Abstract
Background and aims
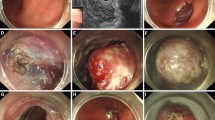
Endoscopic resection of esophageal or cardial subepithelial tumors (SETs) originating from the muscularis propria (MP) is rarely done due to the high risk of perforation, fistula formation, and secondary infection. The aim of this study was to evaluate the preliminary clinical feasibility and safety of tunneling endoscopic muscularis dissection (tEMD) for resection of SETs located in the esophagus and gastric cardia
Methods
Twelve patients with SETs originating from the MP of the esophagus (n = 7) or cardia (n = 5) were treated by tEMD. The procedure included creation of a submucosal tunnel to reach the tumor, dissection of the tumor from the surrounding submucosal tissue and the unaffected MP layer, full-thickness resection of the tumor and affected MP, and subsequent closure of the tunnel mucosal entry with endoscopic clips.
Results
The en bloc resection rate was 100 % (seven lesions affected the deep MP so complete MP resection was performed; five lesions affected the superficial MP for a partial MP resection). The average tumor size was 18.5 ± 6.9 (range 10–30) mm. The mean operating time was 78.3 ± 25.5 (range 50–130) min. The histological diagnoses were two gastrointestinal stromal tumors with very low risk, nine leiomyomas, and one schwannoma. Air leakage and effusion included subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema in eight patients (66.7 %), pneumothorax in four (33.3 %), pneumoperitoneum in three (25.0 %), and small pleural effusion in two (16.7 %). All air leakage and effusion cases were resolved with conservative management. No patient developed delayed hemorrhage and chronic fistula after tEMD. During the mean follow-up time of 7.1 ± 4.3 (range 2–15) months, no tumor recurrence was found in any patient.
Conclusions
tEMD appears to be a feasible minimally invasive and effective treatment for patients with SETs originating from the MP layer of the esophagus and cardia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Connolly EM, Gaffney E, Reynolds JV (2003) Gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br J Surg 90:1178–1186
Polkowski M, Butruk E (2005) Submucosal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 15:33–54
Gill KR, Camellini L, Conigliaro R, Sassatelli R, Azzolini F, Messerotti A, Woodward TA, Wallace MB, Jamil LH, Raimondo M (2009) The natural history of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors: a multicenter endoscopic ultrasound survey. J Clin Gastroenterol 43:723–726
Ha CY, Shah R, Chen J, Azar RR, Edmundowicz SA, Early DS (2009) Diagnosis and management of GI stromal tumors by EUS-FNA: a survey of opinions and practices of endosonographers. Gastrointest Endosc 69:1039–1044
Lok KH, Lai L, Yiu HL, Szeto ML, Leung SK (2009) Endosonographic surveillance of small gastrointestinal tumors originating from muscularis propria. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 18:177–180
Grotz TE, Donohue JH (2011) Surveillance strategies for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Surg Oncol 104:921–927
Dieter RA Jr (1997) Thoracoscopic esophageal surgery. Int Surg 82:119–122
von Rahden BH, Stein HJ, Feussner H, Siewert JR (2004) Enucleation of submucosal tumors of the esophagus: minimally invasive versus open approach. Surg Endosc 18:924–930
Wang BY, Liu CC, Shih CS (2011) Thoracoscopic enucleation of a gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the esophagus. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 59:190–192
Liu BR, Song JT, Qu B, Wen JF, Yin JB, Liu W (2012) Endoscopic muscularis dissection for upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria. Surg Endosc 26:3141–3148
Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y, Kaga M, Suzuki M, Satodate H, Odaka N, Itoh H, Kudo S (2010) Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy 42:265–271
von Renteln D, Inoue H, Minami H, Werner YB, Pace A, Kersten JF, Much CC, Schachschal G, Mann O, Keller J, Fuchs KH, Rösch T (2012) Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a prospective single center study. Am J Gastroenterol 107:411–417
Inoue H, Tianle KM, Ikeda H, Hosoya T, Onimaru M, Yoshida A, Minami H, Kudo SE (2011) Peroral endoscopic myotomy for esophageal achalasia: technique, indication, and outcomes. Thorac Surg Clin 21:519–525
Joensuu H (2008) Risk stratification of patients diagnosed with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Hum Pathol 39:1411–1419
Walz B, von Renteln D, Schmidt A, Caca K (2011) Endoscopic full-thickness resection of subepithelial tumors with the use of resorbable sutures (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 73:1288–1291
Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Qin XY, Cai MY, Xu MD, Zhong YS, Chen WF, Zhang YQ, Qin WZ, Hu JW, Liu JZ (2011) Endoscopic full-thickness resection without laparoscopic assistance for gastric submucosal tumors originated from the muscularis propria. Surg Endosc 25:2926–2931
Brinster CJ, Singhal S, Lee L, Marshall MB, Kaiser LR, Kucharczuk JC (2004) Evolving options in the management of esophageal perforation. Ann Thorac Surg 77:1475–1483
Sumiyama K, Gostout CJ, Rajan E, Bakken TA, Knipschield MA, Marler RJ (2007) Submucosal endoscopy with mucosal flap safety valve. Gastrointest Endosc 65:688–694
Pasricha PJ, Hawari R, Ahmed I, Chen J, Cotton PB, Hawes RH, Kalloo AN, Kantsevoy SV, Gostout CJ (2007) Submucosal endoscopic esophageal myotomy: a novel experimental approach for the treatment of achalasia. Endoscopy 39:761–764
Smith CD, Stival A, Howell DL, Swafford V (2006) Endoscopic therapy for achalasia before Heller myotomy results in worse outcomes than Heller myotomy alone. Ann Surg 243:579–584
Tamiya Y, Nakahara K, Kominato K, Serikawa O, Watanabe Y, Tateishi H, Takedatsu H, Toyonaga A, Sata M (2010) Pneumomediastinum is a frequent but minor complication during esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy 42:8–14
Ren Z, Zhong Y, Zhou P, Xu M, Cai M, Li L, Shi Q, Yao L (2012) Perioperative management and treatment for complications during and after peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia (EA) (data from 119 cases). Surg Endosc 26:3267–3272
Disclosure
Drs. Bing-Rong Liu, Ji-Tao Song, Ling-Jian Kong, Feng-Hua Pei, Xin-Hong Wang, and Ya-Ju Du have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
B.-R. Liu and J.-T. Song contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Video 1 Endoscopic dissection of SET as deep as muscularis propria within submucosal tunnel. Supplementary material 1 (MPG 30024 kb)
Video 2 Endoscopic circumferential full-thickness MP incision at the base of SET. Supplementary material 2 (MPG 46372 kb)
Video 3 Endoscopic snaring of the SET after circumferential full-thickness MP incision. Supplementary material 3 (MPG 37284 kb)
Video 4 Endoscopic observation of full MP defect and submucosal tunnel after removal of the tumor. Supplementary material 4 (MPG 12178 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, BR., Song, JT., Kong, LJ. et al. Tunneling endoscopic muscularis dissection for subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria of the esophagus and gastric cardia. Surg Endosc 27, 4354–4359 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3023-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3023-3