Abstract
Background
The self-help inflatable balloon (SHIB) and autologous skin-grafting surgery (ASGS) were used to prevent stricture after esophageal complete circular endoscopic submucosal dissection (cESD) with promising clinical results. We aim to evaluate which method is more suitable for patients who underwent esophageal cESD.
Methods
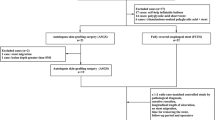
From October 2017 to July 2021, patients whose mucosal defect length were between 30 and 100 mm after esophageal cESD were retrospectively reviewed from two prospective studies. They were enrolled once SHIB or ASGS was used as preventive methods to prevent stricture. Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to balance the baseline characteristics between the two groups. Comparisons were made between the two groups, including operation time, the longitudinal length of ulceration, fasting time, hospitalization days, and the incidence of stricture.
Results
A total of 41 patients who met the inclusion criteria were enrolled in the study. The numbers of patients in SHIB group and ASGS group were 25 and 16, respectively. Fifteen patients in each group were selected after performing PSM. The basic baseline characteristics were comparable between the two groups. The stricture rates were 20% (3/15) in SHIB group and 40% (6/15) in ASGS group, while the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.427). The SHIB group showed significantly shorter operation time, shorter hospitalization days, lower cost, and longer removing balloon/stent time compared with ASGS group (p < 0.001). Comparison of relevant stricture factors between the stricture group and non-stricture group revealed that longer longitudinal length of ulceration (> 60 mm) accounted for a higher proportion in stricture groups (p = 0.035).
Conclusion
Both the SHIB and ASGS had high efficacy and safety in preventing strictures in patients with mucosal defects no longer than 100 mm in length after esophageal cESD. The longitudinal length of ulceration > 60 mm was the independent factor for predicting stricture.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oyama T, Tomori A, Hotta K, Morita S, Kominato K, Tanaka M, Miyata Y (2005) Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early esophageal cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:S67-70
Takahashi H, Arimura Y, Masao H, Okahara S, Tanuma T, Kodaira J, Kagaya H, Shimizu Y, Hokari K, Tsukagoshi H, Shinomura Y, Fujita M (2010) Endoscopic submucosal dissection is superior to conventional endoscopic resection as a curative treatment for early squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 72:255–264
Ishihara R, Arima M, Iizuka T, Oyama T, Katada C, Kato M, Goda K, Goto O, Tanaka K, Yano T, Yoshinaga S, Muto M, Kawakubo H, Fujishiro M, Yoshida M, Fujimoto K, Tajiri H, Inoue H (2020) Endoscopic submucosal dissection/endoscopic mucosal resection guidelines for esophageal cancer. Dig Endosc 32:452–493
Kitagawa Y, Uno T, Oyama T, Kato K, Kato H, Kawakubo H, Kawamura O, Kusano M, Kuwano H, Takeuchi H, Toh Y, Doki Y, Naomoto Y, Nemoto K, Booka E, Matsubara H, Miyazaki T, Muto M, Yanagisawa A, Yoshida M (2019) Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2017 edited by the Japan Esophageal Society: part 1. Esophagus 16:1–24
Tang J, Kong F, Li J, Liu F, Kong X, Li Z (2021) Independent risk factors for esophageal refractory stricture after extensive endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc 35:3618–3627
Shi Q, Ju H, Yao LQ, Zhou PH, Xu MD, Chen T, Zhou JM, Chen TY, Zhong YS (2014) Risk factors for postoperative stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal carcinoma. Endoscopy 46:640–644
Abe S, Iyer PG, Oda I, Kanai N, Saito Y (2017) Approaches for stricture prevention after esophageal endoscopic resection. Gastrointest Endosc 86:779–791
Ishihara R (2018) Prevention of esophageal stricture after endoscopic resection. Dig Endosc 31:134–145
Chu Y, Chen T, Li H, Zhou P, Zhang Y, Chen W, Zhong Y, Yao L, Xu M (2019) Long-term efficacy and safety of intralesional steroid injection plus oral steroid administration in preventing stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection for esophageal epithelial neoplasms. Surg Endosc 33:1244–1251
Nagami Y, Ominami M, Shiba M, Sakai T, Fukunaga S, Sugimori S, Otani K, Hosomi S, Tanaka F, Taira K, Kamata N, Yamagami H, Tanigawa T, Watanabe T, Ishihara T, Yamamoto K, Fujiwara Y (2018) Prediction of esophageal stricture in patients given locoregional triamcinolone injections immediately after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 30:198–205
Kadota T, Yano T, Kato T, Imajoh M, Noguchi M, Morimoto H, Osera S, Yoda Y, Oono Y, Ikematsu H, Ohtsu A, Kaneko K (2016) Prophylactic steroid administration for strictures after endoscopic resection of large superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Endoscopy Int Open 4:E1267–E1274
