Abstract
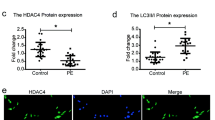
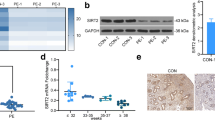
Our study was to pinpoint the significance of histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5) affecting the pathogenesis of preeclampsia (PE) via CD31/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) axis by regulating cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61 (CYR61). Expression of HDAC5, CYR61, and CD31/mTOR in placental tissues of patients with PE and trophoblast cells HTR-8/SVneo cells was determined first followed by their interaction analysis. Following different transfection, the significance of HDAC5 in cell functions was assayed in relation to CYR61 and CD31/mTOR. An in vivo PE mouse model was constructed for further validation. The clinical tissue and in vitro cell experimentations discovered that HDAC5 was downregulated in placental tissues of PE patients and trophoblast cells, while CYR61, CD31, mTOR, and p-mTOR displayed upregulation. After overexpression of HDAC5, trophoblast cell functions were enhanced. HDAC5 reduced the acetylation enrichment of H3K27 to inhibit the expression of CYR61. Furthermore, CYR61 promoted the activation of CD31/mTOR axis, thereby inhibiting HTR-8/SVneo cell functions. The in vivo rat model confirmed the above alterations. Taken together, HDAC5 contributes to downregulation of CYR61 through histone deacetylation, inactivating CD31/mTOR axis, which prevents the occurrence and development of PE.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated/analyzed during the current study are available in the manuscript and supplementary materials.
References
Azar C, Valentine MC, Trausch-Azar J et al (2021) RNA-Seq identifies genes whose proteins are upregulated during syncytia development in murine C2C12 myoblasts and human BeWo trophoblasts. Physiol Rep 9:e14671. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.14671
Chang CW, Cheong ML, Chang GD, Tsai MS, Chen H (2013) Involvement of Epac1/Rap1/CaMKI/HDAC5 signaling cascade in the regulation of placental cell fusion. Mol Hum Reprod 19:745–755. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gat050
Cheng G, Zhang H, Zhang L, Zhang J (2015) Cyr61 promotes growth of glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol 36:2869–2873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2915-8
Chu Y, Chen W, Peng W et al (2020) Amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes-mediated autophagy promotes the survival of trophoblasts under hypoxia through mTOR pathway by the downregulation of EZH2. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:545852. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.545852
Fan Y, Dong Z, Zhou G et al (2020) Elevated miR-23a impairs trophoblast migration and invasiveness through HDAC2 inhibition and NF-kappaB activation. Life Sci 261:118358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118358
Feng J, Wang X, Li H, Wang L, Tang Z (2018) Silencing of Annexin A1 suppressed the apoptosis and inflammatory response of preeclampsia rat trophoblasts. Int J Mol Med 42:3125–3134. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3887
Gan W, Dang Y, Han X et al (2016) ERK5/HDAC5-mediated, resveratrol-, and pterostilbene-induced expression of MnSOD in human endothelial cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 60:266–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201500466
Jeyabalan A (2013) Epidemiology of preeclampsia: impact of obesity. Nutr Rev 71(Suppl 1):S18-25. https://doi.org/10.1111/nure.12055
Klymenko O, Brecklinghaus T, Dille M et al (2020) Histone deacetylase 5 regulates interleukin 6 secretion and insulin action in skeletal muscle. Mol Metab 42:101062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101062
Kuemmerle NB, Lin PS, Krieg RJ Jr, Lin KC, Ward KP, Chan JC (2000) Gene expression after intrarenal injection of plasmid DNA in the rat. Pediatr Nephrol 14:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050033
Lau LF (2011) CCN1/CYR61: the very model of a modern matricellular protein. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:3149–3163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0778-3
Lee KB, Byun HJ, Park SH, Park CY, Lee SH, Rho SB (2012) CYR61 controls p53 and NF-kappaB expression through PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways in carboplatin-induced ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett 315:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2011.10.016
Li XC, Jin F, Wang BY, Yin XJ, Hong W, Tian FJ (2019) The m6A demethylase ALKBH5 controls trophoblast invasion at the maternal-fetal interface by regulating the stability of CYR61 mRNA. Theranostics 9:3853–3865. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.31868
Lin MT, Kuo IH, Chang CC et al (2008) Involvement of hypoxia-inducing factor-1alpha-dependent plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 up-regulation in Cyr61/CCN1-induced gastric cancer cell invasion. J Biol Chem 283:15807–15815. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M708933200
