Abstract
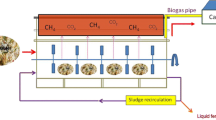
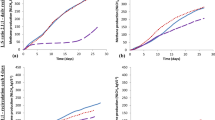
Batch anaerobic digestion was employed to investigate the efficient start-up strategies for the liquefied food waste, and sequencing batch digestion was also performed to determine maximum influent organic loading rate (OLR) for efficient and stable operation. The results indicated that the start-up could be well improved using appropriate wastewater organic load and food-to-microorganism ratios (F/M). When digestion was initialized at low chemical oxygen demand (COD) concentration of 20.0 gCOD L−1, the start-up would go well using lower F/M ratio of 0.5–0.7. The OLR 7.0 gCOD L−1 day−1 was recommended for operating the ASBR digestion, in which the COD conversion of 96.7 ± 0.53 % and biomethane yield of 3.5 ± 0.2 L gCOD−1 were achieved, respectively. The instability would occur when OLR was higher than 7.0 gCOD L−1 day−1, and this instability was not recoverable. Lipid was suggested to be removed before anaerobic digestion. The anaerobic digestion process in engineering project ran well, and good performance was achieved when the start-up and operational strategies from laboratory study were applied. For case application, stable digestion performance was achieved in a digester (850 m3 volume) with biogas production of 1.0–3.8 m3 m−3 day−1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelidaki I, Chen X, Cui J, Kaparaju P, Ellegaard L (2006) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of source-sorted organic fraction of household municipal solid waste: start-up procedure for continuously stirred tank reactor. Water Res 40(14):2621–2628
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Inc, Washington DC
Callaghan FJ, Wase DAJ, Thayanithy K, Forster CF (2002) Continuous co-digestion of cattle slurry with fruit and vegetable wastes and chicken manure. Biomass Bioenerg 22(1):71–77
Chen T, Jin Y, Liu F, Meng X, Li H, Nie Y (2012) Effect of hydrothermal treatment on the levels of selected indigenous microbes in food waste. J Environ Manage 106:17–21
Cheon J, Hidaka T, Mori S, Koshikawa H, Tsuno H (2008) Applicability of random cloning method to analyze microbial community in full-scale anaerobic digesters. J Biosci Bioeng 106(2):134–140
Dague RR, Habben CE, Pidaparti SR (1992) Initial studies on the anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Water Sci Technol 26(9–11):2429–2432
Dasgupta BV, Mondal MK (2012) Bioenergy conversion of organic fraction of Varanasi’s municipal solid waste. Energ Procedia 14:1931–1938
De La Rubia MA, Raposo F, Rincón B, Borja R (2009) Evaluation of the hydrolytic–acidogenic step of a two-stage mesophilic anaerobic digestion process of sunflower oil cake. Bioresour Technol 100(18):4133–4138
Farias De Novaes L, Saratt BL, Rodrigues JAD, Ratusznei SM, de Moraes D, Ribeiro R, Zaiat M, Foresti E (2010) Effect of impeller type and agitation on the performance of pilot scale ASBR and AnSBBR applied to sanitary wastewater treatment. J Environ Manage 91(8):1647–1656
Forster-Carneiro T, Pérez M, Romero LI (2008) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of source-sorted organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Bioresour Technol 99(15):6763–6770
Forster-Carneiro T, Pérez M, Romero LI (2008) Influence of total solid and inoculum contents on performance of anaerobic reactors treating food waste. Bioresour Technol 99(15):6994–7002
Hejnfelt A, Angelidaki I (2009) Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse by-products. Biomass Bioenerg 33(8):1046–1054
Jeganathan J, Nakhla G, Bassi A (2006) Long-term performance of high-rate anaerobic reactors for the treatment of oily wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 40(20):6466–6472
Khalida A, Arshadb M, Anjuma M, Mahmooda T, Dawsonc L (2011) The anaerobic digestion of solid organic waste. Waste Manage 31(8):1737–1744
Kim D, Kim S, Kim K, Shin H (2010) Experience of a pilot-scale hydrogen-producing anaerobic sequencing batch reactor (ASBR) treating food waste. Int J Hydrogen Energ 35(4):1590–1594
