Abstract
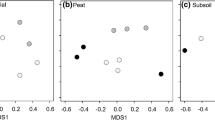
Molecular genetic methods were used to determine whether artificial defoliation affects ectomycorrhizal (EM) colonization, EM fungal species richness, and species composition in a mixed Pinus contorta (lodgepole pine)/Picea engelmannii (Engelmann spruce) forest in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. All lodgepole pines in three replicate plots were defoliated 50%, while Engelmann spruce were left untreated. This was done to determine how defoliation of one conifer species would affect EM mutualisms of both treated and neighboring, untreated conifers. The results indicated no significant effect on either EM colonization (142.0 EM tips/core in control plots and 142.4 in treatment plots) or species richness (5.0 species/core in controls and 4.5 in treatments). However, the relative abundance of EM of the two tree species shifted from a ratio of approximately 6:1 without treatment (lodgepole EM:spruce EM), to a near 1:1 ratio post-treatment. This shift may be responsible for maintaining total EM colonization and species richness following defoliation. In addition, EM species composition changed significantly post-defoliation; the system dominant, an Inocybe species, was rare in defoliation plots, while Agaricoid and Suilloid species that were rare in controls were dominant in treatments. Furthermore, species of EM fungi associating with both lodgepole pine and Engelmann spruce were affected, which indicates that changing the photosynthetic capacity of one species can affect mycorrhizal associations of neighboring non-defoliated trees.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cullings, K., Vogler, D., Parker, V. et al. Defoliation effects on the ectomycorrhizal community of a mixed Pinus contorta/Picea engelmannii stand in Yellowstone Park. Oecologia 127, 533–539 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420000610
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420000610