Abstract
Background
Gastric slow waves regulate peristalsis, and gastric dysrhythmias have been implicated in functional motility disorders. To accurately define slow wave patterns, it is currently necessary to collect high-resolution serosal recordings during open surgery. We therefore developed a novel gastric slow wave mapping device for use during laparoscopic procedures.
Methods
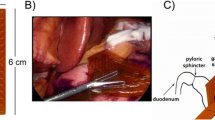
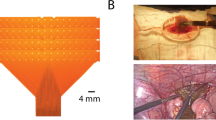
The device consists of a retractable catheter constructed of a flexible nitinol core coated with Pebax. Once deployed through a 5-mm laparoscopic port, the spiral head is revealed with 32 electrodes at 5 mm intervals. Recordings were validated against a reference electrode array in pigs and tested in a human patient.
Results
Recordings from the device and a reference array in pigs were identical in frequency (2.6 cycles per minute; p = 0.91), and activation patterns and velocities were consistent (8.9 ± 0.2 vs 8.7 ± 0.1 mm s−1; p = 0.2). Device and reference amplitudes were comparable (1.3 ± 0.1 vs 1.4 ± 0.1 mV; p = 0.4), though the device signal-to-noise ratio was higher (17.5 ± 0.6 vs 12.8 ± 0.6 dB; P < 0.0001). In the human patient, corpus slow waves were recorded and mapped (frequency 2.7 ± 0.03 cycles per minute, amplitude 0.8 ± 0.4 mV, velocity 2.3 ± 0.9 mm s−1).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the novel laparoscopic device achieves high-quality serosal slow wave recordings. It can be used for laparoscopic diagnostic studies to document slow wave patterns in patients with gastric motility disorders.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farrugia G (2008) Interstitial cells of Cajal in health and disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:54–63
O’Grady G, Du P, Cheng LK, Egbuji JU, Lammers WJEP, Windsor JA, Pullan AJ (2010) The origin and propagation of human gastric slow-wave activity defined by high-resolution mapping. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299:G585–G592
Hinder RA, Kelly KA (1977) Human gastric pacesetter potential—site of origin, spread, and response to gastric transection and proximal gastric vagotomy. Am J Surg 133:29–33
Lin X, Chen JZ (2001) Abnormal gastric slow waves in patients with functional dyspepsia assessed by multichannel electrogastrography. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 280:G1370–G1375
Chen JD, Schirmer BD, McCallum RW (1994) Serosal and cutaneous recordings of gastric myoelectrical activity in patients with gastroparesis. Am J Physiol 266:G90–G98
Hocking MP, Harrison WD, Sninsky CA (1990) Gastric dysrhythmias following pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy. Dig Dis Sci 35:1226–1230
O’Grady G, Wang THH, Du P, Angeli T, Lammers WJEP, Cheng LK (2014) Recent progress in gastric arrhythmia: pathophysiology, clinical significance and future horizons. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 41:854–862
Lammers WJEP, Ver Donck L, Stephen B, Smets D, Schuurkes JAJ (2008) Focal activities and re-entrant propagations as mechanisms of gastric tachyarrhythmias. Gastroenterol 135:1601–1611
O’Grady G, Angeli TR, Du P, Lahr C, Lammers WJEP, Windsor JA, Abell TL, Farrugia G, Pullan AJ, Cheng LK (2012) Abnormal initiation and conduction of slow-wave activity in gastroparesis, defined by high-resolution electrical mapping. Gastroenterol 143(589–598):e583
O’Grady G, Egbuji JU, Du P, Lammers WJEP, Cheng LK, Windsor JA, Pullan AJ (2011) High-resolution spatial analysis of slow wave initiation and conduction in porcine gastric dysrhythmia. Neurogastroenterol Motil 23:e345–e355
Lammers WJEP (2013) Arrhythmias in the gut. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:353–357
Cheng LK, Du P, O’Grady G (2013) Mapping and modeling gastrointestinal bioelectricity: from engineering bench to bedside. Physiology (Bethesda) 28:310–317
Du P, O’Grady G, Egbuji JU, Lammers WJ, Budgett D, Nielsen P, Windsor JA, Pullan AJ, Cheng LK (2009) High-resolution mapping of in vivo gastrointestinal slow wave activity using flexible printed circuit board electrodes: methodology and validation. Ann Biomed Eng 37:839–846
