Abstract
Background
A series of 500 consecutive laparoscopic hernia repairs, performed by one surgeon, was studied to evaluate the procedure for reliability, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Methods
Patients with routine, first-time, recurrent or multiply recurrent, inguinal hernias were operated using the technique described.
Results
The recurrence rate was 0.2%. The complication rate was 0.6%. There were no deaths. Ninety-six percent of patients returned to work in 4–10 days.
Conclusions
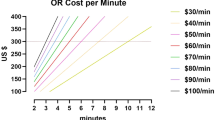
Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair is reliable, safe, and cost-effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liem MSL, et al (1997) Comparison of conventional anterior surgery and laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair. N Engl J Med 336: 1541–1547
Liem MSL, et al (1997) A randomized comparison of physical performance following laparoscopic and open inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 84: 64–67
Miguel PR, et al (1998) Laparoscopic hernia repair—complications. JSLS 2: 35–40
Morfesis FA (1996) The recurrence rate in hernia surgery. Arch Surg 131: 107
Nyhus LM, Condon RE (1989) Hernia, 3rd edn. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 205–206
Nyhus LM, Condon RE (1995) Hernia, 4th edn. Lippincott, pp 253–268
Payne JH Jr, et al (1994) Laparoscopic or open inguinal herniorrhaphy? A randomized prospective trial. Arch Surg 129: 979–981
Peacock E (1969) In: Schwarz SI (ed) Principles of surgery. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 239
Rand Corporation (1983) Conceptualization and measurement of physiologic health for adults, publication No. 15. Rand, Santa Monica, CA, p 3
Stoppa RE (1989) The treatment of complicated groin and incisional hernias. World J Surg 13: 545–554
Vogt DM, et al (1995) Preliminary results of a prospective randomized trial of laparoscopic only versus conventional inguinal herniorrhaphy. Am J Surg 169: 84–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Online publication: 27 February 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fazzio, F.J. Cost-effective, reliable laparoscopic hernia repair. Surg Endosc 16, 931–935 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004640080073
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004640080073