Kim JK, Han GH, Oh BR, Chun YN, Eom C, Kim SW (2008) Volumetric scale-up of a three stage fermentation system for food waste treatment. Bioresour Technol 99(10):4394–4399
Liu G, Zhang R, El-Mashad HM, Dong R (2009) Effect of feed to inoculum ratios on biogas yields of food and green wastes. Bioresour Technol 100(21):5103–5108
Liu X, Wang W, Gao X, Zhou Y, Shen R (2012) Effect of thermal pretreatment on the physical and chemical properties of municipal biomass waste. Waste Manage 32(2):249–255
Mata-Alvarez J, Macé S, Llabrés P (2000) Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes. An overview of research achievements and perspectives. Bioresour Technol 74(1):3–16
Molino A, Nanna F, Ding Y, Bikson B, Braccio G (2013) Biomethane production by anaerobic digestion of organic waste. Fuel 103:1003–1009
Ndegwa PM, Hamilton DW, Lalman JA, Cumba HJ (2008) Effects of cycle-frequency and temperature on the performance of anaerobic sequencing batch reactors (ASBRs) treating swine waste. Bioresour Technol 99(6):1972–1980
Neves L, Pereira MA, Mota M, Alves MM (2009) Detection and quantification of long chain fatty acids in liquid and solid samples and its relevance to understand anaerobic digestion of lipids. Bioresour Technol 100(1):91–96
Palatsi J, Affes R, Fernandez B, Pereira MA, Alves MM, Flotats X (2012) Influence of adsorption and anaerobic granular sludge characteristics on long chain fatty acids inhibition process. Water Res 46(16):5268–5278
Pullammanappallil PC, Chynoweth DP, Lyberatos G, Svoronos SA (2001) Stable performance of anaerobic digestion in the presence of a high concentration of propionic acid. Bioresour Technol 78(2):165–169
Qiao W, Yan X, Ye J, Sun Y, Wang W, Zhang Z (2011) Evaluation of biogas production from different biomass wastes with/without hydrothermal pretreatment. Renew Energ 36(12):3313–3318
Rehl T, Müller J (2011) Life cycle assessment of biogas digestate processing technologies. Resour Conserv Recycl 56(1):92–104
Ren L, Nie Y, Liu J, Jin Y, Sun L (2006) Impact of hydrothermal process on the nutrient ingredients of restaurant garbage. J Environ Sci 18(5):1012–1019
Rodrigues JAD, Ratusznei SM, de Camargo EFM, Zaiat M (2003) Influence of agitation rate on the performance of an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor containing granulated biomass treating low-strength wastewater. Adv Environ Res 7(2):405–410
Ruggeri B, Luongo Malave AC, Bernardi M, Fino D (2013) Energy efficacy used to score organic refuse pretreatment processes for hydrogen anaerobic production. Waste Manage 33(11):2225–2233
Salminen E, Rintala J (2002) Anaerobic digestion of organic solid poultry slaughterhouse waste––a review. Bioresour Technol 83(1):13–26
Sawayama S, Inoue S, Minowa T, Tsukahara K, Ogi T (1997) Thermochemical liquidization and anaerobic treatment of kitchen garbage. J Ferment Bioeng 83(5):451–455
Shen F, Yuan H, Pang Y, Chen S, Zhu B, Zou D, Liu Y, Ma J, Yu L, Li X (2013) Performances of anaerobic co-digestion of fruit and vegetable waste (FVW) and food waste (FW): single-phase vs. two-phase. Bioresour Technol 144:80–85
Weng C, Jeris JS (1976) Biochemical mechanisms in the methane fermentation of glutamic and oleic acids. Water Res 10(1):9–18
Yen H, Brune DE (2007) Anaerobic co-digestion of algal sludge and waste paper to produce methane. Bioresour Technol 98(1):130–134
Zhang RH, Tao J, Dugba PN (2000) Evaluation of two-stage anaerobic sequencing batch reactor systems for animal wastewater treatment. Am Soc Agr Eng 43(6):1795–1801
Acknowledgments
We gave our appreciations to the financial supports from Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral program of Higher Education (20120010110004) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (8142030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Y., Shen, F., Yuan, H. et al. Start-up and operation strategies on the liquefied food waste anaerobic digestion and a full-scale case application. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37, 2333–2341 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1211-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1211-8