Abstract
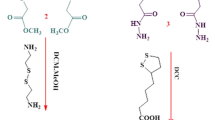
Sol–gel encapsulation is a simple but powerful method to enhance the enantioselectivity of lipase-catalyzed transformations in an isooctane/aqueous buffer solution. Candida rugosa lipase was encapsulated according to a sol–gel procedure in the presence and absence of calix[4]arene hydrazine or carboxylic acid derivatives with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as an additive. The activity of the encapsulated lipases was evaluated for the enantioselective hydrolysis of racemic Naproxen methyl ester and the hydrolysis of p-Nitrophenylpalmitate. The results indicate that the encapsulated lipase without calix[4]arene derivative has lower conversion and enantioselectivity compared to the encapsulated lipase with calix[4]arene derivative. It was found that the calix[4]arene hydrazine and carboxylic acid-based encapsulated lipases have excellent activity and enantioselectivity (E >300) compared to encapsulated lipase without the calix[4]arene derivatives.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheldon RA, Van Pelt S (2013) Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: why, what and how. Chem Soc Rev 42:6223–6235
Hanefeld U, Gardossi L, Magner E (2009) Understanding enzyme immobilisation. Chem Soc Rev 38:453–468
Uyanik A, Sen N, Yilmaz M (2011) Improvement of catalytic activity of lipase from Candida rugosa via sol–gel encapsulation in the presence of calix(aza) crown. Bioresour Technol 102:499–506
Zhong X, Qian J, Guo H, Hu Y, Liu M (2014) Biosynthesis of sucrose-6-acetate catalyzed by surfactant-coated Candida rugosa lipase immobilized on sol–gel supports. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37:813–818
Ueji S, Taniguchi T, Okamoto T, Watanebe K, Ebara Y, Ohta H (2003) Flexibility of lipase brought about by solvent effects controls its enantioselectivity in organic media. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 76:399–403
Mateo C, Palomo JM, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2007) Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1451–1463
Okamoto T, Yasuhito E, Ueji S (2006) Metal ions dramatically enhance the enantioselectivity for lipase-catalysed reactions in organic solvents. Org Biomol Chem 4:1147–1153
Liu YY, Xu JH, Hu Y (2000) Enhancing effect of Tween-80 on lipase performance in enantioselective hydrolysis of ketoprofen ester. J Mol Catal B Enzym 10:523–529
Theil F (2000) Enhancement of Selectivity and Reactivity of Lipases by Additives. Tetrahedron 56:2905–2919
Ozyilmaz E, Sayin S (2013) A magnetically separable biocatalyst for resolution of racemic naproxen methyl ester. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:1803–1806
Reetz MT, Tielmann P, Wisenhofer W, Konen W, Zonta A (2003) Second Generation sol–gel encapsulated lipases: robust heterogeneous biocatalysts. Adv Synth Catal 345:717–728
Sahin O, Erdemir S, Uyanik A, Yilmaz M (2009) Enantioselective hydrolysis of (R/S)-Naproxen methyl ester with sol–gel encapsulated lipase in presence of calix[n]arene derivatives. Appl Catal A Gen 369:36–41
Wenz G (1994) Cyclodextrins as building blocks for supramolecular structures and functional units. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 33:803–822
Itoh T, Takagi Y, Murakami T, Hiyama Y, Tsukube H (1996) Crown ethers as regulators of enzymatic reactions: enhanced reaction rate and enantioselectivity in lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of 2-cyano-1-methylethyl acetate. J Org Chem 61:2158–2163
Yilmaz M, Erdemir S (2013) Calixarene-based receptors for molecular recognition. Turk J Chem 37:558–585
Ozyilmaz E, Sayin S (2013) Preparation of new calix[4]arene-immobilized biopolymers for enhancing catalytic properties of Candida rugosa Lipase by Sol–Gel Encapsulation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:1871–1884
Yilmaz E, Sezgin M (2012) Enhancement of the activity and enantioselectivity of lipase by sol-gel encapsulation immobilization onto β-cyclodextrin-based polymer. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:1927–1940
Reinhoudt DN, Eendebak AM, Nijenhuis WF, Verboom W, Kloosterman M, Schoemaker HE (1989) The effect of crown ethers on enzyme catalysed reactions in organic solvents. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 7:399–400
