Abstract
Background
A novel antireflux procedure combining laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication and Hill repair components was tested in 50 patients with paraesophageal hernia (PEH) and/or Barrett’s esophagus (BE) because these two groups have been found to have a high rate of recurrence with conventional repairs.
Methods
Patients with symptomatic PEH and/or non-dysplastic BE underwent repair. Quality of life (QOL) metrics, manometry, EGD, and pH testing were administered pre- and postoperatively.
Results
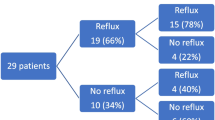
Fifty patients underwent repair. There was no mortality and four major complications. At 13-month follow-up, there was one (2 %) clinical recurrence, and two (4 %) asymptomatic fundus herniations. Mean DeMeester scores improved from 57.2 to 7.7 (p < 0.0001). Control of preoperative symptoms was achieved in 90 % with 6 % resumption of antisecretory medication. All QOL metrics improved significantly.
Conclusions
The hybrid Nissen–Hill repair for patients with PEH and BE appears safe and clinically effective at short-term follow-up. It is hoped that the combined structural components may reduce the rate of recurrence compared to existing repairs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lundell L, Miettinen P, Myrvold HE, Hatlebakk JG, Wallin L, Malm A, Sutherland I, Walan A, Nordic GORD Study Group (2007) Seven-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial comparing proton-pump inhibition with surgical therapy for reflux oesophagitis. Br J Surg 94:198–203
Mehta S, Bennett J, Mahon D, Rhodes M (2006) Prospective trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication versus proton pump inhibitor therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease: seven-year follow-up. J Gastrointest Surg 10:1312–1316
Mahon D, Rhodes M, Decadt B, Hindmarsh A, Lowndes R, Beckingham I, Koo B, Newcombe RG (2005) Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication compared with proton-pump inhibitors for treatment of chronic gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 92:695–699
Oelschlager BK, Quiroga E, Parra JD, Cahill M, Polissar N, Pellegrini CA (2008) Long-term outcomes after laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Am J Gastroenterol 103:280–287
Dallemagne B, Kohnen L, Perretta S, Weerts J, Markiewicz S, Jehaes C (2011) Laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hernia. Long-term follow-up reveals good clinical outcome despite high radiological recurrence rate. Ann Surg 253:291–296
Rathore MA, Andrabi SIH, Bhatti MI, Najfi SM, McMurray A (2007) Metaanalysis of recurrence after laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hernia. JSLS 11:456–460
Jobe BA, Aye RW, Deveney CW, Domreis JS, Hill LD (2002) Laparoscopic management of giant type III hiatal hernia and short esophagus: objective follow-up at three years. J Gastrointest Surg 6:181–188
Hofstetter WL, Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Hagen JA, DeMeester SR, Crookes PF, Tsai P, Banki F, Bremner CG (2001) Long-term outcome of antireflux surgery in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Ann Surg 234:532–538
Zehetner J, DeMeester SR, Ayazi S, Costales JL, Augustin F, Oezcelik A, Lipham JC, Sohn HJ, Hagen JA, DeMeester TR (2010) Long-term follow-up after anti-reflux surgery in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg 14:1483–1491
Csendes A, Braghetto I, Burdiles P, Puente G, Korn O, Díaz JC, Maluenda F (1998) Long-term results of classic antireflux surgery in 152 patients with Barrett’s esophagus: clinical, radiologic, endoscopic, manometric, and acid reflux test analysis before and late after operation. Surgery 123:645–657
Pearson JB, Gray JG (1967) Oesophageal hiatus hernia: long-term results of the conventional thoracic operation. Br J Surg 54:530–533
Stylpoulos N, Rattner D (2005) The history of hiatal hernia surgery. Ann Surg 241:185–193
Luketich JD, Raja S, Fernando HC, Campbell W, Christie NA, Buenaventura PO, Weigel TL, Keenan RJ, Schauer PR (2000) Laparoscopic repair of giant paraesophageal hernia: 100 consecutive cases. Ann Surg 232:608–618
Louie BE, Blitz M, Farivar AS, Orlina J, Aye RW (2011) Repair of symptomatic giant paraesophageal hernias in elderly (>70) years) patients results in improved quality of life. J Gastrointest Surg 15:389–396
Zehetner J, Demeester SR, Ayazi S, Kilday P, Augustin F, Hagen JA, Lipham JC, Sohn HJ, Demeester TR (2011) Laparoscopic versus open repair of paraesophageal hernia: the second decade. J Am Coll Surg 212:813–820
