaki Y, Epstein M, Wesseling-Perry K, Wolf M, Salusky IB, Juppner H (2010) Circulating fibroblast growth factor 23 in patients with end-stage renal disease treated by peritoneal dialysis is intact and biologically active. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:578–585
Goebel S, Lienau J, Rammoser U, Seefried L, Wintgens KF, Seufert J, Duda G, Jakob F, Ebert R (2009) FGF23 is a putative marker for bone healing and regeneration. J Orthop Res 27:1141–1146
Gravesen E, Hofman-Bang J, Mace ML, Lewin E, Olgaard K (2013) High dose intravenous iron, mineral homeostasis and intact FGF23 in normal and uremic rats. BMC Nephrol 14:281
Wohrle S, Henninger C, Bonny O, Thuery A, Beluch N, Hynes NE, Guagnano V, Sellers WR, Hofmann F, Kneissel M, Graus Porta D (2013) Pharmacological inhibition of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor signaling ameliorates FGF23-mediated hypophosphatemic rickets. J Bone Miner Res 28:899–911
Fukumoto S (2014) Anti-fibroblast growth factor 23 antibody therapy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 23:346–351
Ketteler M, Biggar PH, Liangos O (2013) FGF23 antagonism: the thin line between adaptation and maladaptation in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:821–825
Shalhoub V, Shatzen EM, Ward SC, Davis J, Stevens J, Bi V, Renshaw L, Hawkins N, Wang W, Chen C, Tsai MM, Cattley RC, Wronski TJ, Xia X, Li X, Henley C, Eschenberg M, Richards WG (2012) FGF23 neutralization improves chronic kidney disease-associated hyperparathyroidism yet increases mortality. J Clin Invest 122:2543–2553
Acknowledgments
The authors are supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01-DK091392, R01-DK092461), the George M. O’Brien Kidney Research Center at UT Southwestern Medical Center (P30-DK-07938), the Simmons Family Foundation, and the Charles and Jane Pak Foundation. JAN is supported by the Ben J. Lipps Research Fellowship Program of American Society of Nephrology Foundation for Kidney Research, and the Truelson Fellowship Fund at the Charles and Jane Pak Center of Mineral Metabolism and Clinical Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neyra, J.A., Moe, O.W. & Hu, M.C. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol 30, 1909–1918 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-3006-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-3006-1