Abstract
Background
A considerable number of patients require revisional surgery after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB). Studies that compared the outcomes of revisional sleeve gastrectomy (r-SG) and revisional Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (r-RYGB) after failed LAGB are scarce in the literature. Our objective was to determine whether significant differences exist in outcomes between r-SG and r-RYGB after failed LAGB.
Methods
From 2005 to 2012, patients who underwent laparoscopic r-SG and r-RYGB after failed LAGB were retrospectively compared and analyzed. Data included demographics, indication for revision, operative time, hospital stay, conversion rate, percentage excess weight loss (%EWL), and morbidity and mortality.
Results
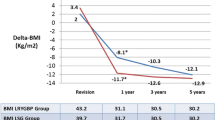
Out of 693 bariatric procedures, 42 r-SG and 53 r-RYGB were performed. The median preoperative weight (107.7 and 117.7 kg, respectively, p = 0.02) and body mass index (BMI) (38.5 vs. 43.2 kg/m2, respectively, p = 0.01) were statistically significantly lower in r-SG than in r-RYGB. The mean operative time and median hospital stay were significantly shorter in r-SG than in r-RYGB (108.4 vs. 161.2 min, p < 0.01) (2 vs. 3 days, p = 0.02), respectively. One patient underwent conversion to open surgery after r-RYGB (p = 0.5). The reoperation rate was lower in r-SG than in r-RYGB (0.0 vs. 3.8 %, p = 0.5). There was one postoperative leak in the r-RYGB, and the overall complication rate was significantly lower in r-SG patients than in r-RYGB patients (7.1 vs. 20.8 %, p = 0.05). The mean follow-up was significantly shorter in the r-SG group (9.8 vs. 29.3 months, p < 0.01). However, the mean postoperative BMI was not different at 1 year (32.3 vs. 34.7, p = 0.29) as well as mean %EWL was (47.4 vs. 45.6 %, p = 0.77).
Conclusions
Both r-SG and r-RYGB are safe procedures with similar outcomes in terms of %EWL. As a result of the long-term potential nutritional complication of r-RYGB, r-SG may be a better option in this group of patients. Longer follow-up is needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belachew M, Jacqet P, Lardinois F, Karler C (1993) Vertical banded gastrosplasty vs adjustable silicone gastric banding in the treatment of morbid obesity: a preliminary report. Obes Surg 3(3):275–278
Weiner R, Blanco-Engert R, Weiner S, Motkowitz R, Schaefer L, Pomhoff I (2003) Outcome after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: 8 years experience. Obes Surg 13(3):427–434
Favretti F, Segato G, Ashton D, Busetto L, De Luca M, Mazza M, Ceoloni A, Banzato O, Calo E, Enzi G (2007) Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in 1,791 consecutive obese patients: 12-year results. Obes Surg 17(2):168–175
O’Brien PE, Macdonald L, Anderson M, Brennan L, Brown WA (2013) Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: fifteen-year follow-up of adjustable gastric banding and a systematic review of the bariatric surgical literature. Ann Surg 257(1):87–94
Suter M, Calmes JM, Paroz A, Giusti V (2006) A 10-year experience with laparoscopic gastric banding for morbid obesity: high long-term complication and failure rates. Obes Surg 16(7):829–835
DeMaria EJ, Sugerman HJ, Meador JG, Doty JM, Kellum JM, Wolfe L, Szucs RA, Turner MA (2001) High failure rate after laparoscopic adjustable silicone gastric banding for treatment of morbid obesity. Ann Surg 233(6):809–818
Morino M, Toppino M, Garrone C (1997) Disappointing long-term results of laparoscopic adjustable silicone gastric banding. Br J Surg 84(6):868–869
Tucker O, Sucandy I, Szomstein S, Rosenthal RJ (2008) Revisional surgery after failed adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis 4(6):740–747
Gagner M, Gumbs AA (2007) Gastric banding: conversion to sleeve, bypass, or DS. Surg Endosc 21(11):1931–1935
Weber M, Muller MK, Michel JM, Belal R, Horber F, Hauser R, Clavien PA (2003) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, but not rebanding, should be proposed as rescue procedure for patients with failed laparoscopic gastric banding. Ann Surg 238(6):827–833
Spivak H, Beltran OR, Slavchev P, Wilson EB (2007) Laparoscopic revision from LAP-BAND to gastric bypass. Surg Endosc 21(8):1388–1392
van Wageningen B, Berends FJ, Van Ramshorst B, Janssen IF (2006) Revision of failed laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg 16(2):137–141
Iannelli A, Schneck A, Ragot E, Liagre A, Anduze Y, Msika S, Gugenheim J (2009) Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as revisional procedure for failed gastric banding and vertical banded gastroplasty. Obes Surg 19:1216–1220
Topart P, Becouarn G, Ritz P (2007) Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch or gastric bypass for failed gastric banding: retrospective study from two institutions with preliminary results. Surg Obes Relat Dis 3(5):521–525
Jones KB Jr (2005) Revisional bariatric surgery: potentially safe and effective. Surg Obes Relat Dis 1(6):599–603
Hallowell PT, Stellato TA, Yao DA, Robinson A, Schuster MM, Graf KN (2009) Should bariatric revisional surgery be avoided secondary to increased morbidity and mortality? Am J Surg 197(3):391–396
