Abstract
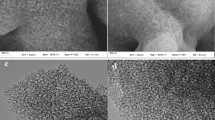
The novel Ni-NTA-functionalized magnetic chitosan microspheres (MCS-NTA-Ni) were prepared via amino functionalization of MCS with epichlorohydrin and ethylenediamine, followed by the introduction of the aldehyde groups and NTA in turn, and nickel (II) ions were chelated in the end. MCS-NTA-Ni contained numerous long-armed NTA-Ni surface groups, ensuring high enzyme loading and providing more space and flexibility to attach enzymes and maintain their activity. This microsphere can have highly selective adsorption of his-tagged recombinant protein. The his-tagged recombinant Microbacterium esterase of E. coli BL21 (DE3)/pET21a-EstSIT01 was first immobilized on MCS-NTA-Ni by affinity fixation, giving high immobilization yield (90.1%) and enzyme loading (120 mg/g). Compared with free esterase, the immobilized esterase was found to exhibit higher pH stability and thermal stability. In addition, the immobilized esterase had excellent reusability for the synthesis of key chiral intermediate of d-biotin and the substrate conversion could still keep 100% after 8 cycles continuously.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CS:
-
Chitosan
- ECH:
-
Epichlorohydrin
- NTA:
-
Nα, Nα-bis (carboxymethyl)-l-lysine
- MCS:
-
Magnetic chitosan microspheres
- MCS-ECH:
-
Magnetic chitosan microspheres functionalized by ECH
- MCS-NH2 :
-
Amino-functionalized magnetic chitosan microspheres
- MCS-CHO:
-
Aldehyde-functionalized magnetic chitosan microspheres
- MCS-NTA:
-
NTA-functionalized magnetic chitosan microspheres
- MCS-NTA-Ni:
-
Ni-NTA-functionalized magnetic chitosan microspheres
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer
- EDS:
-
Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Torresa S, Baigoría MD, Swathy SL, Pandey A, Castrocd GR (2009) Enzymatic synthesis of banana flavour (isoamyl acetate) by Bacillus licheniformis S-86 esterase. Food Res Int 42:454–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2008.12.005
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2009) Methods for detection and characterization of lipases: a comprehensive review. Biotechnol Adv 27(6):782–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.06.001
Ju X, Yu HL, Pan J, Xu JH (2012) Improved production of Pseudomonas sp. ECU1011 acetyl esterase by medium design and fed-batch fermentation. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0570-7
Kikugawa M, Tsuchiyama M, Kai K, Sakamoto T (2012) Synthesis of highly water-soluble feruloyl diglycerols by esterification of an Aspergillus niger feruloyl esterase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(3):615–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4056-6
Kremnicky L, Mastihuba V, Gregory LC (2004) Trichoderma reesei acetyl esterase catalyzes transesterification in water. J Mol Catal B: Enzym 30(5–6):229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2004.05.007
Panda T, Gowrishankar BS (2005) Production and applications of esterases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1840-y
Morlighem, Jean-Étienne RL, Radis-Baptista G (2019) The place for enzymes and biologically active peptides from marine organisms for application in industrial and pharmaceutical biotechnology. Curr Protein Pept Sci 20(4):334–355. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203719666180926121722
Sharifi M, Sohrabi MJ, Hosseinali SH, Kani PH, Falahati M (2020) Enzyme immobilization onto the nanomaterials: application in enzyme stability and prodrug-activated cancer therapy. Int J Biol Macromol 143:665–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.064
Kharrat N, Ali YB, Marzouk S, Gargouri YT, Karra-Châabouni M (2011) Immobilization of Rhizopus oryzae lipase on silica aerogels by adsorption: comparison with the free enzyme. Process Biochem 46:1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.01.029
Velasco-Lozano S, López-Gallego F, Vázquez-Duhalt R, Mateos-Díaz JC, Guisán JM, Favela-Torres E (2014) Carrier-free immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa with polyethyleneimines by carboxyl-activated cross-linking. Biomacromol 15(5):1896–1903. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm500333v
Yadav GD, Jadhav SR (2005) Synthesis of reusable lipases by immobilization on hexagonal mesoporous silica and encapsulation in calcium alginate: Transesterification in non-aqueous medium. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 86(1–3):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.07.018
Huang J, Zhao R, Wang H, Zhao W, Ding L (2010) Immobilization of glucose oxidase on Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol Lett 32:817–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0217-9
Liu J, Pang BQW, Adams JP, Snajdrova R, Li Z (2017) Coupled immobilized amine dehydrogenase and glucose dehydrogenase for asymmetric synthesis of amines by reductive amination with cofactor recycling. ChemCatChem 9:425–431. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201601446
Díaz-Hernández A, Jorge G, García-Almendárez BE, Carlos R, Aldo AR (2018) Characterization of magnetic nanoparticles coated with chitosan: a potential approach for enzyme immobilization. Nanomater 9468574:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9468574
