Abstract
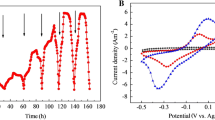
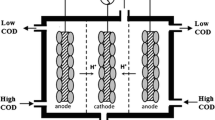
Microbial fuel cell (MFC) is used to remove organic pollutants while generating electricity. Biocathode plays as an efficient electrocatalyst for accelerating the Oxidation Reduction Reaction (ORR) of oxygen in MFC. This study integrated biocathode into a single-chamber microbial fuel cell (BSCMFC) to produce electricity from an organic substrate using aerobic activated sludge to gain more insights into anodic and cathodic biofilms. The maximum power density, current density, chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal, and coulombic efficiency were 0.593 W m−3, 2.6 A m−3, 83 ± 8.4%, and 22 ± 2.5%, respectively. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) produced by biofilm from the biocathode were higher than the bioanode. Infrared spectroscopy and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) examined confirmed the presence of biofilm by the adhesion on electrodes. The dominant phyla in bioanode were Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria, while the dominant phylum in the biocathode was Proteobacteria. Therefore, this study demonstrates the applicable use of BSCMFC for bioelectricity generation and pollution control.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Xu H, Wang L, Lin C et al (2020) Improved simultaneous decolorization and power generation in a microbial fuel cell with the sponge anode modified by polyaniline and chitosan. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 192:698–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03346-2
Xiao B, Yang F, Liu J (2011) Enhancing simultaneous electricity production and reduction of sewage sludge in two-chamber MFC by aerobic sludge digestion and sludge pretreatments. J Hazard Mater 189:444–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.058
Xin X, Chen B-Y, Hong J (2019) Unraveling interactive characteristics of microbial community associated with bioelectric energy production in sludge fermentation fluid-fed microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 289:121652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121652
Lovley DR, Nevin KP (2011) A shift in the current: new applications and concepts for microbe-electrode electron exchange. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.01.009
Chandrasekhar K (2019) Effective and nonprecious cathode catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cells. In: Microbial Electrochemical Technology, p 485–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64052-9.00019-4
Kakaei K, Esrafili MD, Ehsani A (2019) Oxygen reduction reaction. In: Interface Science and Technology, vol 27. p 203–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814523-4.00006-X
Song H-L, Zhu Y, Li J (2019) Electron transfer mechanisms, characteristics and applications of biological cathode microbial fuel cells–a mini review. Arab J Chem 12:2236–2243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.01.008
Milner EM, Popescu D, Curtis T et al (2016) Microbial fuel cells with highly active aerobic biocathodes. J Power Sour 324:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.05.055
Du Y, Feng Y, Dong Y, Qu Y, Liu J, ZX& RN, (2014) Coupling interaction of cathodic reduction and microbial metabolism in aerobic biocathode of microbial fuel cell. RSC Adv 4:34350–34355. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra03441d
Rothballer M, Picot M, Sieper T et al (2015) Monophyletic group of unclassified $γ$-Proteobacteria dominates in mixed culture biofilm of high-performing oxygen reducing biocathode. Bioelectrochemistry 106:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2015.04.004
Wang Z, Zheng Y, Xiao Y et al (2013) Analysis of oxygen reduction and microbial community of air-diffusion biocathode in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 144:74–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.093
Zakaria BS, Dhar BR (2020) Changes in syntrophic microbial communities, EPS matrix, and gene-expression patterns in biofilm anode in response to silver nanoparticles exposure. Sci Total Environ 734:139395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139395
Tan B, Zhou S, Wang Y et al (2019) Molecular insight into electron transfer properties of extracellular polymeric substances of electroactive bacteria by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sci China Technol Sci 62:1679–1687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-018-9437-0
Stöckl M, Teubner NC, Holtmann D et al (2019) Extracellular polymeric substances from Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms in microbial fuel cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:8961–8968. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b14340
Xiao Y, Zhao F (2017) Electrochemical roles of extracellular polymeric substances in biofilms. Curr Opin Electrochem 4:206–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2017.09.016
Pandey P, Shinde VN, Deopurkar RL et al (2016) Recent advances in the use of different substrates in microbial fuel cells toward wastewater treatment and simultaneous energy recovery. Appl Energy 168:706–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.01.056
Vilajeliu-Pons A, Puig S, Pous N et al (2015) Microbiome characterization of MFCs used for the treatment of swine manure. J Hazard Mater 288:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.014