Silecchia G, Boru C, Pecchia A, Rizzello M, Casella G, Leonetti F, Basso N (2006) Effectiveness of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (first stage of biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch) on co-morbidities in super-obese high-risk patients. Obes Surg 16(9):1138–1144
Brethauer S, Hammel J, Schauer P (2009) Systematic review of sleeve gastrectomy as staging and primary bariatric procedure. Surg Obes Relat Dis 5(4):469–475
Lalor PF, Tucker ON, Szomstein S, Rosenthal RJ (2008) Complications after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Obes Relat Dis 4(1):33–38
Roa PE, Kaider-Person O, Pinto D, Cho M, Szomstein S, Rosenthal RJ (2006) Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as treatment for morbid obesity: technique and short-term outcome. Obes Surg 16(10):1323–1326
Berende CA, de Zoete JP, Smulders JF, Nienhuijis SW (2012) Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy feasible for bariatric revision surgery. Obes Surg 22(2):330–334
Jacobs M, Gomez E, Romero R, Jorge I, Fogel R, Celaya C (2011) Failed restrictive surgery: Is sleeve gastrectomy a good revisional procedure? Obes Surg 21(2):157–160
Acholonu E, McBean E, Court I, Bellorin O, Szomstein S, Rosenthal RJ (2009) Safety and short-term outcomes of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as a revisional approach for failed laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of morbid obesity. Obes Surg 19(12):1612–1616
Cohen R, Uzzan B, Bihan H, Khochtali I, Reach G, Catheline JM (2005) Ghrelin levels and sleeve gastrectomy in super-super-obesity. Obes Surg 15(10):1501–1502
Karamanakos SN, Vagenas K, Kalfarentzos F, Alexandrides TK (2008) Weight loss, appetite suppression, and changes in fasting and postprandial ghrelin and peptide-YY levels after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: a prospective, double blind study. Ann Surg 247(3):401–407
Uglioni B, Wölnerhanssen B, Peters T, Christoffel-Courtin C, Kern B, Peterli R (2009) Midterm results of primary versus secondary laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) as an isolated operation. Obes Surg 19:401–406
Goitein D, Feigin A, Segal-Leiberman G, Goitein O, Papa MZ, Zippel D (2011) Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as a revisional option after gastric band failure. Surg Endosc 25:2626–2630
Brolin RE, Cody RP (2008) Weight loss outcome of revisional bariatric operations varies according to the primary procedure. Ann Surg 248(2):227–232
Nesset EM, Kendrick ML, Houghton SG, Mai JL, Thompson GB, Que FG, Thomsen KM, Larson DR, Sarr MG (2007) A two-decade spectrum of revisional bariatric surgery at a tertiary referral center. Surg Obes Relat Dis 3(1):25–30
Khoursheed M, Al-Bader I, Al-Asfar F, Mohammad A, Shukkur M, Dashti H (2011) Revision of failed bariatric procedures or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg 21:1157–1160
Owens BM, Owens ML, Hill CW (1996) Effect of revisional bariatric surgery on weight loss and frequency of complications. Obes Surg 6(6):479–484
Martin MJ, Mullenix PS, Steele SR, Steele SR, See CS, Cuadrado DG, Carter PL (2004) A case-match analysis of failed prior bariatric procedures converted to resectional gastric bypass. Am J Surg 187(5):666–670
Zingg U, McQuinn A, DiValentino D, Kinsey-Trotman S, Game P, Watson D (2010) Revisional vs primary Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a case-matched analysis: less weight loss in revisions. Obes Surg 20(12):1627–1632
Merrouche M, Sabate JM, Jouet P, Harnois F, Scaringi S, Coffin B, Msika S (2007) Gastro-esophageal reflux and esophageal motility disorders in morbidly obese patients before and after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 17(7):894–900
Cadiere GB, Himpens J, Bazi M, Cadiere B, Vouche M, Capelluto E, Dapri G (2011) Are laparoscopic gastric bypass after gastroplasty and primary laparoscopic gastric bypass similar in terms of results? Obes Surg 21(6):692–698
Van Nieuwenhove Y, Ceelen W, Van Renterghem K, Van de Putte D, Henckens T, Pattyn P (2011) Conversion from band to bypass in two steps reduces the risk for anastomotic strictures. Obes Surg 21(4):501–505
Giordano S, Salminen P, Biancari F, Victorzon M (2011) Linear stapler technique may be safer than circular in gastrojejunal anastomosis for laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a meta-analysis of comparative studies. Obes Surg 21(12):1958–1964
Roller JE, Provost DA (2006) Revision of failed gastric restrictive operations to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: impact of multiple prior bariatric operations on outcome. Obes Surg 16(7):865–869
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Joseph Longenecker for his help and support with the statistical analysis.
Disclosures
Dr. Mousa Khoursheed, Dr. Ibtisam Al-Bader I, Dr. Ali Mouzannar, Dr. Abdulla Al-Haddad, Dr. Ali Sayed, Dr. Ali Mohammad, and Dr. Abe Fingerhut have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoursheed, M., Al-Bader, I., Mouzannar, A. et al. Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Surg Endosc 27, 4277–4283 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3038-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3038-9