Rahman MA, Culsum U, Kumar A, Gao H, Hu N (2016) Immobilization of a novel cold active esterase onto Fe3O4∼cellulose nano-composite enhances catalytic properties. Int J Biol Macromol 87:488–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.016
Wu Y, Wang Y, Luo G, Dai Y (2009) In situ preparation of magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles for lipase immobilization by cross-linking and oxidation in aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 100:3459–3464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.02.018
Wood HG, Barden RE (1977) Biotin enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 46:385–413. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002125
Zheng JY, Wang SF, Zhang YJ (2013) Chemoenzymatic synthesis of d-biotin intermediate lactone via lipase-catalyzed desymmetrization of meso diols. J Mol Catal B Enzym 98:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2013.09.014
Choi C, Tian SK, Deng L (2001) A formal catalytic asymmetric synthesis of (+)-biotin with modified cinchona alkaloids. Synthesis 11:1737–1741. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-16748
Chen FE, Dai HF, Kuang YY (2003) Synthetic studies on d-biotin. Part 7: † a practical asymmetric total synthesis of d-biotin via enantioselective reduction of meso-cyclic imide catalyzed by oxazborolidine. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 14:3667–3672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetasy.2003.08.034
Chen FE, Chen XX, Dai HF (2005) Synthetic studies on d-Biotin, Part 8:[1] An Efficient chemoenzymatic approach to the asymmetric total synthesis of d-Biotin via a polymer-supported PLE-mediated desymmetrization of mesosymmetic dicarboxylic esters. Adv Synth Catal 347:549–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.200404311
Xu Y, Wu FH, Chen JB, Zhou YR, Wu XM, Yao YL, Wang DL, Zhu T (2010) Microbacterium chocolatum SIT101 and its application as biocatalyst in preparing (4S, 5R)-half ester. CN102120977A
Melnyk IV, Gdula K, Dabrowski A, Zub YL (2016) Magneto-sensitive adsorbents modified by functional nitrogen-containing groups. Nanoscale Res Lett 11(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1273-4
Zhao H, Heindel ND (1991) Determination of degree of substitution of formyl groups in polyaldehyde dextran by the hydroxylamine hydrochloride method. Pharm Res 8:400–402. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015866104055
Hou C, Wang Y, Zhu H, Wei H (2016) Construction of enzyme immobilization system through metal-polyphenol assisted Fe3O4/chitosan hybrid microcapsules. Chem Eng J 283:397–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.07.067
Zhao X, Shi Y, Cai Y, Mou S (2008) Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-coated magnetic nanoparticles for the preconcentration of phenolic compounds from environmental water samples. Environ Sci Technol 42(4):1201–1206. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071817w
Zou X, Li K, Zhao Y, Zhang Yu, Li B, Song C (2013) Ferroferric oxide/l-cysteine magnetic nanospheres for capturing histidine-tagged proteins. J Mater Chem B 1(38):5108–5113. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb20726a
Vahidi AK, Yang Y, Ngo TPN, Li Z (2015) Simple and efficient immobilization of extracellular his-tagged enzyme directly from cell culture supernatant as active and recyclable nanobiocatalyst: high-performance production of biodiesel from waste grease. ACS Catal 5:3157–3161. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b00550
Zheng YH, Liu J, Ma YZ, Xu Y, Xu F, Hua TC (2012) Temperature effects on enzyme activity of chicken liver esterase used in calorimetric biosensor. Artif Cell Blood Sub Biotechnol 40:125–131. https://doi.org/10.3109/10731199.2011.611470
Li R, Jiang L, Ye L, Lu J, Yu H (2014) Oriented covalent immobilization of esterase BioH on hydrophilic-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 61:603–610. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1211
Bayramoglu G, Arica MY (2014) Immobilization of Mucor miehei esterase on core-shell magnetic beads via adsorption and covalent binding: application in esters synthesis. Fiber Polym 15:2051–2060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-2051-5
Driss D, Haddar A, Ghorbel R, Chaabouni SE (2014) Production of xylooligosaccharides by immobilized his-tagged recombinant xylanase from Penicillium occitanis on nickel-chelate Eupergit C. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 5:274–279. https://doi.org/10.4161/bioe.29596
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (No. 13430503400), the Science Foundation of Shanghai Institute of Technology (YJ2010-04), the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry (No. ZX2012-05), Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. 11YZ227), and the Science Foundation of Shanghai Institute of Technology (ZQ2018-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Wu, X., Ma, B. et al. High specific immobilization of His-tagged recombinant Microbacterium esterase by Ni-NTA magnetic chitosan microspheres for efficient synthesis of key chiral intermediate of d-biotin. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44, 2193–2204 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02595-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02595-7