Rittman BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Halden RU (2008) Pregenomic, genomic and post-genomic study of microbial communities involved in bioenergy. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:604–612. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1939
Wittebolle L, Vooren NV, Verstraete W, Boon N (2009) High reproducibility of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in parallel sequential batch reactors. J Appl Microbiol 107:385–394
Khater DZ, El-Khatib KM, Hassan HM (2017) Microbial diversity structure in acetate single chamber microbial fuel cell for electricity generation. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2017.01.008
Lee K, Zhang L, Lui H et al (2009) Oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyzed by carbon-supported cobalt polypyrrole (Co-PPy/C) electrocatalysts. Electrochim Acta 54:4704–4711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.03.081
Picoreanu C, Head IM, Katuri KP et al (2007) Computational model for biofim-based microbial fuel cells. Water Res 41:2921–2940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.04.009
Andrew DE, Clescenri LS, Breenberg AE (1995) Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. APHA, AWW, WEF , Washington
Reguera G, McCarthy KD, Mehta T et al (2005) Extracellular electron transfer via microbial nanowires. Nature 435:1098–1101. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03661
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK et al (1956) Phenol sulphuric acid method for total carbohydrate. Anal Chem 8:350–356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60111a017
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Borges S, Silva J, Teixeira P (2012) Survival and biofilm formation by Group B streptococci in simulated vaginal fluid at different pHs. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101:677–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9666-y
Richter H, McCarthy K, Nevin KP et al (2008) Electricity generation by Geobacter sulfurreducens attached to gold electrodes. Langmuir 24:4376–4379. https://doi.org/10.1021/la703469y
Kamel MS, Abd-Alla MH, Abdul-Raouf UM et al (2019) Characterization of anodic biofilm bacterial communities and performance evaluation of a mediator-free microbial fuel cell. Environ Eng Res 25:862–870. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2019.412
Zhang G, Zhang H, Zhang C et al (2013) Simultaneous nitrogen and carbon removal in a single chamber microbial fuel cell with a rotating biocathode. Process Biochem 48:893–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.03.008
Bergel A, Féron D, Mollica A (2005) Catalysis of oxygen reduction in PEM fuel cell by seawater biofilm. Electrochem commun 7:900–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2005.06.006
Sharma Y, Li B (2010) Optimizing energy harvest in wastewater treatment by combining anaerobic hydrogen producing biofermentor (HPB) and microbial fuel cell (MFC). Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:3789–3797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.01.042
Freguia S, Rabaey K, Yuan Z, Keller J (2008) Sequential anode–cathode configuration improves cathodic oxygen reduction and effluent quality of microbial fuel cells. Water Res 42:1387–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.007
Huang L, Logan BE (2008) Electricity generation and treatment of paper recycling wastewater using a microbial fuel cell. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1546-7
Samsudeen N, Radhakrishnan TK, Matheswaran M (2015) Bioelectricity production from microbial fuel cell using mixed bacterial culture isolated from distillery wastewater. Bioresour Technol 195:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.023
Ibarbalz FM, Figuerola ELM, Erijman L (2013) Industrial activated sludge exhibit unique bacterial community composition at high taxonomic ranks. Water Res 47:3854–3864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.010
Cai W-F, Geng J-F, Pu K-B et al (2018) Investigation of a two-dimensional model on microbial fuel cell with different biofilm porosities and external resistances. Chem Eng J 333:572–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.189
Sun J, Bi Z, Hou B et al (2010) Further treatment of decolorization liquid of azo dye coupled with increased power production using microbial fuel cell equipped with an aerobic biocathode. Water Res 45:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.07.059
Xu G, Zheng X, Lu Y et al (2019) Development of microbial community within the cathodic biofilm of single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Sci Total Environ 665:641–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.175
Yang N, Zhan G, Wu T et al (2018) Effect of air-exposed biocathode on the performance of a Thauera-dominated membraneless single-chamber microbial fuel cell (SCMFC). J Environ Sci 66:216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.05.013
Xu G, Zheng X, Lu Y et al (2019) Development of microbial community within the cathodic bio fi lm of single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Sci Total Environ 665:641–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.175
Gao C, Wang A, Wu W et al (2014) Enrichment of anodic biofilm inoculated with anaerobic or aerobic sludge in single chambered air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 167:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.120
