Abstract
Background
Synchronous gastric neoplasms are not infrequently detected, thus endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for multiple early gastric neoplasia is occasionally considered. However, there have been few investigations of the safety and feasibility of simultaneous ESD for multiple gastric lesions. This study aims to evaluate the safety and feasibility of simultaneous ESD for multiple gastric neoplasia.
Methods
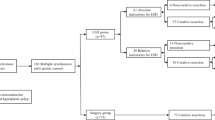
A total of 1823 patients who underwent ESD for 1929 gastric adenomas or early gastric cancers were retrospectively reviewed in this study. Two hundred gastric adenomas or early gastric cancers among 94 patients were treated by ESD simultaneously (multiple group), and 1729 patients were treated with ESD for a single lesion (single group).
Results
En bloc resection (P = 0.060), complete resection (P = 0.362) and curative resection (P = 0.108) rates did not differ between the two groups. Rates of adverse events including bleeding (P = 0.317), perforation (P = 0.316) and aspiration pneumonia (P = 0.563) were not higher in the multiple group. Long-term follow-up showed more frequent local recurrence (P < 0.001), synchronous neoplasia (P = 0.041) and metachronous neoplasia (P < 0.001) per patient in the multiple group; however, local recurrence per lesion did not differ between the two groups (P = 0.103).
Conclusions
Simultaneous ESD for multiple synchronous gastric neoplasms is safe and feasible compared to single ESD. However, thorough examination for local recurrence and synchronous and metachronous neoplasia is required.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamao T, Shirao K, Ono H, Kondo H, Saito D, Yamaguchi H, Sasako M, Sano T, Ochiai A, Yoshida S (1996) Risk factors for lymph node metastasis from intramucosal gastric carcinoma. Cancer 77(4):602–606. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960215)77:4<602:AID-CNCR3>3.0.CO;2-I
Yasuda K, Shiraishi N, Suematsu T, Yamaguchi K, Adachi Y, Kitano S (1999) Rate of detection of lymph node metastasis is correlated with the depth of submucosal invasion in early stage gastric carcinoma. Cancer 85(10):2119–2123
Gotoda T, Yanagisawa A, Sasako M, Ono H, Nakanishi Y, Shimoda T, Kato Y (2000) Incidence of lymph node metastasis from early gastric cancer: estimation with a large number of cases at two large centers. Gastric Cancer 3(4):219–225
Gotoda T, Yamamoto H, Soetikno RM (2006) Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 41(10):929–942. doi:10.1007/s00535-006-1954-3
Miyamoto S, Muto M, Hamamoto Y, Boku N, Ohtsu A, Baba S, Yoshida M, Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa K, Tajiri H, Yoshida S (2002) A new technique for endoscopic mucosal resection with an insulated-tip electrosurgical knife improves the completeness of resection of intramucosal gastric neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc 55(4):576–581
Honmyo U, Misumi A, Murakami A, Haga Y, Akagi M (1989) Clinicopathological analysis of synchronous multiple gastric carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 15(4):316–321
Kim HG, Ryu SY, Lee JH, Kim DY (2012) Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of synchronous multiple gastric carcinomas. Acta Chir Belg 112(2):148–153
Otsuji E, Kuriu Y, Ichikawa D, Okamoto K, Hagiwara A, Yamagishi H (2005) Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis of synchronous multifocal gastric carcinomas. Am J Surg 189(1):116–119. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2004.03.013
Kim HM, Kim HK, Lee SK, Cho JH, Pak KH, Hyung WJ, Noh SH, Kim CB, Lee YC, Song SY, Youn YH (2012) Multifocality in early gastric cancer does not increase the risk of lymph node metastasis in a single-center study. Ann Surg Oncol 19(4):1251–1256. doi:10.1245/s10434-011-2083-7
Choi J, Kim SG, Im JP, Kang SJ, Lee HJ, Yang HK, Kim JS, Kim WH, Jung HC, Song IS (2011) Lymph node metastasis in multiple synchronous early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 74(2):276–284. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.04.009