Maynard SE, Karumanchi SA (2011) Angiogenic factors and preeclampsia. Semin Nephrol 31:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2010.10.004
Niu JM, Lei Q, Lu LJ et al (2013) Evaluation of the diagnostic criteria of gestational metabolic syndrome and analysis of the risk factors. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 48:92–97
Petrozella L, Mahendroo M, Timmons B, Roberts S, McIntire D, Alexander JM (2012) Endothelial microparticles and the antiangiogenic state in preeclampsia and the postpartum period. Am J Obstet Gynecol 207(140):e120-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2012.06.011
Salem M, Kamal S, El Sherbiny W, Abdel Aal AA (2015) Flow cytometric assessment of endothelial and platelet microparticles in preeclampsia and their relation to disease severity and Doppler parameters. Hematology 20:154–159. https://doi.org/10.1179/1607845414Y.0000000178
Sircar M, Thadhani R, Karumanchi SA (2015) Pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 24:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0000000000000105
Sun M, Gao J, Meng T et al (2021) Cyclin G2 upregulation impairs migration, invasion, and network formation through RNF123/Dvl2/JNK signaling in the trophoblast cell line HTR8/SVneo, a possible role in preeclampsia. FASEB J 35:e21169. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202001559RR
Tsou PS, Khanna D, Sawalha AH (2019) Identification of cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61 as a potential antifibrotic and proangiogenic mediator in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheumatol 71:1350–1359. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40890
Tsou PS, Wren JD, Amin MA et al (2016) Histone deacetylase 5 is overexpressed in scleroderma endothelial cells and impairs angiogenesis via repression of proangiogenic factors. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:2975–2985. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39828
Usui T, Okada M, Hara Y, Yamawaki H (2011) Exploring calmodulin-related proteins, which mediate development of hypertension, in vascular tissues of spontaneous hypertensive rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 405:47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.120
Vu HV, Ianosi-Irimie MR, Pridjian CA et al (2005) Involvement of marinobufagenin in a rat model of human preeclampsia. Am J Nephrol 25:520–528. https://doi.org/10.1159/000088461
Wang L, Zhang Y, Qu H et al (2019a) Reduced ELABELA expression attenuates trophoblast invasion through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in early onset preeclampsia. Placenta 87:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2019.08.077
Wang Y, Gu Y, Alexander JS, Lewis DF (2019b) Histone deacetylase inhibition disturbs the balance between ACE and chymase expression in endothelial cells: a potential mechanism of chymase activation in preeclampsia. Hypertens Res 42:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-018-0150-1
Wang Z, Lu S, Liu C et al (2010) Expressional and epigenetic alterations of placental matrix metalloproteinase 9 in preeclampsia. Gynecol Endocrinol 26:96–102. https://doi.org/10.3109/09513590903184100
Wolf N, Yang W, Dunk CE et al (2010) Regulation of the matricellular proteins CYR61 (CCN1) and NOV (CCN3) by hypoxia-inducible factor-1{alpha} and transforming-growth factor-{beta}3 in the human trophoblast. Endocrinology 151:2835–2845. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-1195
Zhang X, Ding L, Diao Z, Yan G, Sun H, Hu Y (2012) CYR61 modulates the vascular endothelial growth factor C expression of decidual NK cells via PI3K/AKT pathway. Am J Reprod Immunol 67:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0897.2011.01080.x
Zupkovitz G, Grausenburger R, Brunmeir R et al (2010) The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 is a crucial target for histone deacetylase 1 as a regulator of cellular proliferation. Mol Cell Biol 30:1171–1181. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01500-09
Funding
This study was supported by Research Fund Project of Zhejiang Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Plan (No. 2016ZA133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peiyue Jiang, Xia Ying, Zhi Li, and Ruoan Jiang designed the study. Jinling Zhou collated the data, designed and developed the database, carried out data analyses, and produced the initial draft of the manuscript. Mengmeng Zhang, Xiaofu Yang, and Xiaojun Zhu contributed to drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, P., Ying, X., Li, Z. et al. HDAC5 inactivates CYR61-regulated CD31/mTOR axis to prevent the occurrence of preeclampsia. Cell Tissue Res 390, 281–292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03652-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03652-7