Abstract
Background and aims
No study has evaluated the diagnostic value of SpyGlass by comparing SpyGlass results and non-SpyGlass results. In this retrospective study, we aimed to compare the diagnostic value of EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) and EUS-FNA combined with SpyGlass to evaluate whether SpyGlass is valuable for increasing the diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA.
Methods
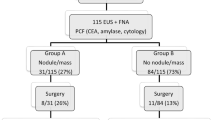
From April 2015 to April 2020, 251 patients suspected of having pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) by imaging techniques who then underwent EUS-FNA were retrospectively enrolled. Only 98 patients who underwent surgical resection with a pathological diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesion (PCL) were studied. The diagnostic performance outcomes were compared between the EUS-FNA group (EUS-FNA alone, n = 40) and the SpyGlass group (EUS-FNA combined with SpyGlass, n = 58) to assess the value of SpyGlass in diagnosing PCLs.
Results
There were 71 females and 27 males with an overall mean age of 47.6 years. The median diameter of the PCLs was 42.2 mm (range, 11.4–100.0 mm). Approximately 37 cysts were localized in the head/neck of the pancreas, while 61 in the body/tail. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and diagnostic accuracy of the EUS-FNA group were 96.4% (27/28), 83.3% (10/12), 93.1% (27/29), 90.9% (10/11) and 92.5% (37/40), while those in the SpyGlass group were 100% (54/54), 75% (3/4), 98.2% (54/55), 100% (3/3) and 98.3% (57/58), respectively. The diagnostic accuracy rate in the SpyGlass group was higher than that in the EUS-FNA group; however, no significant difference was found between the two groups (P = 0.368). The diagnostic accuracy of evaluating specific cyst types in the EUS-FNA group was 85% (34/40), similar to that in the SpyGlass group (85.0% vs 84.5%, P = 0.944).
Conclusion
SpyGlass seems less valuable for the diagnosis of PCLs when EUS and EUS-FNA have been performed by experienced endoscopists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ReMine SG, Frey D, Rossi RL, Munson JL, Braasch JW (1987) Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Arch Surg 122(4):443–446. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400160069010
Fernandez-del Castillo C, Warshaw AL (1995) Cystic tumors of the pancreas. Surg Clin North Am 75(5):1001–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0039-6109(16)46742-3
Attasaranya S, Pais S, LeBlanc J, McHenry L, Sherman S, DeWitt JM (2007) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration and cyst fluid analysis for pancreatic cysts. JOP 8(5):553–563
Okasha HH, Ashry M, Imam HM, Ezzat R, Naguib M, Farag AH, Gemeie EH, Khattab HM (2015) Role of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration and ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration in diagnosis of cystic pancreatic lesions. Endosc Ultrasound 4(2):132–136. https://doi.org/10.4103/2303-9027.156742
Canakis A, Law R, Baron T (2019) An updated review on ablative treatment of pancreatic cystic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 91(3):520–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2019.09.037
Teoh AY, Seo DW, Brugge W, Dewitt J, Kongkam P, Linghu E, Moyer MT, Ryu JK, Ho KY (2019) Position statement on EUS-guided ablation of pancreatic cystic neoplasms from an international expert panel. Endosc Int Open 7(9):E1064–E1077. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0959-5870
Du C, Chai NL, Linghu EQ, Li HK, Sun LH, Jiang L, Wang XD, Tang P, Yang J (2017) Comparison of endoscopic ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of detailed structures of pancreatic cystic neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 23(17):3184–3192. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3184
Barresi L, Tarantino I, Traina M, Granata A, Curcio G, Azzopardi N, Baccarini P, Liotta R, Fornelli A, Maimone A, Jovine E, Cennamo V, Fabbri C (2014) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration and biopsy using a 22-gauge needle with side fenestration in pancreatic cystic lesions. Dig Liver Dis 46(1):45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2013.06.008
Basar O, Yuksel O, Yang DJ, Samarasena J, Forcione D, DiMaio CJ, Wagh MS, Chang K, Casey B, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Pitman MB, Brugge WR (2018) Feasibility and safety of microforceps biopsy in the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts. Gastrointest Endosc 88(1):79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2018.02.039
Tacelli M, Celsa C, Magro B, Barchiesi M, Barresi L, Capurso G, Arcidiacono PG, Camma C, Crino SF (2020) Diagnostic performance of endoscopic ultrasound through-the-needle microforceps biopsy of pancreatic cystic lesions: systematic review with meta-analysis. Dig Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1111/den.13626