Akasaka T, Nishida T, Tsutsui S, Michida T, Yamada T, Ogiyama H, Kitamura S, Ichiba M, Komori M, Nishiyama O, Nakanishi F, Zushi S, Nishihara A, Iijima H, Tsujii M, Hayashi N (2011) Short-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for early gastric neoplasm: multicenter survey by osaka university ESD study group. Dig Endosc 23(1):73–77. doi:10.1111/j.1443-1661.2010.01062.x
Kasuga A, Yamamoto Y, Fujisaki J, Okada K, Omae M, Ishiyama A, Hirasawa T, Chino A, Tsuchida T, Hoshino E, Igarashi M (2012) Simultaneous endoscopic submucosal dissection for synchronous double early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. doi:10.1007/s10120-012-0218-6
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association (2011) Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma: 3rd English edition. Gastric Cancer 14(2):101–112. doi:10.1007/s10120-011-0041-5
Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC, Hughes JM (1988) CDC definitions for nosocomial infections. Am J Infect Control 16(3):128–140
Toyokawa T, Inaba T, Omote S, Okamoto A, Miyasaka R, Watanabe K, Izumikawa K, Horii J, Fujita I, Ishikawa S, Morikawa T, Murakami T, Tomoda J (2012) Risk factors for perforation and delayed bleeding associated with endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric neoplasms: analysis of 1123 lesions. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(5):907–912. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07039.x
Ohta T, Ishihara R, Uedo N, Takeuchi Y, Nagai K, Matsui F, Kawada N, Yamashina T, Kanzaki H, Hanafusa M, Yamamoto S, Hanaoka N, Higashino K, Iishi H (2012) Factors predicting perforation during endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 75(6):1159–1165. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.02.015
Park CH, Kim H, Kang YA, Cho IR, Kim B, Heo SJ, Shin S, Lee H, Park JC, Shin SK, Lee YC, Lee SK (2012) Risk factors and prognosis of pulmonary complications after endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neoplasia. Dig Dis Sci. doi:10.1007/s10620-012-2376-0
Nakajima T, Oda I, Gotoda T, Hamanaka H, Eguchi T, Yokoi C, Saito D (2006) Metachronous gastric cancers after endoscopic resection: how effective is annual endoscopic surveillance? Gastric Cancer 9(2):93–98. doi:10.1007/s10120-006-0372-9
Uemura N, Okamoto S (2000) Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on subsequent development of cancer after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer in Japan. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 29(4):819–827
Arima N, Adachi K, Katsube T, Amano K, Ishihara S, Watanabe M, Kinoshita Y (1999) Predictive factors for metachronous recurrence of early gastric cancer after endoscopic treatment. J Clin Gastroenterol 29(1):44–47
Nasu J, Doi T, Endo H, Nishina T, Hirasaki S, Hyodo I (2005) Characteristics of metachronous multiple early gastric cancers after endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy 37(10):990–993. doi:10.1055/s-2005-870198
Kobayashi M, Narisawa R, Sato Y, Takeuchi M, Aoyagi Y (2010) Self-limiting risk of metachronous gastric cancers after endoscopic resection. Dig Endosc 22(3):169–173. doi:10.1111/j.1443-1661.2010.00987.x
Fukase K, Kato M, Kikuchi S, Inoue K, Uemura N, Okamoto S, Terao S, Amagai K, Hayashi S, Asaka M (2008) Effect of eradication of Helicobacter pylori on incidence of metachronous gastric carcinoma after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 372(9636):392–397. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61159-9
Hanaoka N, Uedo N, Shiotani A, Inoue T, Takeuchi Y, Higashino K, Ishihara R, Iishi H, Haruma K, Tatsuta M (2010) Autofluorescence imaging for predicting development of metachronous gastric cancer after Helicobacter pylori eradication. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25(12):1844–1849. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06442.x
Disclosures
Dong Hoo Joh, Chan Hyuk Park, Sungmo Jung, Seung-Ho Choi, Hyun Ki Kim, Hyuk Lee, Jun Chul Park, Sung Kwan Shin, Yong Chan Lee, Sang Kil Lee have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joh, D.H., Park, C.H., Jung, S. et al. Safety and feasibility of simultaneous endoscopic submucosal dissection for multiple gastric neoplasias. Surg Endosc 29, 3690–3697 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4139-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4139-4