Lammers W, Ver Donck L, Stephen B, Smets D, Schuurkes J (2009) Origin and propagation of the slow wave in the canine stomach: the outlines of a gastric conduction system. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296:1200–1210
O’Grady G, Du P, Egbuji JU, Lammers WJEP, Wahab A, Pullan AJ, Cheng LK, Windsor JA (2009) A novel laparoscopic device for measuring gastrointestinal slow-wave activity. Surg Endosc 23:2842–2848
Familoni BO, Abell T, Voeller G (1994) Measurement of gastric and small bowel electrical activity at laparoscopy. J Laparoendosc Surg 4:325–332
Thierry B, Tabrizian M, Trepanier C, Savadogo O, Yahia LH (2000) Effect of surface treatment and sterilization processes on the corrosion behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy. J Biomed Mater Res 51:685–693
Feldman LA, Hui H (1997) Compatibility of medical devices and materials with low-temperature H2O2 gas plasma. Med Device Diagn Ind 19:63–77
Eldar M, Ohad DG, Goldberger JJ, Rotstein Z, Hsu S, Swanson DK, Greenspon AJ (1997) Transcutaneous multielectrode basket catheter for endocardial mapping and ablation of ventricular tachycardia in the pig. Circulation 96:2430–2437
Schmitt C, Zrenner B, Schneider M, Karch M, Ndrepepa G, Deisenhofer I, Weyerbrock S, Schreieck J, Schömig A (1999) Clinical experience with a novel multielectrode basket catheter in right atrial tachycardias. Circulation 99:2414–2422
Arkema Group Pebax® by Arkema. Arkema
Cote KR, Gill RC (1987) Development of a platinized platinum/iridium electrode for use in vitro. Ann Biomed Eng 15:419–426
O’Grady G, Angeli T, Lammers WJ (2013) The principles and practice of gastrointestinal high-resolution mapping. In: Cheng LK, Farrugia G, Pullan AJ (eds) New advances in gastrointestinal motility research. Springer, New York, pp 51–69
Egbuji J, O’Grady G, Du P (2010) Origin, propagation and regional characteristics of porcine gastric slow wave activity determined by high-resolution mapping. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:e292–e300
Angeli TR, Cheng LK, Du P (2015) Loss of interstitial cells of Cajal and patterns of gastric dysrhythmia in chronic unexplained nausea and vomiting (CUNV). Gastroenterology 149:56–66
Ladabaum U, Koshy SS, Woods ML, Hooper FG, Owyang C, Hasler WL (1998) Differential symptomatic and electrogastrographic effects of distal and proximal human gastric distension. Am J Physiol 275:G418–G424
O’Grady G, Paskaranandavadivel N, Angeli TR, Du P, Windsor JA, Cheng LK, Pullan AJ (2011) A comparison of gold versus silver electrode contacts for high-resolution gastric electrical mapping using flexible printed circuit board arrays. Physiol Meas 32:N13–N22
Yassi R, O’Grady G, Paskaranandavadivel N, Du P, Angeli T, Pullan A, Cheng L, Erickson J (2012) The gastrointestinal electrical mapping suite (GEMS): software for analyzing and visualizing high-resolution (multi-electrode) recordings in spatiotemporal detail. BMC Gastroenterol 12:60
Paskaranandavadivel N, O’Grady G, Du P, Cheng LK (2013) Comparison of filtering methods for extracellular gastric slow wave recordings. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:79–83
Erickson J, O’Grady G, Du P (2010) Falling-edge, variable threshold (FEVT) method for the automated detection of gastric slow wave events in serosal high-resolution electrical recordings. Ann Biomed Eng 38:1511–1529
Erickson J, O’Grady G, Du P, Egbuji J, Pullan A, Cheng L (2011) Automated cycle partitioning and visualization of high-resolution activation time maps of gastric slow wave recordings: the Region Growing Using Polynomial Surface-estimate stabilization (REGROUPS) Algorithm. Ann Biomed Eng 39:469–483
Weeks M (2010) Digital signal processing using matlab and wavelets, 2nd edn. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, London
Paskaranandavadivel N, Cheng L, Du P, O’Grady G, Pullan A (2011) Improved signal processing techniques for the analysis of high resolution serosal slow wave activity in the stomach. In: Conference of IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc:1737–1740
Paskaranandavadivel N, O’Grady G, Du P, Pullan A, Cheng L (2012) An improved method for the estimation and visualization of velocity fields from gastric high-resolution electrical mapping. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59:882–889
