Abstract
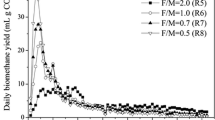
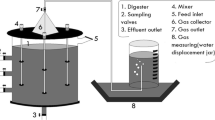
Food wastes have been recognized as the largest waste stream and accounts for 39.25 % of total municipal solid waste in Thailand. Chulalongkorn University has participated in the program of in situ energy recovery from food wastes under the Ministry of Energy (MOE), Thailand. This research aims to develop a prototype single-stage anaerobic digestion system for biogas production and energy recovery from food wastes inside Chulalongkorn University. Here, the effects of sludge recirculation rate and mixing time were investigated as the main key parameters for the system design and operation. From the results obtained in this study, it was found that the sludge recirculation rate of 100 % and the mixing time of 60 min per day were the most suitable design parameters to achieve high efficiencies in terms of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total solids (TS), and total volatile solid (TVS) removal and also biogas production by this prototype anaerobic digester. The obtained biogas production was found to be 0.71 m3/kg COD and the composition of methane was 61.6 %. Moreover, the efficiencies of COD removal were as high as 82.9 % and TVS removal could reach 83.9 % at the optimal condition. Therefore, the developed prototype single-stage anaerobic digester can be highly promising for university canteen application to recover energy from food wastes via biogas production.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn HK, Smith MC, Kondrad SL, White JW (2009) Evaluation of biogas production potential by dry anaerobic digestion of switchgrass-animal manure mixtures. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:965–975
Amani T, Nosrati M, Sreekrishnan TR (2010) Anaerobic digestion from the viewpoint of microbiological, chemical and operational aspects: a review. Environ Rev 18:255–278
Angelidaki I, Boe K, Ellegaard L (2005) Effect of operating conditions and reactor configuration on efficiency of full scale biogas plants. Water Sci Technol 52:189–194
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, New York
Babbitt HE, Baumann ER (1958) Sewerage and sewage treatment. John Wiley & Sons Inc., Toronto
Camp TR, Stein PC (1943) Velocity gradients and internal work in fluid motions. J Boston Soc Civ Eng 30:209
Demirel B, Scherer P (2007) Production of methane from sugar beet silage without manure addition by a single-stage anaerobic digestion process. Biomass & Bioenergy 32:203–209
Digman B, Kim DS (2008) Review: alternative energy from food processing wastes. Environ Prog 27(4):524–534
Droste R (1996) Theory and practice of water and wastewater treatment. John Wiley & Sons Inc., USA
Metcal & Eddy (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. Fourth edition, McGraw-Hill publishing
Fernandez J, Perez M, Romero LI (2008) Effect of substrate concentration on dry mesophilic anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW). Bioresour Technol 99:6075–6080
Fernandez J, Perez M, Romero LI (2010) Kinetics of mesophilic anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste: influence of initial total solid concentration. Bioresour Technol 101:6322–6328
Forster-Carneiro T, Perez M, Romero LI (2008) Anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste: dry thermophilic performance. Bioresour Technol 99:8180–8184
Hobson PN (1990) The treatment of agricultural wastes. In: Wheatley A (eds) Anaerobic digestion. Elsevier Applied Science. London and New York. 93-138
Igoni AH, Ayotamuno MJ, Eze CL, Ogaji SOT, Probert SD (2008) Designs of anaerobic digester for producing biogas from municipal solid waste. Appl Energy 85:430–438
Karim K, Hoffmann R, Thomas Klasson K, Al-Dahhan MH (2005) Anaerobic digestion of animal waste: effect of mode of mixing. Water Res 39(15):3597–3606
Mata-Alvarez J, Macé S, Llabrés P (2000) Anaerobic digestion of solid wastes. An overview of research achievements and perspectives. Bioresour Technol 74:3–16
Pollution Control Department (2007) Summary of state of Thailand’s pollution year 2007. PCD publishing
Slack RJ, Gronow JR, Voulvoulis N (2005) Household hazardous waste in municipal landfills: contaminants in leachate. Sci Total Environ 337:119–137
Stabnikova O, Liu XY, Wang JY (2008) Anaerobic digestion of food waste in a hybrid anaerobic solid–liquid system with leachate recirculation in an acidogenic reactor. Biochem Eng J 41:198–201
Tchobanoglous G, Theisen H, Vigil S (1993) Integrated solid waste management. McGraw-Hill, New York
Zhang R, El-Mashad HM, Hartman K, Wang F, Liu G, Choate C (2007) Characterization of food waste as feed stock for anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 98:929–935
Acknowledgments
This research work is financially supported by the Ministry of Energy, Thailand, and Chulalongkorn University’s research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ratanatamskul, C., Saleart, T. Effects of sludge recirculation rate and mixing time on performance of a prototype single-stage anaerobic digester for conversion of food wastes to biogas and energy recovery. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 7092–7098 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4448-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4448-0