Abstract
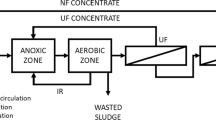
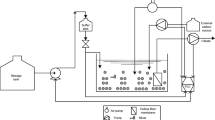
The nutrient removal performance of a membrane bioreactor (MBR) plant treating the wastewater of 10,000 PE was investigated with dynamic simulations. The average process performance with respect to chemical oxygen demand and total nitrogen were reported to be 97 and 81 %, respectively. The modeling study showed that low dissolved oxygen (DO) levels (0.2–0.3 mgO2/L) due to limited aeration capacity within aeration tank that provided additional total nitrogen removal of 15–20 mgN/L. Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process was found to be the reason of performance increase. However, low DO levels <0.3 mgO2/L in the aeration tank triggered the proliferation of filamentous microorganisms within one month as a side effect. In this respect, the morphotypes of Type 0092 and Nocardia (Gordonia) amarae were found to be excessively abundant in the MBR system. Overflow of foam layer covering the tanks was frequently reported during bulking period. A hypochloride dosing of 4.5 gCL/kgMLSS/day was applied to get over filamentous bulking problem as a short term action.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Judd S (2006) The MBR book: principles and applications of membrane bioreactors in water and wastewater treatment. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Orhon D, Artan N (1994) Modelling of activated sludge systems. Technomic, Lancaster
ATV131 (2000) Dimensioning of single stage activated sludge plants. GFA Publishing Company of ATV-DVWK Water, Wastewater and Waste, Hennef ISBN: 3-935669-82-8
Metcalf and Eddy (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment, disposal and reuse. Mc Graw Hill, New York
Barker PS, Dold PL (1997) General model for biological nutrient removal activated-sludge systems: model presentation. Wat Env Res 69(5):969–984
Henze M, Gujer W, Mino T, van Loosdrecht MCM (2000) Activated sludge models: ASM1, ASM2, ASM2d and ASM3, scientific and technical report no: 9. IWA Publishing, London
Naessens W, Maere T, Nopens I (2012) Critical review of membrane bioreactor models––part 1: biokinetic and filtration models. Biores Technol 122(SI):107–118
Manser R, Gujer W, Siegrist H (2005) Consequences of mass transfer effects on the kinetics of nitrifiers. Wat Res 39(19):4633–4642
Hocaoglu SM, Insel G, Ubay Cokgor E, Orhon D (2011) Effect of sludge age on simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in membrane bioreactor. Biores Techno 102(12):6665–6672
Insel G, Hocaoglu SM, Ubay Cokgor E, Orhon D (2011) Modelling the effect of biomass induced oxygen transfer limitations on the nitrogen removal performance of membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 368:54–63
Sarioglu M, Insel G, Artan N, Orhon D (2009) Model evaluation of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in a membrane bioreactor operated without an anoxic reactor. J Membr Sci 337:17–27
Sarioglu M, Insel G, Artan N, Orhon D (2009) Effect of biomass concentration on the performance and modeling of nitrogen removal for membrane bioreactors. J Environ Sci Heal Part A 44(8):733–743
Manser R, Gujer W, Hansruedi S (2005) Consequences of mass transfer effects on the kinetics of nitrifiers. Water Res 39:4633–4642
Jiang T, Sin G, Spanjers H, Nopens I, Kennedy MD, van der Meer W, Futselaar H, Amy G, Vanrolleghem PA (2009) Comparison of modeling approach between membrane bioreactor and conventional activated sludge processes. Wat Environ Res 81(4):342–440
Applegate CS, Wilder B, Deshaw JR (1980) Total nitrogen removal in a multi-channel oxidation systems. J Wat Pollut Cont Fed 52(3):568–577
Ekama GA, Wentzel MC, Casey TG, GvR Marais (1996) Filamentous organism bulking in nutrient removal activated sludge systems. Paper 6: review evaluation and consolidation of results. Wat SA 22(2):147–151
Germain E, Nelles F, Drews A, Pearce P, Kraume M, Reid E, Judd SJ, Stephenson T (2007) Biomass effects on oxygen transfer in membrane bioreactors. Wat Res 41:1038–1044
Meng F, Chae SR, Drewsc A, Kraumec M, Shind HS, Yanga F (2009) Review, recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): membrane fouling and membrane material. Wat Res 43:1489–1512
Jenkins D, Richard MG, Daigger GT (1993) Manual on the causes and control of activated sludge bulking and foaming, 2nd edn. Lewis Publishers, Inc., Michigan
Su Y, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Jiang M (2013) Effect of nitrate concentration on filamentous bulking under low level of dissolved oxygen in an airlift inner circular anoxic-aerobic incorporate reactor. J Environ Sci 25(9):1736–1744