Bayly P, KenKnight BH, Rogers J, Hillsley RE, Ideker R, Smith W (1998) Estimation of conduction velocity vector fields from epicardial mapping data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 45:563–571
Du P, Wenlian Q, O’Grady G, Egbuji JU, Lammers W, Cheng LK, Pullan AJ (2009) Automated detection of gastric slow wave events and estimation of propagation velocity vector fields from serosal high-resolution mapping. In: Conference of IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc:2527–2530
Angeli T, Du P, Paskaranandavadivel N, Janssen PW, Beyder A, Lentle RG, Bissett IP, Bissett Ian P, Cheng LK, O’Grady G (2013) The bioelectrical basis and validity of gastrointestinal extracellular slow wave recordings. J Physiol 591:4567–4579
Miedema BW, Sarr MG, Kelly KA (1992) Pacing the human stomach. Surgery 111:143–150
O’Grady G, Du P, Lammers WJ, Egbuji JU, Mithraratne P, Chen JD, Cheng LK, Windsor JA, Pullan AJ (2010) High-resolution entrainment mapping of gastric pacing: a new analytical tool. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298:G314–G321
Du P, Hameed A, Angeli TR, Lahr C, Abell TL, Cheng LK, O’Grady G (2015) The impact of surgical excisions on human gastric slow wave conduction, defined by high-resolution electrical mapping and in silico modeling. Neurogastroenterol Motil 27:1409–1422
Lerouge S, Tabrizian M, Wertheimer MR, Marchand R, Yahia LH (2002) Safety of plasma-based sterilization: surface modifications of polymeric medical devices induced by Sterrad and Plazlyte™ processes. Biomed Mater Eng 12:3–13
Yin J, Chen JDZ (2013) Electrogastrography: methodology, validation and applications. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19:5–17
Bradshaw LA, Irimia A, Sims JA, Gallucci MR, Palmer RL, Richards WO (2006) Biomagnetic characterization of spatiotemporal parameters of the gastric slow wave. Neurogastroenterol Motil 18:619–631
Cheng LK, O’Grady G, Du P, Egbuji JU, Windsor JA, Pullan AJ (2010) Gastrointestinal system. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2:65–79
Paskaranandavadivel N, Wang R, Sathar S, O’Grady G, Cheng LK, Farajidavar A (2015) Multi-channel wireless mapping of gastrointestinal serosal slow wave propagation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 27:580–585
Ver Donck L, Lammers WJEP, Moreaux B, Smets D, Voeten J, Vekemans J, Schuurkes JAJ, Coulie B (2006) Mapping slow waves and spikes in chronically instrumented conscious dogs: implantation techniques and recordings. Med Biol Eng Comput 44:170–178
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Tim Angeli, Ryash Vather, Linley Nisbet, Grant Beban and the surgical staff at Auckland City Hospital with data collection.
Funding sources
This work was supported in part by grants from the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD), Maurice and Phyllis Paykel Trust (MPPT), Health Research Council of New Zealand, NIH (R01 DK64775), and Medical Technologies Centre of Research Excellence (MedTech CoRE), New Zealand. RB was supported by a Commonwealth Scholarship, PD by the Marsden Fund and LC by a Fraunhofer-Bessel Research Award from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation and the Fraunhofer IPA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Niranchan Paskaranandavadivel, Peng Du, Gregory O’Grady and Leo K. Cheng hold intellectual property and/or patent applications in the field of mapping gastrointestinal electrophysiology. Rachel Berry, Mark L. Trew and John A. Windsor report no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Ethical standards
Ethical approval for pig experiments was obtained from the University of Auckland Animal Ethics Committee. Human studies were approved by the Northern Y Health and Disability Ethics Committee. The patient provided informed consent prior to participating.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berry, R., Paskaranandavadivel, N., Du, P. et al. A novel retractable laparoscopic device for mapping gastrointestinal slow wave propagation patterns. Surg Endosc 31, 477–486 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4936-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4936-4