Abstract
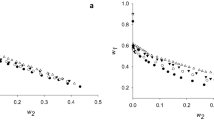
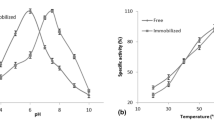
A study was made of the partition and purification of α-amylase from a culture supernatant of Bacillus subtilis in the polyethylene glycol (PEG)—citrate aqueous two-phase system (ATPS). Factors that influenced the partition of the protein in this system, including the molecular weight of the PEG, the tie line length of ATPS, the pH value and the sodium chloride concentration, were investigated. Purification of α-amylase was attained with a purification factor (PF) of 1.8 and 90% yield at pH 6.0 in a PEG1000-citrate ATPS with short tie line length. By utilizing the salt-out effect of neutral salt, the purification of α-amylase was further improved to 2.0 of PF and 80% yield in a PEG3350-citrate ATPS with 4% sodium chloride.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diamond AD, Hsu JT (1992) Aqueous two-phase systems for biomolecule separation. Adv Biochem Eng Biot 47:89–135
Schmid AS, Ventom AM, Asenjo JA (1994) Partitioning and purification of α-amylase in aqueous two-phase systems. Enzyme Microb Tech 16:131–142
Ohlsson R, Hentschel CC, Williams JG (1978) A rapid method for the isolation of circular DNA using an aqueous two-phase partition system. Nucleic Acids Res 5:583–590
Yang WY, Lin CD, Chu IM, Lee CJ (1994) Extraction of cephalosporin C from whole broth and separation of desacetyl cep halosporin C by aqueous two-phase partition. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:439–445
Alberttson PA (1986) Partition of cell particles and macromolecules, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Heriberto C (1996) Theory of phase formation in aqueous two-phase systems. J Chromatogr B 680:3–30
UpaDek H, Kottwits B (1997) Application of amylases in detergents. In: Van Ee JH, Misset O, Baas, E (eds) Enzymes in detergency. New York, pp 203–212
Saito N (1973) A thermophilic extracellular α-amylase from Bacillus licheniformis. Arch Biochem Biophys 155:290–298
Marcos JC, Fonseca LP, Ramalho MT, Cabral JMS (1999) Partial purification of penicillin acylase from Escherichia coli in poly(ethylene glycol)-sodium citrate aqueous two-phase systems. J Chromatogr B 734:15–22
Yoo YJ, Hong J, Hatch RT (1987) Comparison of α-amylase activities from different assay methods. Biotechnol Bioeng 30:147–151
Bradford MM (1972) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the support from the Chinese “863” National High Technology Grant-2002AA217031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, W., Song, J., Bi, J. et al. Partial purification of α-amylase from culture supernatant of Bacillus subtilis in aqueous two-phase systems. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 27, 3–7 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-004-0369-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-004-0369-x