Abstract
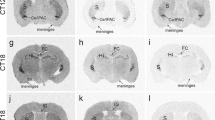
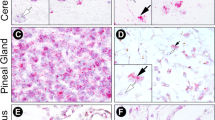
Extracellular purines (ATP, ADP, AMP and adenosine) are important signaling molecules in the CNS. Levels of extracellular purines are regulated by enzymes located at the cell surface referred to as ectonucleotidases. Time-dependent changes in their expression could profoundly influence the availability of extracellular purines and thereby purinergic signaling. Using radioactive in situ hybridization, we analyzed the mRNA distribution of the enzymes NTPDase1, -2 and -3 and ecto-5′-nucleotidase in the prosencephalon of two mouse strains: melatonin-proficient C3H and melatonin-deficient C57Bl. The mRNAs of these enzymes were localized to specific brain regions, such as hippocampus, striatum, medial habenula and ventromedial hypothalamus. NTPDase3 expression was more widely distributed than previously thought. All ectonucleotidases investigated revealed a prominent time-dependent expression pattern. In C3H, the mRNA expression of all four enzymes gradually increased during the day and peaked during the night. In contrast, in C57Bl, ecto-5′-nucleotidase expression peaked at the beginning of the day and gradually decreased to trough levels at night. Recording of locomotor activity revealed higher daytime activity of C57Bl than of C3H. Our results indicate that the expression of ectonucleotidases varies according to time and genotype and suggest that melatonin exerts modulatory effects associated with different regulations of purinergic signaling in the brain. These findings provide an important basis for further examination of the complexity of the purinergic system in the brain.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Anterodorsal thalamic nucleus
- Arc:
-
Arcuate nucleus
- AV:
-
Anteroventral thalamic nucleus
- CA:
-
Cornu ammonis
- CeC and CeL:
-
Capsular and lateral central amygdala
- CeM:
-
Medial central amygdala
- Cg:
-
Cingulate cortex
- CP:
-
Choroid plexus
- CT:
-
Circadian time
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- Dk:
-
Nucleus of Darkschewitsch
- DM:
-
Dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus
- eN:
-
Ecto-5′-nucleotidase
- FC:
-
Fasciola cinerea
- GP:
-
Globus pallidus
- IG:
-
Indusium griseum
- IPAC:
-
Interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure
- ISH:
-
In situ hybridization
- KO:
-
Knock out
- LHb:
-
Lateral habenula
- LV:
-
Lateral ventricle
- MeP:
-
Posterior medial amygdala
- MHb:
-
Medial habenula
- NTPDase:
-
Nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase
- Pir:
-
Piriform cortex
- PMD:
-
Premammillary nucleus dorsal
- PMV:
-
Premammillary nucleus ventral
- Po:
-
Posterior thalamic nuclear group
- PT:
-
Hypophysial pars tuberalis
- PVA:
-
Anterior paraventricular thalamic nucleus
- PVN:
-
Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus
- Rt:
-
Reticular thalamic nucleus
- SCN:
-
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
- SFO:
-
Subfornical organ
- sm:
-
Stria medullaris
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- SON:
-
Supraoptic nucleus
- STh:
-
Subthalamic nucleus
- SVZ:
-
Subventricular zone
- TS:
-
Triangular septal nucleus
- 3V:
-
Third ventricle
- VMH:
-
Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus
- VP:
-
Ventral posterior thalamic nucleus
- VPPC:
-
Ventral posterior parvicellular thalamic nucleus
- WT:
-
Wild-type
- ZI:
-
Zona incerta
References
Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A, Zimmermann H (2009) Purinergic signalling in the nervous system: an overview. Trends Neurosci 32:19–29
Ackermann H (1991) BIAS. A program package for biometrical analysis of samples. Comput Stat Data Anal 11:223–224 [current program version: 10.02 epsilon]
Augusto E, Matos M, Sevigny J, El-Tayeb A, Bynoe MS, Muller CE, Cunha RA, Chen J (2013) Ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73)-mediated formation of adenosine is critical for the striatal adenosine A2A receptor functions. J Neurosci 33:11390–11399
Belcher S, Zsarnovszky A, Crawford P, Hemani H, Spurling L, Kirley T (2006) Immunolocalization of ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3 in rat brain: implications for modulation of multiple homeostatic systems including feeding and sleep–wake behaviors. Neuroscience 137:1331–1346
Bjelobaba I, Stojiljkovic M, Pekovic S, Dacic S, Lavrnja I, Stojkov D, Rakic L, Nedeljkovic N (2007) Immunohistological determination of ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase1 (NTPDase1) and 5′-nucleotidase in rat hippocampus reveals overlapping distribution. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:731–743