Kalathil S, Lee J, Cho MH (2012) Efficient decolorization of real dye wastewater and bioelectricity generation using a novel single chamber biocathode-microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 119:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.059
Yan H, Saito T, Regan JM (2012) Nitrogen removal in a single-chamber microbial fuel cell with nitrifying biofilm enriched at the air cathode. Water Res 46:2215–2224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.050
Zhang G, Zhao Q, Jiao Y et al (2012) Biocathode microbial fuel cell for efficient electricity recovery from dairy manure. Biosens Bioelectron 31:537–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.11.036
Zhang G, Zhao Q, Jiao Y et al (2012) Efficient electricity generation from sewage sludge using biocathode microbial fuel cell. Water Res 46:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.10.036
Chen G, Choi S, Lee T et al (2008) Application of biocathode in microbial fuel cells : cell performance and microbial community. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:379–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1451-0
Zhang G, Zhao Q, Jiao Y et al (2011) Improved performance of microbial fuel cell using combination biocathode of graphite fiber brush and graphite granules. J Power Sour 196:6036–6041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.03.096
Shen L, Yao Y, Meng F (2014) Reactor performance and microbial ecology of a nitritation membrane bioreactor. J Memb Sci 462:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.03.034
Jemaat Z, Suárez-Ojeda ME, Pérez J, Carrera J (2014) Partial nitritation and o-cresol removal with aerobic granular biomass in a continuous airlift reactor. Water Res 48:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.048
Jiang T, Zhang H, Qiang H et al (2013) Start-up of the anammox process and membrane fouling analysis in a novel rotating membrane bioreactor. Desalination 311:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.10.031
Chen Y-P, Li C, Guo J-S et al (2013) Extraction and characterization of extracellular polymeric substances in biofilm and sludge via completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite system. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:526–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9996-x
Ahimou F, Semmens MJ, Haugstad G, Novak PJ (2007) Effect of protein, polysaccharide, and oxygen concentration profiles on biofilm cohesiveness. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2905–2910. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02420-06
Yuvraj C, Aranganathan V (2017) MFC—An Approach in Enhancing Electricity Generation Using Electroactive Biofilm of Dissimilatory Iron-Reducing (DIR) Bacteria. Arab J Sci Eng 42:2341–2347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2529-8
Sun D, Cheng S, Wang A et al (2015) Temporal-spatial changes in viabilities and electrochemical properties of anode biofilms. Environ Sci Technol 49:5227–5235. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00175
Jorand F, Boue-Bigne F, Block JC, Urbain V (1998) Hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties of activated sludge exopolymeric substances. Water Sci Technol 37:307–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00123-1
Yuan S-J, Sun M, Sheng G-P et al (2011) Identification of key constituents and structure of the extracellular polymeric substances excreted by Bacillus megaterium TF10 for their flocculation capacity. Environ Sci Technol 45:1152–1157. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1030905
Comte S, Guibaud G, Baudu M (2006) Biosorption properties of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) resulting from activated sludge according to their type: soluble or bound. Process Biochem 41:815–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.10.014
Nanda PK, Krishna Rao K, Nayak PL (2007) Biodegradable polymers. XI. Spectral, thermal, morphological, and biodegradability properties of environment-friendly green plastics of soy protein modified with thiosemicarbazide. J Appl Polym Sci 103:3134–3142. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.24590
Naumann D (2000) Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry. Wiley, Chichester, pp 102–131
Saif FAAA, Sakr EAE (2020) Characterization and bioactivities of exopolysaccharide produced from probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum 47FE and Lactobacillus pentosus 68FE. Bioact Carbohydr Diet Fibre. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcdf.2020.100231
Guo H, Xie S, Deng H et al (2020) Electricity production and bacterial communities of microbial fuel cell supplied with oily sludge. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13409
Abbas SZ, Rafatullah M, Ismail N, Shakoori FR (2018) Electrochemistry and microbiology of microbial fuel cells treating marine sediments polluted with heavy metals. RSC Adv 8:18800–18813. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01711E
Chouler J, Bentley I, Vaz F et al (2017) Exploring the use of cost-effective membrane materials for Microbial Fuel Cell based sensors. Electrochim Acta 231:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.01.195
Lincy MJA, Kumar BA, Vasantha VS, Varalakshmi P (2015) Microbial fuel cells: a promising alternative energy source. Oppor Chall. https://doi.org/10.1201/b18718-6
