Abstract
Background
This study retrospectively compared the safety and efficacy of two endoscopic techniques for treating newly diagnosed achalasia, pneumatic dilation (PD), and peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM).
Methods
Demographics, clinical and manometric data, and outcomes were collected from the medical records of patients who received POEM or PD as the primary therapy for achalasia at our hospital from January 2012 to August 2015.
Results
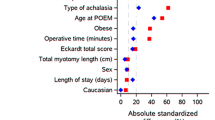
Of 72 patients, 32 and 40 received POEM and PD, respectively. The two groups had similar preoperative features. On short-term follow-up, improvements in high-resolution esophageal manometry and barium esophagogram parameters were similar. For PD, the success rates at 3, 6, 12, 24, and 36 months were 95, 88, 75, 72, and 60%, respectively. For POEM, these were 96, 96, 96, 93, and 93% (P = 0.013, log-rank test). On subgroup analysis, the success rate was higher with POEM than that with PD in all 3 manometric subtypes, but only that of type III was statistically significant. POEM required significantly longer operative time and hospitalization than did PD (P < 0.001). Four POEM patients experienced subcutaneous emphysema. The rate of gastroesophageal reflux was higher in patients treated by POEM (18.8%) than that in PD (10%; P = 0.286).
Conclusions
In the intermediate term, the remission rate of symptoms associated with POEM therapy was better than that with PD for newly diagnosed achalasia, especially in patients with type III achalasia. The short-term outcomes of the two therapies were similar.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Podas T, Eaden J, Mayberry M, Mayberry J (1998) Achalasia: a critical review of epidemiological studies. Am J Gastroenterol 93:2345–2347
Ben-Meir A, Urbach DR, Khajanchee YS, Hansen PD, Swanstrom LL (2001) Quality of life before and after laparoscopic Heller myotomy for achalasia. Am J Surg 181:471–474
Zarate N, Mearin F, Baldovino F, Armengol JR, Malagelada JR (2002) Achalasia treatment in the elderly: Is botulinum toxin injection the best option? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:285–290
Richter JE, Boeckxstaens GE (2011) Management of achalasia: surgery or pneumatic dilation. Gut 60:869–876
Boeckxstaens GE, Annese V, des Varannes SB, Chaussade S, Costantini M, Cuttitta A, Elizalde JI, Fumagalli U, Gaudric M, Rohof WO, Smout AJ, Tack J, Zwinderman AH, Zaninotto G, Busch OR (2011) Pneumatic dilation versus laparoscopic Heller’s myotomy for idiopathic achalasia. N Engl J Med 364:1807–1816
Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y, Kaga M, Suzuki M, Satodate H, Odaka N, Itoh H, Kudo S (2010) Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy 42:265–271
Stavropoulos SN, Desilets DJ, Fuchs KH, Gostout CJ, Haber G, Inoue H, Kochman ML, Modayil R, Savides T, Scott DJ, Swanstrom LL, Vassiliou MC (2014) Per-oral endoscopic myotomy white paper summary. Surg Endosc 28:2005–2019
Bechara R, Ikeda H, Inoue H (2015) Peroral endoscopic myotomy: an evolving treatment for achalasia. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:410–426
Teitelbaum EN, Soper NJ, Santos BF, Arafat FO, Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ, Hirano I, Hungness ES (2014) Symptomatic and physiologic outcomes one year after peroral esophageal myotomy (POEM) for treatment of achalasia. Surg Endosc 28:3359–3365
Inoue H, Sato H, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, Sato C, Minami H, Yokomichi H, Kobayashi Y, Grimes KL, Kudo SE (2015) Per-oral endoscopic myotomy: a series of 500 patients. J Am Coll Surg 221:256–264
Verlaan T, Rohof WO, Bredenoord AJ, Eberl S, Rosch T, Fockens P (2013) Effect of peroral endoscopic myotomy on esophagogastric junction physiology in patients with achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc 78:39–44
