Abstract
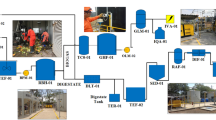
An attempt is presented and discussed to adapt a well-known process successfully employed in the U.S.A. for the simultaneous treatment of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (MSWOF) and sewage sludge to the particular situation of water works in Italy. It consists of preliminary domestic grinding of MSWOF, its discharge into the sewer, screening, and final digestion of the resulting residue together with sewage sludge. In order to avoid extension work of the present activated sludge sections necessary to face the organic load increase, a fine screening is necessary, while the efficiency of anaerobic digestion can be improved by shifting the system from mesophilic (37 °C) to thermophilic (55 °C) conditions. The effects of thermal, chemical, and biological pretreatments of both MSWOF and sewage sludge on methane, carbon dioxide, and biogas productions are investigated either separately or jointly. During these pretreatments, volatile suspended solid (VSS) concentration remarkably decreased while soluble chemical oxygen demand (COD) increased as the result of the progressive hydrolysis of the polymeric materials present in the feed. Finally, the kinetic parameters of the hydrolysis of these materials are estimated and compared in order to provide useful information on the factors limiting the anaerobic digestion as well as to suggest the best way to carry out the process on a large scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Del Borghi, A., Converti, A., Palazzi, E. et al. Hydrolysis and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge and organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Bioprocess Engineering 20, 553–560 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004490050628
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004490050628