Crino SF, Bernardoni L, Brozzi L, Barresi L, Malleo G, Salvia R, Frulloni L, Sina S, Parisi A, Remo A, Larghi A, Gabbrielli A, Manfrin E (2019) Association between macroscopically visible tissue samples and diagnostic accuracy of EUS-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy sampling of pancreatic cystic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 90(6):933–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2019.05.009
Lohr JM, Lonnebro R, Stigliano S, Haas SL, Swahn F, Enochsson L, Noel R, Segersvard R, Del Chiaro M, Verbeke CS, Arnelo U (2015) Outcome of probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a single-center prospective study in 45 patients. United Eur Gastroenterol J 3(6):551–560. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050640615579806
Krishna SG, Brugge WR, Dewitt JM, Kongkam P, Napoleon B, Robles-Medranda C, Tan D, El-Dika S, McCarthy S, Walker J, Dillhoff ME, Manilchuk A, Schmidt C, Swanson B, Shah ZK, Hart PA, Conwell DL (2017) Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy for the diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: an international external interobserver and intraobserver study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 86(4):644–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2017.03.002
Konda VJ, Aslanian HR, Wallace MB, Siddiqui UD, Hart J, Waxman I (2011) First assessment of needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy during EUS-FNA procedures of the pancreas (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 74(5):1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2011.07.018
Antillon MR, Tiwari P, Bartalos CR, Marshall JB (2009) Taking SpyGlass outside the GI tract lumen in conjunction with EUS to assist in the diagnosis of a pancreatic cystic lesion (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 69(3 Pt 1):591–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2008.05.003
Aparicio JR, Martinez J, Niveiro M, Cabezas A, Ruiz F, De Madaria E, Casellas JA (2010) Direct intracystic biopsy and pancreatic cystoscopy through a 19-gauge needle EUS (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 72(6):1285–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2010.08.036
Chai N, Feng J, Guo Y, Li H, Ning B, Wang X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhai Y, Linghu E (2017) Preliminary study of single-operator cholangioscopy for diagnosing pancreatic cystic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 86(1):208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2017.01.038
Barkay O, Bucksot L, Sherman S (2009) Endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage with the SpyGlass cholangiopancreatoscopy system. Gastrointest Endosc 70(5):1039–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2009.03.033
Kawakubo K, Isayama H, Sasahira N, Kogure H, Takahara N, Miyabayashi K, Mizuno S, Yamamoto K, Mohri D, Sasaki T, Yamamoto N, Nakai Y, Hirano K, Tada M, Koike K (2012) Clinical utility of single-operator cholangiopancreatoscopy using a SpyGlass probe through an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography catheter. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(8):1371–1376. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07133.x
Nagayoshi Y, Aso T, Ohtsuka T, Kono H, Ideno N, Igarashi H, Takahata S, Oda Y, Ito T, Tanaka M (2014) Peroral pancreatoscopy using the SpyGlass system for the assessment of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21(6):410–417. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhbp.44
Arnelo U, Siiki A, Swahn F, Segersvard R, Enochsson L, del Chiaro M, Lundell L, Verbeke CS, Lohr JM (2014) Single-operator pancreatoscopy is helpful in the evaluation of suspected intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN). Pancreatology 14(6):510–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2014.08.007
Reuterwall M, Lubbe J, Enochsson L, Lundell L, Konradsson M, Swahn F, Del Chiaro M, Lohr M, Arnelo U (2019) The clinical value of ERCP-guided cholangiopancreatoscopy using a single-operator system. BMC Gastroenterol 19(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-019-0953-9
Ren X, Zhu CL, Qin XF, Jiang H, Xia T, Qu YP (2019) Co-occurrence of IPMN and malignant IPNB complicated by a pancreatobiliary fistula: a case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 7(1):102–108. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i1.102
Zhong L, Chai N, Linghu E, Li H, Yang J, Tang P (2019) A prospective study on contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound for differential diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Dig Dis Sci 64(12):3616–3622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05718-z
