Abstract
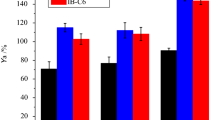
It is known that lipases may have their catalytic properties improved by the action of some salts or by the adsorption on hydrophobic supports. However, what we present in this work is more than that: we evaluate the combination of these two factors of hyperactivation of lipases from Acremonium-like ROG 2.1.9, a study that has not been done so far. This work proves that a synergistic effect occurs when the lipases are immobilized on hydrophobic supports at the presence of sodium chloride and are applied in triacylglycerol hydrolysis. This assay made it possible to achieve the highest hyperactivation of 500 % with the lipases immobilized on Phenyl-Sepharose and applied with 0.1 M of sodium chloride. Besides this positive effect on enzyme activity, the use of these two factors led to the thermal stability increasing of the immobilized lipases. For this derivative, the recovered activity was approximately 85 % after 6 h incubated at 55 °C and 1.0 M of the sodium chloride against 50 % of the same derivative without this salt. Furthermore, others assays were performed to prove the evidences about the synergistic effect, showing a promising method to improve the catalytic properties of the lipases from Acremonium-like ROG 2.1.9.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta S, Ingole P, Singh K, Bhattacharya A (2012) Comparative study of the hydrolysis of different oils by lipase-immobilized membranes. J Appl Polym Sci 124:17–26
Chen GJ, Kuo CH, Chen CI, Yu CC, Shieh CJ, Liu YC (2012) Effect of membranes with various hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties on lipase immobilized activity and stability. J Biosci Bioeng 113:166–172
Pérez D, Martín S, Fernández-Lorente G, Felice M, Guisán JM, Ventosa A, García MT, Mellado E (2011) A novel halophilic lipase, LipBL, showing high efficiency in the production of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). PLoS One 6:1–11
Secundo F, Correa G, Tarabiono C, Gatti-Lafranconi P, Brocca S, Lotti M, Jaeger KE, Puls M, Eggert T (2006) The lid is a structural and functional determinant of lipase activity and selectivity. J Mol Catal B Enzym 39:166–170
Quilles JCJ, Brito RR, Borges JP, Aragon CC, Fernandez-Lorente G, Bocchni-Martins DA, Gomes E, da Silva R, Boscolo M, Guisán JM (2015) Modulation of the activity and selectivity of the immobilized lipases by surfactants and solvents. Biochem Eng J 93:274–280
Mateo C, Palomo JM, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2007) Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1453–1463
Manol EA, Santos JCS, Freire DMC, Rueda N, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2015) Immobilization of lipases on hydrophobic supports involves the open form of the enzyme. Enzyme Microb Technol 71:53–57
Siodmiak T, Mangelings D, Heyden YV, Borowska MZ, Marszall MP (2015) High enantioselective novozym 435-catalyzed esterification of (R, S)-flurbiprofen monitored with a chiral stationary phase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:2769–2785
Ashajari M, Mohammadi M, Badri R (2015) Chemical amination of Rhiopus oryzae lipase for multipoint covalent immobilization on epoxy-functionalized supports: modulation of stability and selectivity. J Mol Catal B Enzym 115:128–134
Tavano OL, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Goulart AJ, Monti R (2013) Optimization of the immobilization of sweet potato amylase using glutaraldehyde-agarose support. Characterization of the immobilized enzyme. Process Biochem 48:1054–1058
Sheldon RA (2007) Enzyme Immobilization: the quest for optimum performance. Adv Synth Catal 349:1289–1307
Romero O, Ribero CW, Guisan JM, Palomo JM (2013) Novel enzyme-polymer conjugates for biotechnological applications. Peer J 27:1–17
Fernandez-Lafuente R, Armisen P, Sabuquillo P, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM (1998) Immobilization of lipases by selective adsorption on hydrophobic supports. Chem Phys Lipids 93:185–197
Kurtovic I, Marshall SN, Zhao X (2011) Hydrophobic immobilization of a bile salt activated lipase from Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). J Mol Catal B Enzym 72:168–174
Zivkovic LTI, Zivkovi LS, Balic BM, Kokunesoski MJ, Jokic BM, Karadzic IM (2015) Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase by adsorption onto biosafe meso/macroporous silica zirconia. Biochem Eng J 93:73–83
Coteron A, Martinez M, Aracil J (1998) Reactions of olive oil and glycerol over immobilized lipases. J Am Oil Chem Soc 75:657–660
Arab-Tehrany E, Jacquot M, Gaiani C, Imran M, Desobry S, Linder M (2012) Beneficial effects and oxidative stability of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Trends Food Sci Technol 25:24–33
Mendes AA, Castro HF, Rodrigues DS, Adriano WS, Tardiolli PW, Mammarella EJ, Giordano RC, Giordano RLC (2011) Multipoint covalent immobilization of lipase on chitosan hybrid hydrogels: influence of the polyelectrolyte complex type and chemical modification on the catalytic properties of the biocatalysts. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:1055–1066
Rooney D, Weatherley LR (2001) The effect of reaction conditions upon lipase catalysed hydrolysis of high oleate sunflower oil in a stirred liquid–liquid reactor. Process Biochem 2001(36):947–953
Santos KC, Cassimiro DMJ, Avelar MHM, Hirata DB, Castro HF, Fernández-Lafuente R, Mendes AA (2013) Characterization of the catalytic properties of lipases from plant seeds for the production of concentrated fatty acids from different vegetable oils. Ind Crops Prod 49:462–470
