Abstract
Background
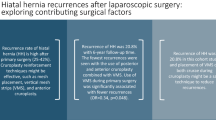
The laparoscopic management of large hiatal hernias still is controversial. Recent studies have presented a high recurrence rate.
Methods
In this study, 65 patients underwent elective laparoscopic repair of large hiatal hernia. A short esophagus was diagnosed in 13 cases. A primary closure of the hiatal defect was performed in 14 cases. “Tension-free” repair using a mesh was performed in 37 cases, and 14 patients underwent a Collis–Nissen gastroplasty. For the last 38 patients in the series, an intraoperative endoscopy was performed to identify the esophagogastric junction.
Results
There was no mortality, no conversions to open surgery, and no intraoperative complications. A recurrent hernia was present in 23 of the 77 patients (30%). The recurrence rate was 77% when a direct suture was used and 35% when a mesh was used (p < 0.05). No recurrences were observed in the patients treated with the Collis–Nissen technique, but in one case, perforation of the distal esophagus developed 3 weeks after surgery. The multivariate analysis showed that recurrences are statistically correlated with the type of hiatal hernia and surgical technique.
Conclusions
To reduce recurrences after laparoscopic management of large hiatal hernias, it is essential to identify all cases of short esophagus using intraoperative endoscopy and to perform a Collis–Nissen procedure in such cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MS, Trastek VF, Deschamps C, Pairolero (1993) Intrathoracic stomach: presentation and results of operation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 105: 253–259
Basso N, Rosato P, De Leo A, Genco A, Rea S, Neri T (1999) “Tension-free” hiatoplasty, gastrophrenic anchorage, and 360-degree fundoplication in the laparoscopic treatment of paraesophageal hernia. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 9: 257–262
Carlson MA, Condon RE, Ludwig KA, Schulte WJ (1998) Management of intrathoracic stomach with polypropylene mesh prosthesis reinforced transabdominal hiatus hernia repair. J Am Coll Surg 187: 227–230
Collis JL (1957) An operation for hiatus hernia with short esophagus. Thorax 12: 181–188
Collis JL (1961) Gastroplasty. Thorax 16: 197–206
Dahlberg PS, Deschamps C, Miller DL, Allen MS, Nichols FC, Pairolero PC (2001) Laparoscopic repair of large paraesophageal hiatal hernia. Ann Thorac Surg 72: 1125–1129
DeMeester TR, Stein JH (1992) Minimizing the side effects of antireflux surgery. World J Surg 16: 335–336
Frantzides CT, Carlson MA (1995) Laparoscopic versus conventional fundoplication. J Laparoendosc Surg 5: 137–143
Frantzides CT, Madan AK, Carlson MA, Stavropoulos GP (2002) A prospective, randomized trial of laparoscopic polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) patch repair vs simple cruroplasty for large hiatal hernia. Arch Surg 137: 649–652
Frantzides CT, Richards CG, Carlson MA (1999) Laparoscopic repair of large hiatal hernia with polytetrafluoroethylene. Surg Endosc 13: 906–908
Hashemi M, Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Huprich JE, Quek M, Hagen JA, Crookes PF, Theisen J, DeMeester SR, Sillin LF, Bremner CG (2000) Laparoscopic repair of large type III hiatal hernia: objective follow-up reveals high recurrence rate. J Am Coll Surg 190: 553–560
Hill LD (1973) Incarcerated paraesophageal hernia: a surgical emergency. Am J Surg 126: 286–291
Hinder RA, Filipi CJ, Wetscher G, Neary P, DeMeester TR, Perdikis G (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 220: 472–483
Hinder RA, Klingler PJ, Perdikis G, Smith SL (1997) Management of the failed antireflux operation. Surg Clin North Am 77: 1083–1098
Horgan S, Pohl D, Bogetti D, Eubanks T, Pellegrini C (1999) Failed antireflux surgery. Arch Surg 134: 809–817
Hui TT, Thoman DS, Spyrou M, Phillips EH, David T (2002) Mesh crural repair of large paraesophageal hiatal hernias. Am Surg 48: 406
Jamieson GG, Watson DI, Britten-Jones R, Mitchell PC, Anvari M (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Ann Surg 220: 137–145