Derdeyn J, Laleman W (2018) Current role of endoscopic cholangioscopy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 34(5):301–308. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0000000000000457
Urakami Y, Seifert E, Butke H (1977) Peroral direct cholangioscopy (PDCS) using routine straight-view endoscope: first report. Endoscopy 9(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1098481
Moon JH, Choi HJ, Lee YN (2014) Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Endoscopy 46(9):775–778. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1377506
Nanashima A, Imamura N, Hiyoshi M, Hamada T, Yano K, Wada T, Kawakami H, Ban T, Kubota Y, Sato Y, Harada K (2020) Planned limited resection of the extrahepatic bile duct in a case of intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct based on preoperative examinations. Clin J Gastroenterol 13(2):233–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-019-01049-8
Bekkali NL, Murray S, Johnson GJ, Bandula S, Amin Z, Chapman MH, Pereira SP, Webster GJ (2017) Pancreatoscopy-directed electrohydraulic lithotripsy for pancreatic ductal stones in painful chronic pancreatitis using SpyGlass. Pancreas 46(4):528–530. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000000790
Ito K, Igarashi Y, Okano N, Mimura T, Kishimoto Y, Hara S, Takuma K (2014) Efficacy of combined endoscopic lithotomy and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, and additional electrohydraulic lithotripsy using the SpyGlass direct visualization system or X-ray guided EHL as needed, for pancreatic lithiasis. Biomed Res Int 2014:732781. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/732781
Maydeo A, Kwek A, Bhandari S, Bapat M, Mathew P (2011) SpyGlass pancreatoscopy-guided cannulation and retrieval of a deeply migrated pancreatic duct stent. Endoscopy 43(Suppl 2 UCTN):E137–E138. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1256205
Tanaka SA, McKee JD, Conway WC (2015) Intracystic biopsy and diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm via SpyGlass pancreatoscopy. Ochsner 15(4):452–454
Zhao S, Xia T, Li ZS, Bai Y (2018) Spyglass-guided pancreatic stent placement for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with recurrent pancreatitis. Dig Liver Dis 50(5):513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2017.11.009
Wang T, Liu DQ, Wen XD, Zhang BY, Liu WH (2019) Endoscopic dissection of refractory pancreatic duct stricture via accessory pancreatic duct approach for concurrent treatment of anomalous pancreaticobiliary junction in aging patients. Clin Interv Aging 14:557–563. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S191055
Chen YK, Parsi MA, Binmoeller KF, Hawes RH, Pleskow DK, Slivka A, Haluszka O, Petersen BT, Sherman S, Deviere J, Meisner S, Stevens PD, Costamagna G, Ponchon T, Peetermans JA, Neuhaus H (2011) Single-operator cholangioscopy in patients requiring evaluation of bile duct disease or therapy of biliary stones (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 74(4):805–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2011.04.016
Kalaitzakis E, Webster GJ, Oppong KW, Kallis Y, Vlavianos P, Huggett M, Dawwas MF, Lekharaju V, Hatfield A, Westaby D, Sturgess R (2012) Diagnostic and therapeutic utility of single-operator peroral cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary lesions and bile duct stones. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24(6):656–664. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283526fa1
Khalid A, McGrath KM, Zahid M, Wilson M, Brody D, Swalsky P, Moser AJ, Lee KK, Slivka A, Whitcomb DC, Finkelstein S (2005) The role of pancreatic cyst fluid molecular analysis in predicting cyst pathology. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3(10):967–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1542-3565(05)00409-x
Laquiere AE, Lagarde A, Napoleon B, Bourdariat R, Atkinson A, Donatelli G, Pol B, Lecomte L, Curel L, Urena-Campos R, Helbert T, Valantin V, Mithieux F, Buono JP, Grandval P, Olschwang S (2019) Genomic profile concordance between pancreatic cyst fluid and neoplastic tissue. World J Gastroenterol 25(36):5530–5542. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i36.5530
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by two research grants from National Key R&D Programs of China (2016YFC1303601 and 2020YFC2002705).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Drs. Chen Du, Ningli Chai, Enqiang Linghu, Huikai Li, Xiuxue Feng, Jing Yang, Xiangdong Wang and Ping Tang have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, C., Chai, N., Linghu, E. et al. Diagnostic value of SpyGlass for pancreatic cystic lesions: comparison of EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration and EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration combined with SpyGlass. Surg Endosc 36, 904–910 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08347-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08347-8