Abstract
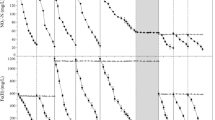
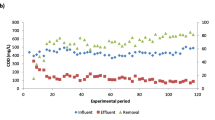
This study investigates the impacts of influent ammonium concentrations on the microbial community in immobilized heterotrophic ammonium removal system. Klebsiella sp. FC61, the immobilized species, has the ability to perform simultaneous ammonium removal and Fe3+ reduction. It was found that average ammonium removal rate decreased from 0.308 to 0.157 mg/L/h, as the influent NH4 +-N was reduced from 20 to 10 mg/L. Meanwhile, at a total Fe3+ concentration of 20 mg/L, the average Fe3+ reduction removal efficiency and rate decreased from 44.61% and 0.18 mg/L/h, to 27.10% and 0.11 mg/L/h, respectively. High-throughput sequencing was used to observe microbial communities in bioreactor Samples B1, B2, and B3, after exposure to different influent NH4 +-N conditions. Results show that higher influent NH4 +-N concentrations increased microbial richness and diversity and that Klebsiella sp. FC61 play a functional role in the simultaneous removal of NH4 +-N and Fe3+ reduction in bioreactor systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boon N, De Gelder L, Lievens H, Siciliano SD, Top EM, Verstraete W (2002) Bioaugmenting bioreactors for the continuous removal of 3-chloroaniline by a slow release approach. Environ Sci Technol 36:4698–4704
Chen D, Wang HY, Ji B, Yang K, Wei L, Jiang Y (2015) A high-throughput sequencing study of bacterial communities in anautohydrogenotrophic denitrifying bio-ceramsite reactor. Process Biochem 50:1904–1910
Cheng Z, Hu X, Sun ZR (2016) Microbial community distribution and dominant bacterial species analysis in the bio-electrochemical system treating low concentration cefuroxime. Chem Eng J 303:137–144
El-Latif Hesham A, Qi R, Yang M (2011) Comparison of bacterial community structures in two systems of a sewage treatment plant using PCR-DGGE analysis. J Environ Sci 23(12):2049–2054
Fykse EM, Aarskaug T, Madslien EH, Dybwad M (2016) Microbial community structure in a full-scale anaerobic treatment plant during start-up and first year of operation revealed by high-throughput 16s rrna gene amplicon sequencing. Bioresour Technol 222:380–387
Hao T, Wei L, Lu H, Chui HK, Mackey HR, Loosdrecht MCM, Chen GH (2013) Characterization of sulfate-reducing granular sludge in the SANI process. Water Res 47:7042–7052
Hao X, Wang Q, Zhang X, Cao Y, Mark Loosdrecht CMV (2009) Experimental evaluation of decrease in bacterial activity due to cell death and activity decayin activated sludge. Water Res 43:3604–3612
Huang G, Liu F, Yang Y, Deng W, Li S, Huang Y, Kong X (2015) Removal of ammonium-nitrogen from groundwater using a fully passive permeable reactive barrier with oxygen-releasing compound and clinoptilolite. J Environ Manag 154:1–7
Huang S, Jaffe PR (2015) Characterization of incubation experiments and development of an enrichment culture capable of ammonium oxidation under iron reducing conditions. Biogeosciences 12:769–779
Jin D, Wang P, Bai Z, Wang X, Peng H, Qi R, Yu Z, Zhuang G (2011) Analysis of bacterial community in bulking sludge using culture-dependent and -independent approaches. J Environ Sci China 23(11):1880–1887
Lee OO, Wang Y, Yang J, Lafi FF, Al-Suwailem A, Qian P (2010) Pyrosequencingreveals highly diverse and species-specific microbial communities in sponges from the Red Sea. ISME J 5:650–664
Lovley DR, Holmes DE, Kelly PN (2004) Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Microb Physiol 49:119–186
Lv X, Jiang G, Xue X, Wu D, Sheng T, Sun C, Xu X (2013) Fe0-Fe3O4 nanocomposites embedded polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate beads for chromium (VI) removal. J Hazard Mater 262:748–758
Ma Z, Wen X, Zhao F, Xia Y, Huang X, Waite D, Guan J (2013) Effect of temperature variation on membrane fouling and microbial community structure in membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 133:462–468