Mittal SK, Awad ZT, Tasset M, Filipi CJ, Dickason TJ, Shinno Y, Marsh RE, Tomonaga TJ, Lerner C (2000) The preoperative predictability of the short esophagus in patients with stricture or paraesophageal hernia. Surg Endosc 14:464–468
Awais O, Luketich JD (2009) Management of giant paraesophageal hernia. Minerva Chir 64:159–168
Johnson AB, Oddsdottir M, Hunter JG (1998) Laparoscopic Collis gastroplasty and Nissen fundoplication. A new technique for the management of esophageal foreshortening. Surg Endosc 12:1055–1060
Lugaresi M, Mattioli S, Aramini B, D’Ovidio F, Di Simone MP, Perrone O (2013) The frequency of true short oesophagus in type II–IV hiatal hernia. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 43:e30–e36
Morino M, Giaccone C, Pellegrino L, Rebecchi F (2006) Laparoscopic management of giant hiatal hernia: factors influencing long-term outcome. Surg Endosc 20:1011–1016
Oelschlager BK, Yamamoto K, Woltman T, Pellegrini C (2008) Vagotomy during hiatal hernia repair: a benign esophageal lengthening procedure. J Gastrointest Surg 12:1155–1162
Aye RW, Swanstrom LL, Kapur S, Buduhan G, Dunst CM, Knight A, Malmgren JA, Louie BE (2012) A randomized multiinstitution comparison of the laparoscopic Nissen and Hill repairs. Ann Thorac Surg 94:951–957
Qureshi AP, Aye RW, Buduhan G, Knight A, Orlina J, Farivar AS, Wagner OJ, McHugh S, Louie BE (2013) The laparoscopic Nissen–Hill hybrid: pilot study of a combined antireflux procedure. Surg Endosc 27:1945–1952
Seely AJE, Ivanovic J, Threader J, Al-Hussaini A, Al-Shehab D, Ramsay T, Gilbert S, Maziak DE, Shamji FM, Sundaresan RS (2010) Systematic classification of morbidity and mortality after thoracic surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 90:936–942
Wiklund IK, Junghard O, Grace E, Talley NJ, Kamm M, Veldhuyzen van Zanten S, Paré P, Chiba N, Leddin DS, Bigard MA, Colin R, Schoenfeld P (1998) Quality of life in reflux and dyspepsia patients. Psychometric documentation of a new disease-specific questionnaire (QOLRAD). Eur J Surg Suppl 583:41–49
Velanovich V (2007) The development of the GERD-HRQL symptom severity instrument. Dis Esophagus 20:130–134
Dakkak M, Bennett J (1992) A new dysphagia score with objective validation. J Cliln Gastroenterol 14:99–100
Aye R (2004) The hill procedure for gastroesophageal reflux. In: Yang S, Cameron DE (eds) Current therapy in thoracic and cardiovascular surgery, 1st edn. Mosby, Pennsylvania, pp 400–405
Zehetner J, Lipham JC, Ayazi S, Oezcelik A, Abate E, Chen W, Demeester SR, Sohn HJ, Banki F, Hagen JA, Dickey M, Demeester TR (2010) A simplified technique for intrathoracic stomach repair: laparoscopic fundoplication with Vicryl mesh and BioGlue crural reinforcement. Surg Endosc 24:675–679
Oelschlager BK, Pellegrini CA, Hunter J, Soper N, Brunt M, Sheppard B, Jobe B, Polissar N, Mitsumori L, Nelson J, Swanstrom L (2006) Biologic prosthesis reduces recurrence after laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia repair: a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial. Ann Surg 244:481–490
Luketich JD, Nason KS, Christie NA, Pennathur A, Jobe BA, Landreneau RJ, Schuchert MJ (2010) Outcomes after a decade of laparoscopic giant paraesophageal hernia repair. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 139:395–404
Hatch KF, Daily MF, Christensen BJ, Glasgow RE (2004) Failed fundoplications. Am J Surg 188:786–791
Parrilla P, Martínez de Haro LF, Ortiz A, Munitiz V, Molina J, Bermejo J, Canteras M (2003) Long-term results of a randomized prospective study comparing medical and surgical treatment of Barrett’s esophagus. Ann Surg 237:291–298
Alicuben ET, Worrell SG, DeMeester SR (2014) Impact of crural relaxing incisions, Collis gastroplasty, and non-cross-linked human dermal mesh crural reinforcement on early hiatal hernia recurrence rates. J Am Coll Surg 219:988–992
Jutric Z et al (2013) A combined Nissen fundoplication with Hill gastroplasty is an alternative to Collis–Nissen repair in the treatment of short esophagus. Poster session presented at Digestive Diseases Week, 2013 May 18–21; Orlando, FL
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the contribution of Justine Rees, the Hill Foundation and the Foundation for Surgical Fellowships.
Disclosure
Aye, Qureshi, Wilshire, Farivar, Vallières, and Louie have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aye, R.W., Qureshi, A.P., Wilshire, C.L. et al. Feasibility, safety, and short-term efficacy of the laparoscopic Nissen–Hill hybrid repair. Surg Endosc 30, 551–558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4238-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4238-2