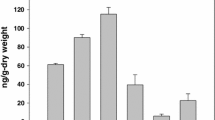
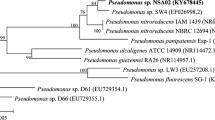
Abstract
Biodegradation of pyridine and α-picoline (2-methyl pyridine) by Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes-KPN and Nocardia sp. isolated from garden soil were investigated in batch culture experiments. Pyridine and α-picoline (50–200 mg L−1) were used as sole source of carbon and energy in the investigation. The kinetic constants were evaluated for pyridine and α-picoline degradation under optimized nutritional (C, N, P) and environmental (pH, temperature) conditions. The values of bio-kinetic constant obtained in the present investigation indicate the usefulness of both the cultures for treatment of waste containing pyridine and its derivatives.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Da:
-
effective dispersion coefficient (m2 s−1)
- L :
-
characteristic length (m)
- C:N ratio:
-
carbon to nitrogen ratio
- CMAS:
-
completely mixed activated sludge
- K d :
-
decay coefficient (day−1)
- K s :
-
half saturation rate constant (mg L−1)
- O.D:
-
optical density
- Peclet number:
-
UL/Da (U = superficial velocity m s−1)
- USEPA:
-
United States Environmental Protection Agency
- UV–Vis spectrophotometer:
-
Ultra violet–visible spectrophotometer
- Y :
-
yield coefficient (g biomass g substrate−1)
- μ :
-
growth rate constant (day−1)
- μmax :
-
maximum specific growth rate constant (day−1)
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Ren NQ (2007) Biodegradation of pyridine using aerobic granules in the presence of phenol. Wat Res 41:2903–2910
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1987) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York
Doughlas MC (1976) Von nostrands scientific encyclopedia. Von Nostrand Rein Hold Company, New York
Edwards U, Rogall T, Blocker H, Emde M, Böttger EC (1989) Isolation and direct nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7843–7853
Feasibility studies on treatment of wastewater containing pyridine generated at M/s Jubilant Organosys Limited (JOL), Bhartiyagram, J. P. Nagar, UP (2004), Technical report, National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, September
Fetzner S (1998) Bacterial degradation of pyridine, indole, quinoline and their derivatives under different redox conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:237–250
Foght JM, Westlake DWS (1988) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and aromatic heterocycles by a Pseudomonas species. Can J Microbiol 34:1135–1141
Gupta RC, Shukla OP (1975) Microbial metabolism of 2-hydroxypyridine. Ind J Biochem Biophys 12:296–298
Healy JB, Langlois GW, Daughton CG (1985) Biooxidation of organic solutes in oil shale wastewaters. Wat Res 19:1429–1435
Houghton C, Cain RB (1972) Microbial metabolism of the pyridine ring. Biochem J 130:879–893
Kaiser JP, Feng Y, Bollag JM (1996) Microbial metabolism of pyridine, quinoline, acridine and their derivatives under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Microbiol Rev 60:483–498
Koch B, Ostermann H, Hoke H, Hempel DC (1991) Sand and activated carbon as biofilm carriers for microbial degradation of phenols and nitrogen containing aromatic compounds. Wat Res 25:1–8
Korosteleva LA, Kost AN, Vorobeva LI, Modyanova LV, Terentev PB, Kulikov NS (1981) Microbiological degradation of pyridine and 3-methylpyridine. Appl Biochem Microbiol 17:276
Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) (1984) Bergeys manual of systematic bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins, USA
Lee ST, Rhee SK, Lee GM (1994) Biodegradation of pyridine by freely suspended and immobilized Pimelobacter species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41:652–657
Lee JJ, Rhee SK, Lee ST (2001) Degradation of 3-methylpyridine and 3-ethylpyridine by Gordonia nitida LE31. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4342–4345
Leenheer JA, Noyes TI, Stuber HA (1982) Determination of polar organic solutes in oil shale retort water. Environ Sci Technol 16:714–723
Lodha B, Bhadane R, Patel B, Killedar D (2008) Biodegradation of pyridine by a isolated bacterial strain and bio-augmentation of strain into activated sludge to enhance pyridine biodegradation. Biodegradation. doi:10.1007/s10532-008-9176-4