Chan SM, Wu JC, Teoh AY, Yip HC, Ng EK, Lau JY, Chiu PW (2016) Comparison of early outcomes and quality of life after laparoscopic Heller’s cardiomyotomy to peroral endoscopic myotomy for treatment of achalasia. Dig Endosc 28:27–32
Marano L, Pallabazzer G, Solito B, Santi S, Pigazzi A, De Luca R, Biondo FG, Spaziani A, Longaroni M, Di Martino N, Boccardi V, Patriti A (2016) Surgery or peroral esophageal myotomy for achalasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e3001
Schneider AM, Louie BE, Warren HF, Farivar AS, Schembre DB, Aye RW (2016) A matched comparison of per oral endoscopic myotomy to laparoscopic heller myotomy in the treatment of achalasia. J Gastrointest Surg 20:1789–1796
Rohof WO, Salvador R, Annese V, des Varannes SB, Chaussade S, Costantini M, Elizalde JI, Gaudric M, Smout AJ, Tack J, Busch OR, Zaninotto G, Boeckxstaens GE (2013) Outcomes of treatment for achalasia depend on manometric subtype. Gastroenterology 144:718–725 (quiz e13–e14)
Salvador R, Costantini M, Zaninotto G, Morbin T, Rizzetto C, Zanatta L, Ceolin M, Finotti E, Nicoletti L, Da Dalt G, Cavallin F, Ancona E (2010) The preoperative manometric pattern predicts the outcome of surgical treatment for esophageal achalasia. J Gastrointest Surg 14:1635–1645
Zerbib F, Roman S (2015) Current therapeutic options for esophageal motor disorders as defined by the Chicago Classification. J Clin Gastroenterol 49:451–460
Eckardt VF (2001) Clinical presentations and complications of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 11:281–292
Pandolfino JE, Kwiatek MA, Nealis T, Bulsiewicz W, Post J, Kahrilas PJ (2008) Achalasia: a new clinically relevant classification by high-resolution manometry. Gastroenterology 135:1526–1533
Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Gyawali CP, Roman S, Smout AJ, Pandolfino JE (2015) The Chicago classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol Motil 27:160–174
Persson J, Johnsson E, Kostic S, Lundell L, Smedh U (2015) Treatment of achalasia with laparoscopic myotomy or pneumatic dilatation: long-term results of a prospective, randomized study. World J Surg 39:713–720
Pandolfino JE, Gawron AJ (2015) Achalasia: a systematic review. JAMA 313:1841–1852
Katzka DA, Castell DO (2011) Review article: an analysis of the efficacy, perforation rates and methods used in pneumatic dilation for achalasia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 34:832–839
Smith CD, Stival A, Howell DL, Swafford V (2006) Endoscopic therapy for achalasia before Heller myotomy results in worse outcomes than heller myotomy alone. Ann Surg 243:579–584 (discussion 584–576)
Pratap N, Kalapala R, Darisetty S, Joshi N, Ramchandani M, Banerjee R, Lakhtakia S, Gupta R, Tandan M, Rao GV, Reddy DN (2011) Achalasia cardia subtyping by high-resolution manometry predicts the therapeutic outcome of pneumatic balloon dilatation. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 17:48–53
Zhang XC, Li QL, Xu MD, Chen SY, Zhong YS, Zhang YQ, Chen WF, Ma LL, Qin WZ, Hu JW, Cai MY, Yao LQ, Zhou PH (2016) Major perioperative adverse events of peroral endoscopic myotomy: a systematic 5-year analysis. Endoscopy 48:967–978
Swanstrom LL, Kurian A, Dunst CM, Sharata A, Bhayani N, Rieder E (2012) Long-term outcomes of an endoscopic myotomy for achalasia: the POEM procedure. Ann Surg 256:659–667
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Fandong Meng, Peng Li, Yongjun Wang, Ming Ji, Yongdong Wu, Li Yu, Yinglin Niu, Fujing Lv, Wei Li, Wenyan Li, Huihong Zhai, Shanshan Wu, and Shutian Zhang have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, F., Li, P., Wang, Y. et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy compared with pneumatic dilation for newly diagnosed achalasia. Surg Endosc 31, 4665–4672 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5530-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5530-0