Braun N, Sévigny J, Robson SC, Enjyoji K, Guckelberger O, Hammer K, Di Virgilio F, Zimmermann H (2000) Assignment of ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1/cd39 expression to microglia and vasculature of the brain. Eur J Neurosci 12:4357–4366
Braun N, Sévigny J, Mishra SK, Robson SC, Barth SW, Gerstberger R, Hammer K, Zimmermann H (2003) Expression of the ecto-ATPase NTPDase2 in the germinal zones of the developing and adult rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 17:1355–1364
Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic signalling. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):172–181
Burnstock G (2009) Purinergic signalling: past, present and future. Braz J Med Biol Res 42:3–8
Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A (2012) Purinergic signalling and the nervous system. Springer, Heidelberg
Chatterjee S, Thyagarajan K, Kesarwani P, Song JH, Soloshchenko M, Fu J, Bailey SR, Vasu C, Kraft AS, Paulos CM, Yu XZ, Mehrotra S (2014) Reducing CD73 expression by IL1β-Programmed Th17 cells improves immunotherapeutic control of tumors. Cancer Res 74:6048–6059
Cunha RA, Brendel P, Zimmermann H, Ribeiro JA (2000) Immunologically distinct isoforms of ecto-5′-nucleotidase in nerve terminals of different areas of the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 74:334–338
Deaglio S, Robson SC (2011) Ectonucleotidases as regulators of purinergic signaling in thrombosis, inflammation, and immunity. Adv Pharmacol 61:301–332
Detanico BC, de Souza A, Medeiros LF, Rozisky JR, Caumo W, Hidalgo MPL, Battastini AMO, Torres ILS (2010) 24-hour temporal pattern of NTPDase and 5′-nucleotidase enzymes in rat blood serum. Chronobiol Int 27:1751–1761
Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA (2001) The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:31–55
Ena SL, De Backer J, Schiffmann SN, de Kerchove d’Exaerde A (2013) FACS array profiling identifies ecto-5′ nucleotidase as a striatopallidal neuron-specific gene involved in striatal-dependent learning. J Neurosci 33:8794–8809
Figueiró F, Mendes FB, Corbelini PF, Janarelli F, Jandrey EH, Russowsky D, Eifler-Lima VL, Battastini AM (2014) A monastrol-derived compound, LaSOM 63, inhibits ecto-5′nucleotidase/CD73 activity and induces apoptotic cell death of glioma cell lines. Anticancer Res 34:1837–1842
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (2008) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, New York
Gampe K, Hammer K, Kittel Á, Zimmermann H (2012) The medial habenula contains a specific nonstellate subtype of astrocyte expressing the ectonucleotidase NTPDase2. Glia 60:1860–1870
Gampe K, Stefani J, Hammer K, Brendel P, Pötzsch A, Enikolopov G, Enjyoji K, Acker-Palmer A, Robson SC, Zimmermann H (2014) NTPDase2 and purinergic signaling control progenitor cell proliferation in neurogenic niches of the adult mouse brain. Stem Cells 33:253–264
Goto M, Matsuo H, Iigo M, Furuse M, Korf HW, Yasuo S (2013) Melatonin-induced changes in the expression of thyroid hormone-converting enzymes in hypothalamus depend on the timing of melatonin injections and genetic background in mice. Gen Comp Endocrinol 186:33–40
Haskó G, Cronstein BN (2004) Adenosine: an endogenous regulator of innate immunity. Trends Immunol 25:33–39
Korf HW, von Gall C (2006) Mice, melatonin and the circadian system. Mol Cell Endocrinol 252:57–68
Korf HW, von Gall C, Stehle J (2003) The circadian system and melatonin: lessons from rats and mice. Chronobiol Int 20:697–710
Kukulski F, Lévesque SA, Sévigny J (2011) Impact of ectoenzymes on p2 and p1 receptor signaling. Adv Pharmacol 61:263–299
Kulesskaya N, Võikar V, Peltola M, Yegutkin GG, Salmi M, Jalkanen S, Rauvala H (2013) CD73 is a major regulator of adenosinergic signalling in mouse brain. PLoS ONE 8:e66896
Langer D, Hammer K, Koszalka P, Schrader J, Robson SC, Zimmermann H (2008) Distribution of ectonucleotidases in the rodent brain revisited. Cell Tissue Res 334:199–217
Mackiewicz M, Nikonova EV, Zimmerman JE, Galante RJ, Zhang L, Cater JR, Geiger JD, Pack AI (2003) Enzymes of adenosine metabolism in the brain: diurnal rhythm and the effect of sleep deprivation. J Neurochem 85:348–357
Mills JH, Thompson LF, Mueller C, Waickman AT, Jalkanen S, Niemela J, Airas L, Bynoe MS (2008) CD73 is required for efficient entry of lymphocytes into the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:9325–9330
Mimee A, Smith PM, Ferguson AV (2013) Circumventricular organs: targets for integration of circulating fluid and energy balance signals? Physiol Behav 121:96–102
Mutafova-Yambolieva VN, Durnin L (2014) The purinergic neurotransmitter revisited: a single substance or multiple players? Pharmacol Ther 144:162–191
Petrovic-Djergovic D, Hyman MC, Ray JJ, Bouis D, Visovatti SH, Hayasaki T, Pinsky DJ (2012) Tissue-resident ecto-5′ nucleotidase (CD73) regulates leukocyte trafficking in the ischemic brain. J Immunol 188:2387–2398