Mathur AK, Majumdar CB, Chatterjee S, Roy P (2008) Biodegradation of pyridine by the new bacterial isolates S. putrefaciens and B. sphaericus. J Haz Mat. Available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com
Milleman RE, Birge WJ, Black JA, Cushman RM, Daniels KL, Franco PJ, Giddings JM, McCarthy JF, Stewart AJ (1984) Comparative acute toxicity to aquatic organisms of components of coal-derived synthetic fuels. Trans Am Fish Soc 113:74
Padoley KV (2002) Treatment of industrial wastewater containing heterocyclic bases. PhD Thesis, Nagpur University
Padoley KV, Rajvaidya AS, Subbarao TV, Pandey RA (2006) Biodegradation of pyridine in a completely mixed activated sludge process. Bioresource Technol 97:1225–1236
Quail BE, Hill GA (1991) A packed column bioreactor for phenol degradation: model and experimental verification. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 52:545–557
Rhee SK, Lee GM, Yoon JH, Park YH, Bae HS, Lee ST (1997) Anaerobic and aerobic degradation of pyridine by a newly isolated denitrifying bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2578–2585
Rhee SK, Lee KY, Chung JC, Lee ST (1997) Degradation of pyridine of Nocardioides sp. strain OS4 isolated from the oxic zone of a spent shale column. Can J Microbiol 43:205–209
Ronen Z, Bollag JM (1991) Pyridine metabolism by a denitrifying bacterium. Can J Microbiol 37:725–729
Rothenburger S, Atlas RM (1993) Hydroxylation and biodegradation of 6-methylquinoline by Pseudomonads in aqueous and nonaqueous immobilized-cell bioreactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2139–2144
Saravanan P, Pakshirajan K, Saha P (2008) Growth kinetics of an indigenous mixed microbial consortium during phenol degradation in a batch reactor. Bioresource Technol 99:205–209
Shukla OP, Kaul SM (1986) Microbial transformation of pyridine-N-oxide and pyridine by Nocardia sp. Can J Microbiol 32:330
Shukla OP (1984) 8-Hydroxycoumarin: an intermediate in the microbial transformation of quinoline. Curr Sci 53:1145–1147
Shukla OP (1986) Microbial transformation of quinoline by a Pseudomonas. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:1332–1342
Sims GK, O’Loughlin EJ (1989) Degradation of pyridines in the environment. Crit Rev Environ Ctrl 4:311–340
Sims GK, Sommers LE (1986) Biodegradation of pyridine derivatives in soil suspensions. Environ Toxicol Chem 5:503
Sneath PHA, Mair NS, Sharpe ME, Holt JG (eds) (1986) Bergeys manual of systematic bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins, USA (2)
Standard Methods for the examination of water and wastewater 20th edn (1998) American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC, USA
Steven BH, Robert ES (1984) Emission of organic air pollutants from shale oil wastewaters. Environ Sci Technol 18:483–490
Stuerner DH, Ng DJ, Morris CJ (1982) Organic contaminants in ground water near an underground coal gasification site in northeastern Wyoming. Environ Sci Technol 16:582–587
Sutton SD, Pfaller SL, Shann JR, Warshawskii D, Kinkle BK, Vestal JR (1996) Aerobic biodegradation of 4-methylquinoline by a soil bacterium. Appl Environ Microbial 62:2910–2914
Uma B, Sandhya S (1997) Pyridine degradation and heterocyclic nitrification by Bacillus coagulans. Can J Microbiol 43:595–598
Uma B, Sandhya S (1998) Kinetics of pyridine degradation along with toluene and methylene chloride with Bacillus sp. in packed bed reactor. Bioprocess Eng 18:303–305
Verschueren K (1977) Handbook of environmental data on organic chemicals. Rein hold company, New York
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Director, NEERI for his kind permission for publishing this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padoley, K.V., Mudliar, S.N. & Pandey, R.A. Microbial degradation of pyridine and α-picoline using a strain of the genera Pseudomonas and Nocardia sp.. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32, 501–510 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-008-0270-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-008-0270-0