Abstract
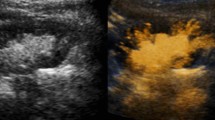
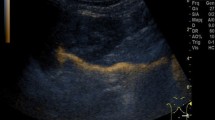
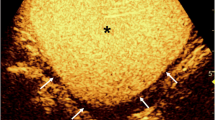
The purpose of our prospective study was to determine the value of indirect voiding urosonography without the use of contrast-media and without filling of the bladder through a catheter (IVUS) for detection of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in children, compared with echo-enhanced voiding urosonography (VUS). Among 57 children (45 girls and 12 boys, aged 2.7 to 12.0 years) admitted for echo-enhanced VUS either as part of routine evaluation after urinary tract infection (UTI) or follow-up of a previously detected VUR, IVUS was also successfully performed in 47 children. The results were considered positive when there was any increase in pelvis size and/or ureter lumen width during voiding. The overall sensitivity of IVUS in the detection of VUR was 49%, specificity 75%. The most accurate results were obtained with VUR grade III, where IVUS correctly detected 6 out of 7 cases, a sensitivity of 86%. The average increase of AP pelvis diameter during voiding was highly significant only in uretero-renal units with VUR grade III. Considering the obstacles in conducting the investigation and its relatively low overall sensitivity and specificity, it seems that IVUS is not sufficiently reliable to replace echo-enhanced VUS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kenda RB, Novljan G, Kenig A, Hojker S, Fettich JJ (2000) Echo-enhanced ultrasound voiding cystography in children: a new approach. Pediatr Nephrol 4:297–300
Novljan G, Kenig A, Rus R, Kenda RB (2003) Cyclic voiding urosonography in detecting vesicoureteric reflux in children. Pediatr Nephrol 10:992–995
Fettich JJ, Kenda RB (1992) Cyclic direct radionuclide voiding cystography: increasing reliability in detecting vesicoureteric reflux in children. Pediatr Radiol 22:337–338
Polito C, Moggio G, La Manna A, Cioce F, Cappabianca S, Di Toro R (2000) Cyclic voiding cystourethrography in the diagnosis of occult vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 14:39–41
Kenda RB, Kenig A, Novljan G, Ponikvar R, Buturović Ponikvar J (2001) Cyclic voiding urosonography for detecting vesicoureteric reflux in renal transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:2229–2231
Hiraoka M, Hori C, Tsukahara H, Kasuga K, Ishihara Y, Kotsuji F, Mayumi M (1999) Vesicoureteral reflux in male and female neonates as detected by voiding ultrasonography. Kidney Int 55:1486–1490
Evans ED, Meyer JS, Harty MP, Bellah RD (1999) Assessment of increase in renal pelvic size on post-void sonography as a predictor of vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatr Radiol 29:291–294
Koff SA (1983) Estimating bladder capacity in children. Urology 21:248
Fritzsch T, Schlief R (1995) Levovist. Drugs Future 20:1224–1227
Darge K, Troeger J, Duetting T, Zieger B, Rohrschneider W, Moehring K, Weber C, Toenshoff B (1999) Reflux in young patients: comparison of voiding US of the bladder and retrovesical space with echo enhancement versus voiding cystourethrography for diagnosis. Radiology 210:201–207
Bosio M (1998) Cystosonography with echocontrast: a new imaging modality to detect vesicoureteric reflux in children. Pediatr Radiol 28:250–255
Avni EF, Ayadi K, Rypens F, Hall M, Schulman CC (1997) Can careful ultrasound examination of the urinary tract exclude vesicoureteral reflux in the neonate? Br J Radiol 70:977–982
Acknowledgements
This study received financial support from the Slovenian Ministry for Research and Technology (grant J3-6402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopač, M., Kenig, A., Ključevšek, D. et al. Indirect voiding urosonography for detecting vesicoureteral reflux in children. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 1285–1287 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1961-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1961-2