Bitton G (1994) Wastewater microbiology. John Wiley and Sons Publishing, New York
Casey TG, Wentzel MC, Ekama GA (1999) Filamentous organism bulking in nutrient removal activated sludge systems. Paper 11. A biochemical/microbiological model for proliferation of anoxic-aerobic (AA) filamentous organisms. Wat SA 25(4):443–451
Kampschreur MJ, Temmink H, Kleerebezem R, Jetten MSM, van Loosdrecht MCM (2009) Nitrous oxide emission during wastewater treatment. Wat Res 43(17):4093–4103
Martins AMP, Pagilla K, Heijnen JJ, van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) Filamentous bulking sludge-a critical review. Wat Res 38:793–817
Vanrolleghem PA, Insel G, Petersen B, Sin G, De Pauw D, Nopens I, Dovermann H, Weijers S, Gernaey K (2003) A comprehensive model calibration procedure for activated sludge models, WEFTEC 2003, 76th annual technical exhibition and conference, Los Angeles, California, USA, 11–15 October 2003
Roeleveld PJ, van Loosdrecht MCM (2002) Experiences with guidelines for wastewater characterization in the Netherlands. Wat Sci Tech 45(6):77–87
Insel G, Guder B, Gunes G, Ubay Cokgor E (2012) Are standard wastewater treatment plant design methods suitable for any municipal wastewater? Wat Sci Tech 66(2):328–335
Eikelboom DH (1975) Filamentous organisms observed in activated sludge. Wat Res 9:365–388
Eikelboom DH (1977) Identification of filamentous organisms in bulking activated sludge. Prog Wat Technol 8:153–162
Eikelboom DH (2000) Process control of activated sludge plants by microscopic investigation. IWA Publishing, London
Sezgin M, Jenkins D, Parker DS (1978) A unified theory of filamentous activated sludge bulking. J Wat Pol Cont Fed 50:362–381
Krampe J, Krauth K (2003) Oxygen transfer into activated sludge with high MLSS concentrations. Wat Sci Technol 47(11):297–303
Racault Y, Stricker AE, Husson A, Gillot S (2009) Effect of mixed liquor suspended solids on the oxygen transfer rate in full scale membrane bioreactors. WEFTEC2009, Water Environment Federation, Florida, USA
Tian Y, Su X, Chen L, Jiang T (2010) Impact of organic loading rate and DO on filamentous bulking sludge and the study of its characteristics in membrane bioreactor. Adv Mat Res 113–114:1280–1284
Wilen BM, Balmer P (1999) The effect of dissolved oxygen concentration on the structure, size, and size distribution of activated sludge flocs. Wat Res 33(2):391–400
Nowak G, Brown G, Yee A (1986) Effects of feed pattern and dissolved oxygen on growth of filamentous bacteria. J Wat Poll Cont Fed 58(10):978–984
Gaval G, Pernelle JJ (2003) Impact of the repetition of oxygen deficiencies on the filamentous bacteria proliferation in activated sludge. Wat Res 37:1991–2000
Carr EL, Eales KL, Seviour RJ (2006) Substrate uptake by Gordonia amarae in activated sludge foams by FISH-MAR. Wat Sci Technol 54(1):39–45
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA (1974) Nocardia amarae sp. Nov., an actinomycete common in foaming activated sludge. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:278–288
Wang Z, Wang P, Wang Q, Wu Z, Zhou Q, Yang D (2010) Effective control of membrane fouling by filamentous bacteria in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Chem Eng J 158:608–615
Cosenza A, Di Bella G, Mannina G, Torregrossa M (2013) The role of EPS in fouling and foaming phenomena for a membrane bioreactor. Biores Technol 147:184–192
Ovez S, Ors C, Murat S, Orhon D (2006) Effect of hypochloride on microbial ecology of bulking and foaming activated sludge treatment for tannery wastewater. J Environ Sci Health Part A 41(10):2163–2174
Ni BJ, Yuan Z, Chandran K, Vanrolleghem PA, Murthy S (2013) Evaluating four mathematical models for nitrous oxide production by autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 110(1):153–163
Acknowledgments
Bodrum Konacık Municipality is kindly acknowledged for sharing the MBR data. The authors are also thankful to MBR plant personnel, Mr. Güven Semet and Mr. Orhan Gök for the discussions on plant data and operation strategy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Insel, G., Erol, S. & Övez, S. Effect of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification on nitrogen removal performance and filamentous microorganism diversity of a full-scale MBR plant. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37, 2163–2173 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1193-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1193-6