Abstract
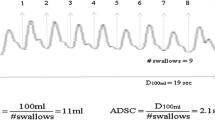
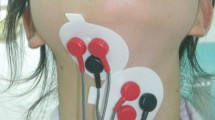
Our goal was to study deglutition of Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients and normal controls (NC) using surface electromyography (sEMG). The study included 15 patients with idiopathic PD and 15 age-matched normal controls. Surface electromyography was collected over the suprahyoid muscle group. Conditions were the following: swallow at once 10 and 20 ml of water and 5 and 10 ml of yogurt of firm consistency, and freely drink 100 ml of water. During swallowing, durations of sEMG were significantly longer in PD patients than in normal controls but no significant differences of amplitudes were found. Eighty percent of the PD patients and 20 % of the NC needed more than one swallow to consume 20 ml of water, while 70 % of the PD patients and none of the NC needed more than one swallow to consume 5 ml of yogurt. PD patients took significantly more time and needed significantly more swallows to drink 100 ml of water than normal controls. We conclude that sEMG might be a simple and useful tool to study and monitor deglutition in PD patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scalzo P, Kummer A, Cardoso F, et al. Depressive symptoms and perception of quality of life in Parkinson’s disease. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2009;67(2-A):203–8.
Findley LJ. The economic impact of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007;13(Suppl):S8–12.
Lana RC, et al. Percepção da qualidade de vida de indivíduos com doença de Parkinson através do PDQ-39. Rev Bras Fisioter. 2007;11(5):397–402.
Jankovic J, Tolosa E. Parkinson’s disease & movement disorders. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 79.
Linazanoro G. A global view of Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis: implications for natural history and neuroprotection. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009;15:401–5.
Manor Y, Balas M, Giladi N, et al. Anxiety, depression and swallowing disorders in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009;15:453–6.
Tolosa E, Compta Y, Gaig C. The premotor phase of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007;13(Suppl):S2–7.
Schneider MG, Swearinger CJ, Shulman LM, et al. Minority enrollment in Parkinson’s disease clinical trials. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009;15:258–62.
Dray TG, Hillel AD, Miller RM, et al. Dysphagia caused by neurologic deficits. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1998;31(3):507–24.
Olszewski J. Causes, diagnosis and treatment of neurogenic dysphagia as an interdisciplinary clinical problem. Otolaryngol Pol. 2006;60(4):491–500.
Eisenhuber E, Schima W, Schober E, et al. Videofluoroscopic assessment of patients with dysphagia: pharyngeal retention is a predictive factor for aspiration. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178:393–8.
Carrara-Angelis E. Voz e deglutição. In: Andrade LAS, Barbosa ER, Cardoso F et al ,editors Doença de Parkinson, estratégias atuais de tratamento. ABDR. 2006;13:197–207.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yüceyar N. Piecemeal deglutition and dysphagia limit in normal subjects and in patients with swallowing disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996;61:491–6.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yüceyar N, et al. Electrodiagnostic methods for neurogenic dysphagia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1998;109:331–40.
Alfonsi E, Versino M, Merlo IM, et al. Electrophysiologic patterns of oral-pharyngeal swallowing in parkinsonian syndromes. Neurology. 2007;68:583–90.
Coriolano MG, Belo LR, Carneiro D, et al. Monitorando a deglutição através da eletromiografia de superfície. Rev CEFAC. 2010;12(3):434–40.
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology. 1967;17(5):427–42.
Ertekin C, Tarlaci S, Aydogdu I, et al. Electrophysiological evaluation of pharyngeal phase of swallowing in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2002;17(5):942–9.
Potulska A, Friedman AA, Królicki L, et al. Swallowing disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2003;9:349–53.
Vaiman M, Eviatar E, Segal S. Surface electromyographic studies of swallowing in normal subjects: a review of 440 adults. Report 1. Quantitative data: timing measures. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;131(4):548–55.
Vaiman M, Eviatar E, Segal S. Surface electromyographic studies of swallowing in normal subjects: a review of 440 adults. Report 2. Quantitative data: amplitude measures. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;135(5):773–80.
Vaiman M, Eviatar E, Segal S. Surface electromyographic studies of swallowing in normal subjects: a review of 440 adults. Report 3. Qualitative data. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;131(6):977–85.
Vaiman M. Standardization of surface electromyography utilized to evaluate patients with dysphagia. Head Face Med. 2007;3:26.
Vaiman M, Chaim G, Eviatar E, et al. Surface electromyography of continuous drinking in healthy adults. Laryngoscope. 2005;115:68–73.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yüceyar N, et al. Effects of bolus volume on oropharyngeal swallowing: an electrophysiologic study in man. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(11):2049–53.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114:2226–44.
Dantas RO, Kern MK, Massey BT, et al. Effect of swallowed bolus variables on oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Am J Physiol. 1990;258:G675–81.
Ruark JL, McCullough GH, Peters RL, et al. Bolus consistency and swallowing in children and adults. Dysphagia. 2002;17:24–33.
Taniguchi H, Tsukada T, Ootaki S, et al. Correspondence between food consistency and suprahyoid muscle activity, tongue pressure, and bolus transit times during the oropharyngeal phase of swallowing. J Appl Physiol. 2008;105:791–9.
Daniels SK, Foundas AL. Swallowing physiology of sequential straw drinking. Dysphagia. 2001;16:176–82.
Leder SB, Suiter DM, Gree BG. Silent aspiration risk is volume-dependent. Dysphagia. 2011;26:304–9.
Aydogdu I, Tanriverdi Z, Ertekin C. Dysfunction of bulbar central pattern generator in ALS patients with dysphagia during sequential deglutition. Clinl Neurophysiol. 2011;122:1219–28.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WS Coriolano, M.d.G., R Belo, L., Carneiro, D. et al. Swallowing in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Surface Electromyography Study. Dysphagia 27, 550–555 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-012-9406-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-012-9406-0