Palomo JM, Segura RL, Fernández-Lorente G, Fernández-Lafuente R, Guisán JM (2007) Glutaraldehyde modification of lipases adsorbed on aminated supports: a simple way to improve their behaviour as enantioselective biocatalyst. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:704–707
Wei HN, Wu B (2008) Screening and immobilization Burkholderia sp. GXU56 lipase for enantioselective resolution of (R, S)-methyl mandelate. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 149:79–88
Kaewprapan K, Wongkongkatep J, Panbangred W, Phinyocheep P, Marie E, Durand A, Inprakhon P (2011) Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of hydrophobically modified dextrans: activity and regioselectivity of lipase from Candida rugose. J Biosci Bioeng 112:124–129
Matsumae H, Furui M, Shibatani T, Tosa T (1994) Production of optically active 3-phenylglucidic acid ester by the lipase from Serratia marcescens on a hollow-fiber membrane reactor. J Ferment Bioeng 78:59–63
Jegannathan KR, Jun-Yee L, Chan ES, Ravindra P (2009) Design an immobilized lipase enzyme of biodiesel production. J Renew Sustain Energy 1:1–8
Li X, He XY, Li LZ, Wang YD, Wang CY, Shi H, Wang F (2012) Enzymatic production of biodiesel from Pistacia chinensis bge seed oil using immobilized lipase. Fuel 92:89–93
Lu J, Deng L, Nie K, Wang F, Tan T (2012) Stability of immobilized Candida sp. 99–125 lipase for biodiesel production. Chem Eng Technol 35:2120–2124
Azócar L, Ciudad G, Heipieper HJ, Muñoz R, Navia R (2011) Lipase-catalyzed process in an anhydrous medium with enzyme reutilization to produce biodiesel with low acid value. J Biosci Bioeng 112:583–589
Hama S, Tamalampudi S, Fukumizu T, Miura K, Yamaji H, Kondo A, Fukuda A (2008) Lipase localization in Rhizopus oryzae cells immobilized within biomass support particles for use as whole-cell biocatalyst in biodiesel-fuel production. J Biosci Bioeng 101:328–333
Wang A, Liu M, Wang H, Zhou C, Du Z, Zhu S, Shen S, Ouyang P (2008) Improving enzyme immobilization in mesocellular siliceous foams by microwave irradiation. J Biosci Bioeng 106:286–291
Trivedi A, Heinemann M, Spiess AC, Daussmann T, Buchs J (2005) Optimization of adsorptive immobilization of alcohol dehydrogenases. J Biosci Bioeng 99:340–347
Jun C, Jeon BW, Joo JC, Lee QAT, Gu SA, Byun S, Cho DH, Kim D, Sang BI, Kim YH (2013) Thermostabilization of Candida antarctica lipase B by double immobilization: adsorption on a macroporous polyacrylate carrier and R1 silaffin-mediated biosilicification. Process Biochem 48:1181–1187
Cui C, Tao Y, Ge C, Zhen Y, Chen B, Tan T (2015) Synergistic effects of amine and protein modified epoxy-support on immobilized lipase activity. Colloids Surf B 133:51–57
Vasconcellos A, Paula AS, Luizon RAF, Farias LA, Gomes E, Aranda DAG, Nery JG (2012) Synergistic effect in the catalytic activity of lipase Rhizomucor miehei immobilized on zeolites for the production of biodiesel. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 163:343–355
Ibrahim NA, Guo Z, Xu X (2008) Enzymatic interesterification of palme stearin and coconut oil by a dual lipase system. J Am Oil Chem Soc 85:37–45
Cherif S, Mnif S, Hadrich F, Adbelkafi S, Sayadi S (2008) A newly high alkaline lipase: an ideal choice for application in detergent formulations. Lipids Health Dis 10:1–8
Fernandez-Lorente G, Palomo JM, Cocca J, Mateo C, Moro P, Terreni M, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Guisan JM (2003) Regio-selective deprotection of peracetylated sugars via lipase hydrolysis. Tetrahedron 59:5705–5711
Fernández-Lorente G, Betancor L, Carrascosa AV, Palomo JM, Guisán JM (2012) Release of omega-3 fatty acids by the hydrolysis of fish oil catalyzed by lipases immobilized on hydrophobic supports. J Am Oil Chem Soc 89:97–102
Galvis M, Barbosa O, Ruiz M, Cruz J, Ortiz C, Torres R, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2012) Chemical amination of lipase B from Candida antarctica is an efficient solution for the preparation of crosslinked enzyme aggregates. Process Biochem 47:2373–2378
Brabcová J, Demianová Z, Vondrasek J, Jágr M, Zarevúcka M, Palomo JM (2013) Highly selective purification of three lipases from Geotrichum candidum 4013 and their characterization and biotechnological applications. J Mol Catal B Enzym 98:62–72
Abreu L, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Rodrigues RC, Volpato G, Ayub MAZ (2014) Efficient purification-immobilization of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Staphylococcus warneri EX17 on porous styrene-divinylbenzene beads. J Mol Catal B Enzym 99:51–55
Barbosa O, Torres R, Ortiz C, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2012) The slow-down of the CALB immobilization rate permits to control the inter and intra molecular modification produced by glurataldehyde. Process Biochem 47:766–774
Ferrarezi AL, Pivetta DH, Bonilla-Rodriguez GO, Silva R, Guisán JM, Gomes E, Pessela BC (2013) Partial purification, immobilization and preliminary biochemical characterization of lipases from Rhizomucor pusillus. Adv Enzyme Res 1:79–90
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 277:680–685
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial support from São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), Grants 2012/09054-3 and 2013/00530-0 and to Dr. André Rodrigues, expert systematics of fungi and researcher at the State University of São Paulo (UNESP, Rio Claro, SP, Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quilles Junior, J.C., Ferrarezi, A.L., Borges, J.P. et al. Hydrophobic adsorption in ionic medium improves the catalytic properties of lipases applied in the triacylglycerol hydrolysis by synergism. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39, 1933–1943 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1667-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1667-9