Abstract
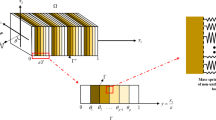
Local mechanical fields at inplane loaded interface corners with discontinuous transitions of anisotropic material properties are of particular interest. This is due to the fact that the structural situation of a corner geometry with different material properties can cause singular behavior of the mechanical inplane fields. The boundary finite element method is employed in this study for the investigation of such structural problems. The results obtained with the boundary finite element method agree excellently with reference results and in addition give a deeper insight into the singular behavior of the problem considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barroso A, Mantič V, París F (2003) Singularity analysis of anisotropic multimaterial corners. Int J Fracture 119:1–23
Chen HP (1998) Stress singularities in anisotropic multi-material wedges and junctions. Int J Solids Struct 35:1057–1073
Chue CH, Chen TH, Lee HT (2002) A general solution on stress singularities in the junction of two anisotropic materials. Composite Struct 55:81–93
Chue CH, Weng SM (2002) Stress singularities in anisotropic three-material wedges and junctions with applications. Composite Struct 58:443–456
Deeks AJ, Wolf JP (2002) A virtual work derivation of the scaled boundary finite-element method for elastostatics. Comput Mech 28:489–504
Jones RG (1975) Mechanics of Composite Materials. McGraw-Hill, Tokyo
Mantič V, París F, Berger J Singularities in 2D anisotropic potential problems in multi-material corners. Int J Solids Struct 40:5197–5218
Pageau SS, Joseph PF, Biggers B (1995) A finite element analysis of the singular stress fields in anisotropic materials loaded in antiplane shear. Int J Numer Meth Eng 38:81–97
Ting TCT (1996) Anisotropic Elasticity: Theory and Applications. Oxford University Press, New York
Wigger HM, Becker W (2005) Inplane Stress Singularities at the Interface Corner of a Bimaterial Junction. Composite Struct 69:193–199
Wolf JP (2003) The Scaled Boundary Finite Element Method. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Wolf JP, Song C (1996) Finite Element Modelling of Unbounded Media. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Wolf JP, Song C (1997) The scaled boundary finite element method – alias consistent infinitesimal finite–element cell method – for elastodynamics. Comput Meth Appl Mech Eng 147:329–355
Yin W-L (2003) Anisotropic elasticity and multi-material singularities. J Elasticity 71:263–292
Yosibash Z, Szabó B Numerical analysis of singularities in two-dimensions Part 1: computation of eigenpairs. Int J Numer Meth Eng 38:2055–2082
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wigger, H.M., Becker, W. Characterization of inplane loaded anisotropic interface corners with the boundary finite element method. Comput Mech 37, 153–162 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-005-0686-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-005-0686-1