Johnson AB, Oddsdottir M, Hunter JG (1998) Laparoscopic Collis gastroplasty and Nissen fundoplication: a new technique for the management of esophageal foreshortening. Surg Endosc 12: 1055–1060
Landreneau RJ, Hazelrigg SR, Johnson JA (1990) The giant paraesophageal hernia: a particularly morbid condition of the esophageal hiatus. Missouri Med 87: 884–888
Landreneau RJ, Marshall JM, Hazelrigg SR, Johnson JA, Boley TM, Curtis JJ (1992) The clinical spectrum of paraesophageal herniation. Digest Dis Sci 37: 537–544
Maziak D, Todd T, Pearson FG (1998) Massive hiatus hernia: evaluation and surgical management. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 115: 53–62
Mercer CD, Velasco N, Hill LD. Paraesophageal hernia (1998) In: Hill L, Kozarek R, McCallum R, Mercer CD (eds) The esophagus: medical and surgical management. WB Saunders, Philadelphia pp 148–156
Morino M, De Giuli M, Festa V, Garrone C, Miglietta C (1994) Laparoscopic management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. In: Steichen F, Welter R (eds) Minimally invasive surgery. Quality Medical Publishing, St. Louis, Missouri pp 573–576
Paul MG, DeRosa RP, Petrucci PE, Palmer ML, Danovitch SH (1997) Laparoscopic tension-free repair of large paraesophageal hernias. Surg Endosc 11: 303–307
Pearson FG, Cooper JD, Ilves R, Todd TRJ, Jamieson WRE (1983) Massive hiatal hernia with incarceration: a report of 53 cases. Ann Thorac Surg 35: 45–51
Pearson FG, Langer B, Henderson RD (1971) Gastroplasty and Belsey hiatus hernia repair: an operation for the management of peptic stricture with acquired short esophagus. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 61: 50–63
Pierre AF, Luketich JD, Fernando HC, Christie NA, Buenaventura PO, Litle VR, Schauer PR (2002) Results of laparoscopic repair of giant paraesophageal hernias: 200 consecutive patients. Ann Thorac Surg 74: 1909–1015
Seeling MH, Hinder RA, Klinger PJ, Floch NR, Branton SA, Smith SL (1999) Paraesophageal herniation as a complication following laparoscopic antireflux surgery. J Gastrointest Surg 3: 95–99
Skinner D, Belsey R (1967) Surgical management of esophageal reflux and hiatus hernia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 53: 33–54
Stirling MC, Orringer MB (1988) The combined Collis–Nissen operation for esophageal reflux stricture. Ann Thorac Surg 45: 148–157
Swanstrom LL, Marcus DR, Galloway GQ (1996) Laparoscopic Collis gastroplasty is the treatment of choice for the shortened esophagus. Am J Surg 171: 477–481
Treacy PJ, Jamieson GG (1987) An approach to the management of paraoesophageal hiatus hernias. Aust NZ J Surg 57: 813–817
Velanovich V, Vallance SR, Gusz JR, Tapia FV, Harkabus MA (1996) Quality-of-life scale for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 183: 217–224
Visick AH (1948) Measured radical gastrectomy: review of 505 operations for peptic ulcer. Lancet 254: 505–510
Watson DI, Davies N, DeVitt PG, Jamieson GG (1999) Importance of dissection of the hernial sac in laparoscopic surgery for large hiatal hernias. Arch Surg 134: 1069–1073
Wiechmann RJ, Ferguson MK, Naunheim KS, McKesey P, Hazelrigg SJ, Santucci TS, Macherey RS, Landreneau RJ (2001) Laparoscopic management of giant paraesophageal herniation. Ann Thorac Surg 71: 1080–1087
Willekes CL, Edoga JK, Frezza EE (1997) Laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hernia. Ann Surg 225: 31–38
Wu JS, Dunnegan DL, Soper NJ (1998) Clinical and radiologic assessment of laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia repair. Surg Endosc 13: 497–502
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Riccardo Ragona for his support in statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morino, M., Giaccone, C., Pellegrino, L. et al. Laparoscopic management of giant hiatal hernia: factors influencing long-term outcome. Surg Endosc 20, 1011–1016 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0550-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0550-6