Abstract
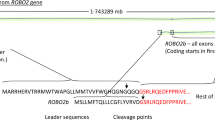
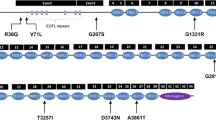
Familial clustering of vesico-ureteral reflux (VUR) suggests that genetic factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of this condition. The SLIT2 protein and its receptor, ROBO2, have key functions in the formation of the ureteric bud. Two recent studies have found that ROBO2 gene missense mutations are associated with VUR. In the study reported here, we investigated the genetic contribution of the SLIT2 and ROBO2 genes in non-syndromic familial VUR by mutation screening of 54 unrelated patients with primary VUR. Direct sequencing of all 26 exons and the exon–intron boundaries revealed six ROBO2 gene variants, two of which were new. Direct sequencing of all 37 exons and the exon–intron boundaries identified 20 SLIT2 gene variants, two of which were new. One variant, c.4253C > T, which was found in two families, leads to an amino acid substitution in a relatively well-conserved amino acid, p.Ala1418Val, which was predicted to cause an altered secondary structure but to have little impact on the three-dimensional structure. This missense variant did not segregate with VUR in these two families and was not found in 96 control subjects. We conclude that gene variants in ROBO2 and SLIT2 are rare causes of VUR in humans. Our results provide further evidence for the genetic heterogeneity of this disorder.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott JE, Swallow V, Coulthard MG, Lambert HJ, Lee RE (1997) Screening of newborn babies for familial ureteric reflux. Lancet 350:396–400
Smellie J, Edwards D, Hunter N, Normand IC, Prescod N (1975) Vesico-ureteric reflux and renal scarring. Kidney Int Suppl 4:S65–S72
Silva JM, Santos Diniz JS, Marino VS, Lima EM, Cardoso LS, Vasconcelos MA, Oliveira EA (2006) Clinical course of 735 children and adolescents with primary vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 21:981–988
Ardissino G, Dacco V, Testa S, Bonaudo R, Claris-Appiani A, Taioli E, Marra G, Edefonti A, Sereni F (2003) Epidemiology of chronic renal failure in children: data from the ItalKid project. Pediatrics 111:e382–e387
Kincaid-Smith PS, Bastos MG, Becker GJ (1984) Reflux nephropathy in the adult. Contrib Nephrol 39:94–101
Brakeman P (2008) Vesicoureteral reflux, reflux nephropathy and end-stage renal disease. Adv Urol 2008:508949
Kaefer M, Curran M, Treves ST, Bauer S, Hendren WH, Peters CA, Atala A, Diamond D, Retik A (2000) Sibling vesicoureteral reflux in multiple gestation births. Pediatrics 105:800–804
Kenda RB, Fettich JJ (1992) Vesicoureteric reflux and renal scars in asymptomatic siblings of children with reflux. Arch Dis Child 67:506–508
Connolly LP, Treves ST, Connolly SA, Zurakowski D, Share JC, Bar-Sever Z, Mitchell KD, Bauer SB (1997) Vesicoureteral reflux in children: incidence and severity in siblings. J Urol 157:2287–2290
Celik A, Ulman I, Aydin M, Arikan A, Avanoğlu A, Gökdemir A (2002) Familial vesicoureteral reflux in asymptomatic siblings. Turk J Pediatr 44:240–243
Hollowell JG, Greebfield SP (2002) Screening siblings for vesico-ureteral reflux. J Urol 168:2138–2141
Aggarwal VK, Verrier Jones K (1989) Vesicoureteric reflux: screening of first degree relatives. Arch Dis Child 64:1538–1541
Noe HN, Wyatt RJ, Peeden JN Jr, Rivas ML (1992) The transmission of vesicoureteral reflux from parent to child. J Urol 148:1869–1971
North RA, Taylor RS, Gunn TR (2000) Pregnancy outcome in women with reflux nephropathy and the inheritance of vesico-ureteric reflux. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 40:280–285
Chapman CJ, Bailey RR, Janus ED, Abbott GD, Lynn KL (1985) Vesicoureteric reflux: segregation analysis. Am J Med Genet 20:577–584
Feather SA, Malcolm S, Woolf AS, Wright V, Blaydon D, Reid CJ, Flinter FA, Proesmans W, Devriendt K, Carter J, Warwicker P, Goodship TH, Goodship JA (2000) Primary, nonsyndromic vesicoureteric reflux and its nephropathy is genetically heterogeneous, with a locus on chromosome 1. Am J Hum Genet 66:1420–1425
Kelly H, Molony CM, Darlow JM, Pirker ME, Yoneda A, Green AJ, Puri P, Barton DE (2007) A genome-wide scan for genes involved in primary vesicoureteric reflux. J Med Genet 44:710–717
Conte ML, Bertoli-Avella AM, de Graaf BM, Punzo F, Lama G, La Manna A, Grassia C, Rambaldi PF, Oostra BA, Perrotta S (2008) A genome search for primary vesicoureteral reflux shows further evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Pediatr Nephrol 23:587–595
Sanna-Cherchi S, Reese A, Hensle T, Caridi G, Izzi C, Kim YY, Konka A, Murer L, Scolari F, Ravazzolo R, Ghiggeri GM, Gharavi AG (2005) Familial vesicoureteral reflux: testing replication of linkage in seven new multigenerational kindreds. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1781–1787
Grieshammer U, Ma Le, Plump AS, Wang F, Tessier-Lavigne M, Martin GR (2004) SLIT2-Mediated ROBO2 Signaling Restricts Kidney Induction to a Single Site. Dev Cell 6:709–717
Lu W, van Eerde AM, Fan X, Quintero-Rivera F, Kulkarni S, Ferguson H, Kim HG, Fan Y, Xi Q, Li QG, Sanlaville D, Andrews W, Sundaresan V, Bi W, Yan J, Giltay JC, Wijmenga C, de Jong TP, Feather SA, Woolf AS, Rao Y, Lupski JR, Eccles MR, Quade BJ, Gusella JF, Morton CC, Maas RL (2007) Disruption of ROBO2 is associated with urinary tract anomalies and confers risk of vesicoureteral reflux. Am J Hum Genet 80:616–632
Bertoli-Avella AM, Conte ML, Punzo F, de Graaf BM, Lama G, La Manna A, Polito C, Grassia C, Nobili B, Rambaldi PF, Oostra BA, Perrotta S (2008) ROBO2 gene variants are associated with familial vesicoureteral reflux. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:825–831
Rothberg JM, Artavanis-Tsakonas S (1992) Modularity of the slit protein, characterization of a conserved carboxy-terminal sequence in secreted proteins and a motif implicated in extracellular protein Interactions. J Mol Biol 227:367–370
Morlot C, Thielens NM, Ravelli RB, Hemrika W, Romijn RA, Gros P, Cusack S, McCarthy AA (2007) Structural insights into the Slit-Robo complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14923–14928
Bagri A, Marin O, Plump AS, Mak J, Pleasure SJ, Rubenstein JL, Tessier-Lavigne M (2002) Slit proteins prevent midline crossing and determine the dorsoventral position of major axonal pathways in the mammalian forebrain. Neuron 33:233–248
Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kidd T (1999) Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell 96:795–806
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Kristina Lagerstedt, Fredrik Lundberg, and Hanh T.T. Trinh for excellent laboratory assistance. This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council, HRH Crownprincess Lovisa Foundation, Foundation Frimurarna and Sven Jerring Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zu, S., Bartik, Z., Zhao, S. et al. Mutations in the ROBO2 and SLIT2 genes are rare causes of familial vesico-ureteral reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 1501–1508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1179-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1179-9