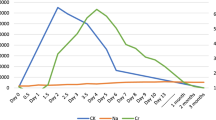
Abstract
Hypokalemia is a recognized cause of rhabdomyolysis but very few reports document its association with inborn renal tubular disorders. We report our experience with hypokalemic rhabdomyolysis in 5 pediatric patients affected by inborn renal tubular disorders and the results of a careful review of the literature disclosing 9 further cases for a total of 14 patients (8 male and 6 female subjects, aged between 1.6 and 46, median 16 years). The inborn renal tubular disorders underlying rhabdomyolysis were classic distal renal tubular acidosis (n = 7), Gitelman syndrome (n = 5), classic Bartter syndrome (n = 1), and antenatal Bartter syndrome (n = 1). In 8 patients rhabdomyolysis followed an acute intestinal disease, an upper respiratory illness or the discontinuation of regular medication. Five patients experienced two or more episodes of rhabdomyolysis. In 10 patients the underlying renal tubular disorder was recognized concurrently with the episode of rhabdomyolysis or some weeks later. In conclusion some congenital renal tubular disorders predispose to hypokalemic rhabdomyolysis. Prevention of discontinuation of regular medication and electrolyte repair in the context of acute intercurrent illnesses might avoid the development of hypokalemic rhabdomyolysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lane R, Phillips M (2003) Rhabdomyolysis. BMJ 327:115–116
Mannix R, Tan ML, Wright R, Baskin M (2006) Acute pediatric rhabdomyolysis: causes and rates of renal failure. Pediatrics 118:2119–2125
Ng YT, Johnston HM (2006) Clinical rhabdomyolysis. J Paediatr Child Health 36:397–400
Elsayed EF, Reilly RF (2009) Rhabdomyolysis: a review, with emphasis on the pediatric population. Pediatr Nephrol 25:7–18
Gennari FJ (1998) Hypokalemia. N Engl J Med 339:451–458
Singhal PC, Abramovici M, Venkatesan J, Mattana J (1991) Hypokalemia and rhabdomyolysis. Miner Electrolyte Metab 17:335–339
Rodríguez-Soriano J, Vallo A (1990) Renal tubular acidosis. Pediatr Nephrol 4:268–275
Rodríguez Soriano J (2002) Renal tubular acidosis: the clinical entity. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2160–2170
Bettinelli A, Vezzoli G, Colussi G, Bianchetti MG, Sereni F, Casari G (1998) Genotype-phenotype correlations in normotensive patients with primary renal tubular hypokalemic alkalosis. J Nephrol 11:61–70
Colussi G, Bettinelli A, Tedeschi S, De Ferrari ME, Syrén ML, Borsa N, Mattiello C, Casari G, Bianchetti MG (2007) A thiazide test for the diagnosis of renal tubular hypokalemic disorders. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2:454–460
Bierbach H, Bohl J, Göldner HJ, Majdandzic J (1983) Hypokalemic rhabdomyolysis associated with Bartter’s syndrome. Klin Wochenschr 61:183–186
Van der Loos TL (1986) Rhabdomyolysis in Bartter’s syndrome. Acta Clin Belg 41:131
Van der Loos TL (1986) Profound hypokalemia with rhabdomyolysis in Bartter’s syndrome. JAMA 256:2518
Hanip MR, Cheong IK, Chin GL, Khalid BA (1990) Rhabdomyolysis associated with hypokalaemic periodic paralysis of renal tubular acidosis. Singapore Med J 31:159–161
Nishihara G, Higashi H, Matsuo S, Yasunaga C, Sakemi T, Nakamoto M (1998) Acute renal failure due to hypokalemic rhabdomyolysis in Gitelman’s syndrome. Clin Nephrol 50:330–332
Abad S, Park S, Grimaldi D, Rollot F, Blanche P (2005) Hypokalaemia tetraparesis and rhabdomyolysis: aetiology discovered on a normal lung radiograph. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2571–2572
Kim CJ, Woo YJ, Ma JS, Hwang TJ, Kang HC, Kim PK, Lee JS, Kim DH (2005) Hypokalemic paralysis and rhabdomyolysis in distal renal tubular acidosis. Pediatr Int 47:211–213
Pela I, Materassi M, Seracini D, Lavoratti G, Bettinelli A (2005) Hypokalemic rhabdomyolysis in a child with Bartter’s syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1189–1191
Tasic V, Korneti P, Gucev Z, Hoppe B, Blau N, Cheong HI (2008) Atypical presentation of distal renal tubular acidosis in two siblings. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1177–1181
Batlle D, Moorthi KM, Schlueter W, Kurtzman N (2006) Distal renal tubular acidosis and the potassium enigma. Semin Nephrol 26:471–478
Longo N, di San A, Filippo C, Pasquali M (2006) Disorders of carnitine transport and the carnitine cycle. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 142C:77–85
Emma F, Pizzini C, Tessa A, Di Giandomenico S, Onetti-Muda A, Santorelli FM, Bertini E, Rizzoni G (2006) "Bartter-like" phenotype in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 21:355–360
Cortesi C, Bettinelli A, Emma F, Fischbach M, Bertolani P, Bianchetti MG (2005) Severe syncope and sudden death in children with inborn salt-losing hypokalaemic tubulopathies. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:1981–1983
Phillips DR, Ahmad KI, Waller SJ, Meisner P, Karet FE (2006) A serum potassium level above 10 mmol/L in a patient predisposed to hypokalemia. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2:340–347
Acknowledgement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Vigier, R.O., Ortisi, M.T., La Manna, A. et al. Hypokalemic rhabdomyolysis in congenital tubular disorders: a case series and a systematic review. Pediatr Nephrol 25, 861–866 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1388-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1388-2