Kapoor M, Gupta MN (2012) Lipase promiscuity and its biochemical applications. Process Biochem 47:555–569
Yilmaz E, Sezgin M, Yilmaz M (2010) Enantioselective hydrolysis of racemic naproxen methyl ester with sol–gel encapsulated lipase in the presence of sporopollenin. J Mol Catal B Enzym 62:162–168
Oshima T, Sato M, Shikaze Y, Ohto K, Inoue K, Baba Y (2007) Enzymatic polymerization of o-phenylenediamine with cytochrome c activated by a calixarene derivative in organic media. Biochem Eng J 35:66–70
Sayin S, Yilmaz E, Yilmaz M (2011) Improvement of catalytic properties of Candida rugosa lipase by sol–gel encapsulation in the presence of magnetic calix[4]arene nanoparticles. Org Biomol Chem 9:4021–4024
Akoz E, Akbulut OY, Yilmaz M (2014) Calix[n]arene carboxylic acid derivatives as regulators of enzymatic reactions: enhanced enantioselectivity in lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of (R/S)-naproxen methyl ester. Appl Biochem Biotech 172:509–523
Wu JY, Liu SW (2000) Influence of alcohol concentration on lipase catalyzed enantioselective esterification of racemic Naproxen in isooctane: under controlled water activity. Enzym Microbiol Technol 26:124–130
Arneud-Neu F, Collins EM, Deasy M, Ferguson G, Harris SJ, Kaitner B, Lough AJ, McKervey MA, Marques E, Ruhl BL, Weill MJS, Seward EM (1989) Synthesis, X-ray crystal structures, and cation-binding properties of alkyl calixaryl esters and ketones, a new family of macrocyclic molecular receptors. J Am Chem Soc 111:8681–8691
Alekseeva EA, Bacherikov VA, Gren AI, Mazepa AV, Gorbatyuk VY, Krasnoshchekaya SP (2000) Synthesis of N-Substituted Carbamoylmethyloxy-p-tert-butylcalix[4]arenes. Russ J Org Chem 36:1321–1325
Bitter l, Grün A, Toth G, Balazs B, Horvath G, Toke L (1998) Studies on calix(aza)crowns, II. Synthesis of novel proximal doubly bridged calix[4]arenes by intramolecular ring closure of syn 1,3-and 1,2-ω-chloroalkylamides. Tetrahedron 54:3857–3870
Chiou SH, Wu WT (2004) Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase on chitosan with activation of the hydroxyl groups. Biomaterials 25:197–204
Akceylan E, Sahin O, Yilmaz M (2014) Improvement of catalytic activity of lipase in the presence of wide rim substituted calix[4]arene carboxylic acid-grafted magnetic nanoparticles. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 79:113–123
Bradford MMA (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen CS, Fujimoto Y, Girdaukas G, Sih CJ (1982) Quantitative analyses of biochemical kinetic resolutions of enantiomers. J Am Chem Soc 104:7294–7299
Puthli MS, Rathod VK, Pandit AB (2006) Enzymatic hydrolysis of castor oil: process intensification studies. Biochem Eng J 31:31–41
Faber K, Ottolina G, Riva S (1993) Selectivity-Enhancement of Hydrolase Reactions. Biocatalysis 8:91–132
Rubin B, Jamison P, Harrison D (1991) Crystallization and characterization of Candida rugosa lipase. In: Alberghina L, Schmid RD, Verger R (eds) Lipases: Structure, Mechanism and Genetic Engineering, GBF Monographs, vol 16. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbll, Weinheim, pp 63–66
Grochulski P, Li Y, Schrag JD, Cygler M (1994) Two conformational states of Candida rugosa lipase. Protein Sci 3:82–91
Colton IJ, Sharmin NA, Kazlauskas RJ (1995) A 2-propanol treatment increases the enantioselectivity of Candida rugosa lipase toward esters of chiral carboxylic acids. J Org Chem 60:212–217
Fernandez-Lorente G, Terreni M, Mateo C, Bastida A, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Dalmases P (2012) Modulation of lipase properties in macroaqueous system by controlled enzyme immobilization: enantioselective hydrolysis of a chiral ester by immobilized Pseudomonas lipase. Enzyme Microb Technol 8:389–396
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK Grant Number 111T027) and the CMST COST Action No: CM1005 and the Research Foundation of Selcuk University (BAP) for financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akoz, E., Sayin, S., Kaplan, S. et al. Improvement of catalytic activity of lipase in the presence of calix[4]arene valeric acid or hydrazine derivative. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38, 595–604 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1299-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1299-x