Abstract
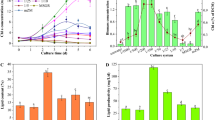
Microalgae hold great promise as a source of biofuels and biochemicals. The main obstacles to their industrial application are the high cultivation and downstream costs related to media and harvesting. In the work, we explored the multiple potentials of seawater to address key issues relating to the cultivation of Scenedesmus obliquus. Seawater can sufficiently replace some of the key elements in BG11 medium such as MgSO4, CaCl2, and NaCO3, and its use can significantly reduce the quantity of water required for the preparation of culture media. Among our results, the total chlorophyll content in cells grown in modified BG11 using 10 % (v/v) seawater was increased 1.47-fold without sacrificing biomass or lipid production. More than 70 % of the total algal biomass was auto-flocculated within one hour when cells were grown in seawater-supplemented media, which compares very favorably with a yield of only 3 % from cells grown in BG11.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong DD, Anh HTL, Thu NTH (2011) Study on biological characteristics of heterotrophic marine microalga—Schizochytrium mangrovei PQ6 isolated from Phu Quoc Island, Kien Giang province. Vietnam J Phycol 47:944–954
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306
Chinnasamy S, Bhatnagar A, Hunt RW, Das K (2010) Microalgae cultivation in a wastewater dominated by carpet mill effluents for biofuel applications. Bioresour Technol 101:3097–3105
Singh A, Nigam PS, Murphy JD (2011) Renewable fuels from algae: an answer to debatable land based fuels. Bioresour Technol 102:10–16
IWMI (2008) Water implications of biofuel crops: understanding tradeoffs and identifying options. Water Policy Brief
Jung J-Y, Kim S, Lee H, Kim K, Kim W, Park MS, Kwon J-H, Yang J-W (2014) Use of extracts from oyster shell and soil for cultivation of Spirulina maxima. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. doi:10.1007/s004490141216
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev 14:217–232
Beach ES, Eckelman MJ, Cui Z, Brentner L, Zimmerman JB (2012) Preferential technological and life cycle environmental performance of chitosan flocculation for harvesting of the green algae Neochloris oleoabundans. Bioresour Technol 121:445–449
Sander K, Murthy GS (2010) Life cycle analysis of algae biodiesel. Int J Life Cycle Assess 15:704–714
Ahmad A, Mat Yasin N, Derek C, Lim J (2012) Crossflow microfiltration of microalgae biomass for biofuel production. Desalination 302:65–70
Zhang X, Hu Q, Sommerfeld M, Puruhito E, Chen Y (2010) Harvesting algal biomass for biofuels using ultrafiltration membranes. Bioresour Technol 101:5297–5304
Salim S, Bosma R, Vermuë MH, Wijffels RH (2011) Harvesting of microalgae by bio-flocculation. J Appl Phycol 23:849–855
Sukenik A, Shelef G (1984) Algal autoflocculation-verification and proposed mechanism. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:142–147
Vandamme D, Foubert I, Muylaert K (2013) Flocculation as a low-cost method for harvesting microalgae for bulk biomass production. Trends Biotechnol 31:233–239
Vandamme D, Foubert I, Fraeye I, Meesschaert B, Muylaert K (2012) Flocculation of Chlorella vulgaris induced by high pH: role of magnesium and calcium and practical implications. Bioresour Technol 105:114–119
Chen C-Y, Chang J-S, Chang H-Y, Chen T-Y, Wu J-H, Lee W-L (2013) Enhancing microalgal oil/lipid production from Chlorella sorokiniana CY1 using deep-sea water supplemented cultivation medium. Biochem Eng J 77:74–81
Moran R (1982) Formulae for determination of chlorophyllous pigments extracted with N,N-dimethylformamide. Plant Physiol 69:1376–1381
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley G (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Salim S, Kosterink N, Wacka N, Vermuë M, Wijffels R (2014) Mechanism behind autoflocculation of unicellular green microalgae Ettlia texensis. J Biotechnol 174:34–38
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Pt Rebers, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Guo S-L, Zhao X-Q, Wan C, Huang Z-Y, Yang Y-L, Asraful Alam M, Ho S-H, Bai F-W, Chang J-S (2013) Characterization of flocculating agent from the self-flocculating microalga Scenedesmus obliquus AS-6-1 for efficient biomass harvest. Bioresour Technol 145:285–289
Millero FJ, Feistel R, Wright DG, McDougall TJ (2008) The composition of standard seawater and the definition of the reference-composition salinity scale. Deep Sea Res 55:50–72
Demetriou G, Neonaki C, Navakoudis E, Kotzabasis K (2007) Salt stress impact on the molecular structure and function of the photosynthetic apparatus-the protective role of polyamines. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1767:272–280
Murata N, Takahashi S, Nishiyama Y, Allakhverdiev SI (2007) Photoinhibition of photosystem II under environmental stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1767:414–421
Von Wettstein D, Gough S, Kannangara CG (1995) Chlorophyll biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7:1039
Fodorpataki L, Bartha C (2004) Salt stress tolerance of a freshwater green alga under different photon flux densities. Sludia Universities Babes-Bolyai Biologia 49:85–93
Kaewkannetra P, Enmak P, Chiu T (2012) The effect of CO2 and salinity on the cultivation of Scenedesmus obliquus for biodiesel production. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 17:591–597
Takagi M, Yoshida T (2006) Effect of salt concentration on intracellular accumulation of lipids and triacylglyceride in marine microalgae Dunaliella cells. J Biosci Bioeng 101:223–226
Fujii S, Uenaka M, Nakayama S, Yamamoto R, Mantani S (2001) Effects of sodium chloride on the fatty acids composition in Boekelovia hooglandii (Ochromonadales, Chrysophyceae). Phycol Res 49:73–77
Spilling K, Seppälä J, Tamminen T (2011) Inducing autoflocculation in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum through CO2 regulation. J Appl Phycol 23:959–966
Henderson R, Parsons S, Jefferson B (2008) Successful removal of algae through the control of zeta potential. Sep Sci Technol 43:1653–1666
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Advanced Biomass R&D Center (ABC) of the Global Frontier Project funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (ABC-2010-0029728).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
J-Y. Jung and H. Lee contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, JY., Lee, H., Shin, WS. et al. Utilization of seawater for cost-effective cultivation and harvesting of Scenedesmus obliquus . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38, 449–455 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1284-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1284-4