Abstract
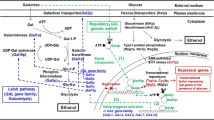
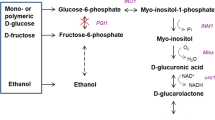
A recombinant strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae harboring GOD gene originated from Aspergillus niger was used for the production of extracellular glucose oxidase. The effect of continuous galactose feeding on the induction of GAL-10 promoter was examined in a 5 l bioreactor. The highest enzyme production level (164 U cm−3) was achieved at 96 h of cultivation. The production performance was compared with the results of fed-batch cultivations carried out in the same laboratory. Continuous feeding mode was found to be less productive due to excess ethanol formation and plasmid instability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapat, A., Jung, J. & Park, Y. Effect of continuous feeding of galactose on the production of recombinant glucose oxidase using Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Bioprocess Engineering 23, 37–40 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004499900117
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004499900117