Pfeffer M, Rauch A, Korf HW, von Gall C (2012) The Endogenous Melatonin (MT) signal facilitates reentrainment of the circadian system to light-induced phase advances by acting upon MT2 receptors. Chronobiol Int 29:415–429
Porkka-Heiskanen T, Strecker R, McCarley R (2000) Brain site-specificity of extracellular adenosine concentration changes during sleep deprivation and spontaneous sleep: an in vivo microdialysis study. Neuroscience 99:507–517
Radulovacki M (1985) Role of adenosine in sleep in rats. Rev Clin Basic Pharm 5:327–339
Radulovacki M, Virus RM, Djuricic-Nedelson M, Green RD (1984) Adenosine analogs and sleep in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 228:268–274
Robson SC, Sévigny J, Zimmermann H (2006) The E-NTPDase family of ectonucleotidases: Structure function relationships and pathophysiological significance. Purinergic Signal 2:409–430
Shukla V, Zimmermann H, Wang L, Kettenmann H, Raab S, Hammer K, Sévigny J, Robson SC, Braun N (2005) Functional expression of the ecto-ATPase NTPDase2 and of nucleotide receptors by neuronal progenitor cells in the adult murine hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 80:600–610
Thom VT, Wendel M, Deussen A (2013) Regulation of ecto-5′-nucleotidase by docosahexaenoic acid in human endothelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 32:355–366
Ticho SR, Radulovacki M (1991) Role of adenosine in sleep and temperature regulation in the preoptic area of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40:33–40
Vandenbeuch A, Anderson CB, Parnes J, Enjyoji K, Robson SC, Finger TE, Kinnamon SC (2013) Role of the ectonucleotidase NTPDase2 in taste bud function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:14789–14794
Virus RM, Djuricic-Nedelson M, Radulovacki M, Green RD (1983) The effects of adenosine and 2′-deoxycoformycin on sleep and wakefulness in rats. Neuropharmacology 22:1401–1404
von Gall C, Duffield GE, Hastings MH, Kopp MD, Dehghani F, Korf HW, Stehle JH (1998) CREB in the mouse SCN: a molecular interface coding the phase-adjusting stimuli light, glutamate, PACAP, and melatonin for clockwork access. J Neurosci 18:10389–10397
von Gall C, Lewy A, Schomerus C, Vivien-Roels B, Pevét P, Korf HW, Stehle JH (2000) Transcription factor dynamics and neuroendocrine signalling in the mouse pineal gland: a comparative analysis of melatonin-deficient C57BL mice and melatonin-proficient C3H mice. Eur J Neurosci 12:964–972
Vongtau HO, Lavoie EG, Sévigny J, Molliver DC (2011) Distribution of ecto-nucleotidases in mouse sensory circuits suggests roles for nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-3 in nociception and mechanoreception. Neuroscience 193:387–398
Vorhoff T, Zimmermann H, Pelletier J, Sévigny J, Braun N (2005) Cloning and characterization of the ecto-nucleotidase NTPDase3 from rat brain: Predicted secondary structure and relation to other members of the E-NTPDase family and actin. Purinergic Signal 1:259–270
Wicht H, Korf HW, Ackermann H, Ekhart D, Fischer C, Pfeffer M (2014) Chronotypes and rhythm stability in mice. Chronobiol Int 31:27–36
Wink MR, Tamajusuku AS, Braganhol E, Casali EA, Barreto-Chaves ML, Sarkis JJ, Battastini AM (2003) Thyroid hormone upregulates ecto-5′- nucleotidase/CD73 in C6 rat glioma cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 205:107–114
Yasuo S, Yoshimura T, Ebihara S, Korf HW (2009) Melatonin transmits photoperiodic signals through the MT1 melatonin receptor. J Neurosci 29:2885–2889
Zimmermann H (2000) Extracellular metabolism of ATP and other nucleotides. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 362:299–309
Zimmermann H, Vogel M, Laube U (1993) Hippocampal localization of 5′-nucleotidase as revealed by immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience 55:105–112
Zimmermann H, Zebisch M, Sträter N (2012) Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signal 8:437–502
Zylka MJ (2011) Pain-relieving prospects for adenosine receptors and ectonucleotidases. Trends Mol Med 17:188–196
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Dr. Senckenbergische Stiftung, Frankfurt am Main. We would like to thank Dr. Hanns Ackermann (Institute for Biostatistics und Mathematic Modelling, Goethe University, Frankfurt am Main, Germany) for his kind help with the statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Homola, M., Pfeffer, M., Fischer, C. et al. Expression of ectonucleotidases in the prosencephalon of melatonin-proficient C3H and melatonin-deficient C57Bl mice: spatial distribution and time-dependent changes. Cell Tissue Res 362, 163–176 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2179-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2179-7