Zou J, Chai N, Linghu E, Li H, Chai M, Shi Y, Wang Z, Li L (2021) Autologous skin-grafting surgery to prevent esophageal stricture after complete circular endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection: a case-matched controlled study. Surg Endosc 35(11):5962–5970
Li L, Linghu E, Chai N, Xiang J, Wang Z, Zou J, Du C, Wang X (2019) Clinical experience of using a novel self-help inflatable balloon to prevent esophageal stricture after circumferential endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 31:453–459
Zhang W, Zhai Y, Chai N, Linghu E, Li H, Feng X (2018) Single- and double-tunnel endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for large superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Endoscopy 50:505–510
Chai N, Zhang W, Linghu E, Han Y, Chai M, Li Z, Zou J, Li L, Xiong Y (2018) Autologous skin-grafting surgery for the prevention of esophageal stenosis after complete circular endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection. Am J Gastroenterol 113(7):938
Kishida Y, Kakushima N, Kawata N, Tanaka M, Takizawa K, Imai K, Hotta K, Matsubayashi H, Ono H (2015) Complications of endoscopic dilation for esophageal stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection of superficial esophageal cancer. Surg Endosc 29:2953–2959
Ezoe Y, Muto M, Horimatsu T, Morita S, Miyamoto S, Mochizuki S, Minashi K, Yano T, Ohtsu A, Chiba T (2011) Efficacy of preventive endoscopic balloon dilation for esophageal stricture after endoscopic resection. J Clin Gastroenterol 45:222–227
Siersema PD (2019) How to approach a patient with refractory or recurrent benign esophageal stricture. Gastroenterology 156:7–10
Minashi K, Nihei K, Mizusawa J, Takizawa K, Yano T, Ezoe Y, Tsuchida T, Ono H, Iizuka T, Hanaoka N, Oda I, Morita Y, Tajika M, Fujiwara J, Yamamoto Y, Katada C, Hori S, Doyama H, Oyama T, Nebiki H, Amagai K, Kubota Y, Nishimura K, Kobayashi N, Suzuki T, Hirasawa K, Takeuchi T, Fukuda H, Muto M (2019) Efficacy of endoscopic resection and selective chemoradiotherapy for stage I esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 157:382-390.e383
Zhang Y, Ding H, Chen T, Zhang X, Chen WF, Li Q, Yao L, Korrapati P, Jin XJ, Zhang YX, Xu MD, Zhou PH (2019) Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection vs esophagectomy for T1 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a real-world cohort. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:73-81.e73
Kadota T, Yoda Y, Hori K, Shinmura K, Oono Y, Ikematsu H, Yano T (2020) Prophylactic steroid administration against strictures is not enough for mucosal defects involving the entire circumference of the esophageal lumen after esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). Esophagus 17:440–447
Sakaguchi Y, Tsuji Y, Shinozaki T, Ohki D, Mizutani H, Minatsuki C, Niimi K, Yamamichi N, Koike K (2020) Steroid injection and polyglycolic acid shielding to prevent stricture after esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection: a retrospective comparative analysis (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 92:1176-1186.e1171
Shibagaki K, Yuki T, Taniguchi H, Aimi M, Miyaoka Y, Yuki M, Ishimura N, Oshima N, Mishiro T, Tamagawa Y, Mikami H, Izumi D, Yamashita N, Sato S, Ishihara S, Kinoshita Y (2020) Prospective multicenter study of the esophageal triamcinolone acetonide-filling method in patients with subcircumferential esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 32:355–363
Bao Y, Li Z, Li Y, Chen T, Cheng Y, Xu M (2021) Recent advances of biomedical materials for prevention of post-ESD esophageal stricture. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:792929
Liao Z, Liao G, Yang X, Peng X, Zhang X, Xie X, Zhao X, Yang S, Fan C, Bai J (2018) Transplantation of autologous esophageal mucosa to prevent stricture after circumferential endoscopic submucosal dissection of early esophageal cancer (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 88:543–546
Funding
The study was supported by Grants or donations from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.82100697 and 81270564).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Our research was mainly designed by NC and EL. All operations were operated by NC and EL. LL, ZW and NW devoted themselves to collecting data and follow-up. LL and ZW drafted the article. Analysis and interpretation: LL, ZW, NW, BZ, JZ, JX, CD, NX, PW, XW, JF. Critical revision of the article for important intellectual content: NC and EL. Final approval of the article: NC and EL.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Longsong Li, Zixin Wang, Nanjun Wang, Bo Zhang, Jiale Zou, Jingyuan Xiang, Chen Du, Ning Xu, Pengju Wang, Xiangyao Wang, Jiancong Feng, Enqiang Linghu and Ningli Chai have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Wang, Z., Wang, N. et al. Self-help inflatable balloon versus autologous skin-grafting surgery for preventing esophageal stricture after complete circular endoscopic submucosal dissection: a propensity score matching analysis. Surg Endosc 37, 3710–3719 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09789-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09789-4