Zafar Z, Ayaz K, Sharafat I et al (2018) Enrichment of electricigenic biofilm for synchronized generation of electric current and waste water treatment in microbial fuel cells. Int J Electrochem Sci 13:4424–4437
Angelaalincy MJ, Navanietha Krishnaraj R, Shakambari G et al (2018) Biofilm engineering approaches for improving the performance of microbial fuel cells and bioelectrochemical systems. Front Energy Res 6:63. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2018.00063
Chae K-J, Choi M-J, Lee J-W et al (2009) Effect of different substrates on the performance, bacterial diversity, and bacterial viability in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 100:3518–3525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.02.065
Richter H, Nevin KP, Jia H et al (2009) Cyclic voltammetry of biofilms of wild type and mutant Geobacter sulfurreducens on fuel cell anodes indicates possible roles of OmcB, OmcZ, type IV pili, and protons in extracellular electron transfer. Energy Environ Sci 2:506–516. https://doi.org/10.1039/B816647A
Nimje VR, Chen C-Y, Chen C-C et al (2009) Stable and high energy generation by a strain of Bacillus subtilis in a microbial fuel cell. J Power Sour 190:258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.01.019
Córdova-Bautista Y, Ramirez-Morales E, Perez-Hernandez B et al (2020) Electricity production and bioremediation from synthetic sugar industry wastewater by using microbial isolate in microbial fuel cell. Sugar Tech 22:820–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-020-00830-1
Rabaey K, Boon N, Hofte M, Verstraete W (2005) Microbial phenazine production enhances electron transfer in biofuel cells. Env Sci Technol 39:3401–3408. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048563o
Uria N, Ferrera I, Mas J (2017) Electrochemical performance and microbial community profiles in microbial fuel cells in relation to electron transfer mechanisms. BMC Microbiol 17(208):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-017-1115-2
Rabaey K, Boon N, Siciliano SD, Verhaege M, Vestraete W (2004) Biofuel cells select for microbial consortia that self-mediate electron transfer. Appl Env Microbiol 70:5373–5382. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.9.5373-5382.2004
Thatoi H, Das S, Mishra J et al (2014) Bacterial chromate reductase, a potential enzyme for bioremediation of hexavalent chromium: a review. J Environ Manage 146:383–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.07.014
Wang X, Yu P, Zeng C et al (2015) Enhanced denitrification rate of Alcaligenes faecalis with electrode as electron donor. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00683-15
Cournet A, Délia M-L, Bergel A et al (2010) Electrochemical reduction of oxygen catalyzed by a wide range of bacteria including Gram-positive. Electrochem commun 12:505–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2010.01.026
Majumder D, Maity JP, Tseng M-J et al (2014) Electricity generation and wastewater treatment of oil refinery in microbial fuel cells using Pseudomonas putida. Int J Mol Sci 15:16772–16786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150916772
Rosenbaum M, Aulenta F, Villano M, Angenent LT (2011) Cathodes as electron donors for microbial metabolism: which extracellular electron transfer mechanisms are involved? Bioresour Technol 102:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.07.008
Cristiani P, Franzetti A, Gandolfi I et al (2013) Bacterial DGGE fingerprints of biofilms on electrodes of membraneless microbial fuel cells. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 84:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.05.040
Vejarano F, Benitez-Campo N, Bravo E et al (2018) Electrochemical monitoring and microbial characterization of a domestic wastewater-fed microbial fuel cell inoculated with anaerobic sludge. Rev Ciencias 22:13–32
Kim IS, Chae K-J, Choi M-J, Verstraete W (2008) Microbial fuel cells: recent advances, bacterial communities and application beyond electricity generation. Environ Eng Res 13:51–65. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2008.13.2.051
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial support provided by the Public Administration of Environmental Projects—Applied research committee, Community Service and Environmental Development Sector, Ain shams university. The authors would like to thank the participants of the research theme from National Research Centre (NRC) for the fruitful discussions, research facilities, and their support.
Funding
The financial support provided by the Public Administration of Environmental Projects—Applied research committee, Community Service and Environmental Development Sector, Ain shams university.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EAES, DZK, KME-k conceived and designed the study ES and DK performed the experiments. All the authors wrote the original draft preparation, validation, reviewing, and editing, read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Yes.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakr, E.A.E., Khater, D.Z. & El-khatib, K.M. Anodic and cathodic biofilms coupled with electricity generation in single-chamber microbial fuel cell using activated sludge. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44, 2627–2643 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02632-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02632-5