Abstract
Background
Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas is an uncommon but distinctive pancreatic neoplasm with low metastatic potential [1]. Therefore, whenever feasible, an organ-preserving operation should be performed. As previously reported, women with solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas may be best treated by more conservative procedures [2]. Recently, laparoscopic pancreatic resections became more common and are being performed in highly specialized centers. There are only six cases of laparoscopic resection for solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of pancreas published in the English literature and, to our knowledge, laparoscopic resection of uncinate process of the pancreas has never been reported [3–6]. This video demonstrates the technical aspects of a totally laparoscopic resection of the uncinate process of the pancreas in a patient with solid pseudopapillary neoplasm.
Methods
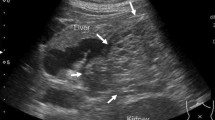
A 26-year-old woman with a 4-cm solid pseudopapillary pancreatic neoplasm was referred for surgical treatment. According to preoperative echoendoscopy, there was a safe margin between neoplasm and main pancreatic duct. The patient was placed in supine position with the surgeon standing between her legs. Four trocars, one 10-mm and three 5-mm, were used. At inspection, the inferior vena cava, transverse colon, duodenum, and pancreas are clearly identified. A Kocher maneuver was performed with complete exposure of pancreatic head and uncinate process. The uncinate process was dissected from the superior mesenteric vein and venous branches were divided between metallic clips or by use of laparoscopic coagulation shears (LCS; Ethicon Endo Surgery Industries, Cincinnati, OH, USA). Blood supply of the duodenum was preserved by ligature of small pancreatic branches from inferior pancreatoduodenal artery. Transection of pancreatic parenchyma was performed using laparoscopic coagulation shears, which is an effective tool for cutting the pancreas [7, 8]. Surgical specimen was removed through a suprapubic incision inside a retrieval bag. A hemostatic absorbable tissue (Surgicel; Ethicon Inc., Cincinnati, OH) was placed in the cutting pancreatic surface, and one round 19F Blake abdominal drain (Ethicon) was left in place.
Results
Operative time was 180 minutes and blood loss estimated in 40 ml with no blood transfusion. Hospital stay was 4 days. The patient did not have postoperative pancreatitis or pancreatic leakage, and the abdominal drain was removed on the tenth postoperative day. Final pathology confirmed the diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of pancreas with free surgical margins. The patient was well and asymptomatic 2 months after the procedure.
Conclusions
Laparoscopic resection of uncinate process of the pancreas is safe and feasible and should be considered for patients suffering from pancreatic neoplasms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klimstra DS, Wenig BM, Heffess CS (2000) Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a typically cystic carcinoma of low malignant potential. Semin Diagn Pathol 17:66–80
Machado MC, Machado MA, Bacchella T, Jukemura J, Almeida JL, Cunha JE (2008) Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: distinct patterns of onset, diagnosis, and prognosis for male versus female patients. Surgery 143:29–34
Laxa BU, Carbonell AM 2nd, Cobb WS, Rosen MJ, Hardacre JM, Mekeel KL, Harold KL (2008) Laparoscopic and hand-assisted distal pancreatectomy. Am Surg 74:481–486
Kang CM, Kim HG, Kim KS, Choi JS, Lee WJ, Kim BR (2007) Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas-report of two cases. Hepatogastroenterology 54:1053–1056
Melotti G, Cavallini A, Butturini G, Piccoli M, Delvecchio A, Salvi C, Pederzoli P (2007) Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy in children: case report and review of the literature. Ann Surg Oncol 14:1065–1069
Carricaburu E, Enezian G, Bonnard A, Berrebi D, Belarbi N, Huot O, Aigrain Y, de Lagausie P (2003) Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for Frantz’s tumor in a child. Surg Endosc 17:2028–2031
Takao S, Shinchi H, Maemura K, Aikou T (2000) Ultrasonically activated scalpel is an effective tool for cutting the pancreas in biliary-pancreatic surgery: experimental and clinical studies. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 7:58–62
Sharma MS, Brams DM, Birkett DH, Munson JL (2006) Uncinatectomy: a novel surgical option for the management of intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Dig Surg 23:121–124
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1 (WMV 58777 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machado, M.A., Makdissi, F.F., Surjan, R.C. et al. Laparoscopic resection of uncinate process of the pancreas. Surg Endosc 23, 1391–1392 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0390-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0390-x