Mulla SI, Talwar MP, Bagewadi ZK, Hoskeri RS, Ninnekar HZ (2013) Enhanced degradation of 2-nitrotoluene by immobilized cells of Micrococcus sp. strain SMN-1. Chemosphere 90:1920–1924
Okoniewska E, Lach J, Kacprzak M, Neczaj E (2007) The removal of manganese, iron and ammonium nitrogen on impregnated activated carbon. Desalination 206:251–258
Scala DJ, Hacherl EL, Cowan R, Young LY, Kosson DS (2006) Characterization of Fe(III)-reducing enrichment cultures and isolation of Fe(III)-reducing bacteria from the Savannah River site, South Carol. Microbiology 157:772–783
Schloss PD, Gevers D, Westcott SL (2011) Reducing the effects of PCR amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies. PLoS One 6(12):e0027310
Shelobolina ES, Nevin KP, Blakeney-hayward JD (2007) Geobacter pickeringii sp. nov., Geobacter argillaceus sp. nov. and Pelosinus fermentans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from subsurface kaolin lenses. Syst Evol Microbiol 57:126–162
Shrestha J, Rich JJ, Ehrenfeld JG, Jaffe PR (2009) Oxidation of ammonium to nitrite under iron-reducing conditions in wetland soils: laboratory, field demonstrations, and push–pull rate determination. Soil Sci 174(3):156–164
Su JF, Cheng C, Huang TL, Ma F, Lu JS, Shao SC (2016) Novel simultaneous Fe(III) reduction and ammonium oxidation of sp. FC61 under the anaerobic conditions. Rsc Adv 6(15):12584–12591
Su JF, Cheng C, Ma F (2016) Comparison of the NH4 +-N removal ability by Klebsiella sp. FC61 in a bacterial suspension system and a bacterial immobilization system. Sep Purif Technol 66:106–114
Wang J, Li Q, Qi R, Tandoi V, Yang M (2014) Sludge bulking impact on relevant bacterial populations in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant. Process Biochem 49(12):2258–2265
Weon SY, Lee CW, Lee SI, Koopman B (2002) Nitrite inhibition of aerobic growth of Acinetobacter sp. Water Res 36(18):4471–4476
Wilkinson L, Friendly M (2009) The history of the cluster heat map. Am Stat 63:179–184
Yang WH, Weber KA, Silver WL (2012) Nitrogen loss from soil through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction. Nat Geosci 5(8):538–541
Ye L, Zhang T (2013) Bacterial communities in different sections of a municipal wastewater treatment plant revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(6):2681–2690
Zhang T, Shao MF, Ye L (2012) 454 Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial diversity of activated sludge from 14 sewage treatment plants. ISME J 6(6):1137–1147
Zhang Y, Tian Z, Liu MM, Shi ZJ, Hale L, Zhou JZ, Yang M (2015) High concentrations of the antibiotic spiramycin in wastewater lead to high abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in nitrifying populations. Environ Sci Technol 49:9124–9132
Zhou S, Huang T, Ngo HH, Zhang H, Fei L, Zeng M (2016) Nitrogen removal characteristics of indigenous aerobic denitrifiers and changes in the microbial community of a reservoir enclosure system via in situ oxygen enhancement using water lifting and aeration technology. Bioresour Technol 214:63–73
Acknowledgements
This research work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 51678471), the National Key Research and Development Project (No. 2016YFC0200706), and the Science and technology overall Plan of Shaanxi Province under Grant (No. 2016KTCG01-17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, J.f., Lian, T.t., Huang, T.l. et al. Microbial community analysis of simultaneous ammonium removal and Fe3+ reduction at different influent ammonium concentrations. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40, 1555–1563 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1811-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1811-1