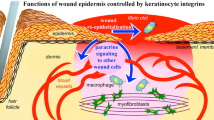
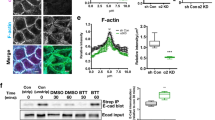
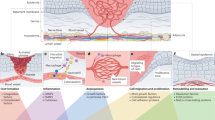
Abstract
Integrin receptors mediate the interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix. They not only provide anchorage and a physical linkage to the matrix but also participate in cell signaling and the regulation of diverse cellular functions. In the epidermis of the skin, integrins are essential for tissue structure and integrity, and, under normal homeostatic conditions, the β1 subunit specifically controls the balance between proliferation and terminal differentiation. Integrin expression can also dynamically respond to changes in the cell’s environment, and integrin-mediated adhesion is required for keratinocyte migration and re-epithelialization during wound repair. Importantly, integrins participate in keratinocyte mechanotransduction and could potentially regulate cell behavior within the altered mechanical microenvironment of a wound. While the complete functions of integrin receptors in cutaneous wound healing have yet to be determined, recent evidence suggests that cell–matrix interactions are perturbed in chronic and non-healing wounds. Integrins may therefore be a potential therapeutic target for improving wound repair and tissue regeneration.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair BD, Xiong J-P, Maddock C et al (2005) Three-dimensional EM structure of the ectodomain of integrin αVβ3 in a complex with fibronectin. J Cell Biol 168:1109–1118
Adams JC, Watt FM (1989) Fibronectin inhibits the terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes. Nature 340:307–309
Adams JC, Watt FM (1991) Expression of beta 1, beta 3, beta 4, and beta 5 integrins by human epidermal keratinocytes and non-differentiating keratinocytes. J Cell Biol 115:829–841
AlDahlawi S, Eslami A, Häkkinen L, Larjava HS (2006) The alphavbeta6 integrin plays a role in compromised epidermal wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 14:289–297. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00123.x
Ansell DM, Holden KA, Hardman MJ (2012) Animal models of wound repair: Are they cutting it? Exp Dermatol 21:581–585. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01540.x
Arthur WT, Petch LA, Burridge K (2000) Integrin engagement suppresses RhoA activity via a c-Src-dependent mechanism. Curr Biol 10:719–722
Bishop A (2008) Role of oxygen in wound healing. J Wound Care 17:399–402
Blanpain C, Fuchs E (2009) Epidermal homeostasis: a balancing act of stem cells in the skin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:207–217. doi:10.1038/nrm2636
Boekhoven J, Rubert Pérez CM, Sur S et al (2013) Dynamic display of bioactivity through host-guest chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. doi:10.1002/anie.201306278
Borradori L, Sonnenberg A (1999) Structure and function of hemidesmosomes: more than simple adhesion complexes. J Invest Dermatol 112:411–418. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00546.x
Brem H, Tomic-Canic M (2007) Cellular and molecular basis of wound healing in diabetes. J Clin Invest 117:1219–1222
Brizzi MF, Defilippi P, Rosso A et al (1999) Integrin-mediated adhesion of endothelial cells induces JAK2 and STAT5A activation: role in the control of c-fos gene expression. Mol Biol Cell 10:3463–3471
Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA (1994) Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264:569–571
Broughton G, Janis JE, Attinger CE (2006) The basic science of wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:12s–34s
Byzova TV, Goldman CK, Pampori N et al (2000) A mechanism for modulation of cellular responses to VEGF: activation of the integrins. Mol Cell 6:851–860
Calderwood DA, Campbell ID, Critchley DR (2013) Talins and kindlins: partners in integrin-mediated adhesion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:503–517. doi:10.1038/nrm3624
Carter WG, Ryan MC, Gahr PJ (1991) Epiligrin, a new cell adhesion ligand for integrin alpha 3 beta 1 in epithelial basement membranes. Cell 65:599–610
Caskey RC, Zgheib C, Morris M et al (2014) Dysregulation of collagen production in diabetes following recurrent skin injury: contribution to the development of a chronic wound. Wound Repair Regen 22:515–520. doi:10.1111/wrr.12199
Caswell PT, Chan M, Lindsay AJ et al (2008) Rab-coupling protein coordinates recycling of alpha5beta1 integrin and EGFR1 to promote cell migration in 3D microenvironments. J Cell Biol 183:143–155
Cavani A, Zambruno G, Marconi A et al (1993) Distinctive integrin expression in the newly forming epidermis during wound healing in humans. J Invest Dermatol 101:600–604
Chen CS, Mrksich M, Huang S et al (1997) Geometric control of cell life and death. Science 276:1425–1428
Chen J, Diacovo TG, Grenache DG et al (2002) The alpha(2) integrin subunit-deficient mouse: a multifaceted phenotype including defects of branching morphogenesis and hemostasis. Am J Pathol 161:337–344
Choma DP, Pumiglia K, DiPersio CM (2004) Integrin alpha3beta1 directs the stabilization of a polarized lamellipodium in epithelial cells through activation of Rac1. J Cell Sci 117:3947–3959
Choma DP, Milano V, Pumiglia KM, DiPersio CM (2007) Integrin alpha3beta1-dependent activation of FAK/Src regulates Rac1-mediated keratinocyte polarization on laminin-5. J Invest Dermatol 127:31–40. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700505
Choquet D, Felsenfeld DP, Sheetz MP (1997) Extracellular matrix rigidity causes strengthening of integrin-cytoskeleton linkages. Cell 88:39–48
Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M, Burridge K (1996) Rho-stimulated contractility drives the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions. J Cell Biol 133:1403–1415
Clark RA, Lanigan JM, DellaPelle P et al (1982) Fibronectin and fibrin provide a provisional matrix for epidermal cell migration during wound reepithelialization. J Invest Dermatol 79:264–269
Clark RA, Ashcroft GS, Spencer MJ et al (1996) Re-epithelialization of normal human excisional wounds is associated with a switch from alpha v beta 5 to alpha v beta 6 integrins. Br J Dermatol 135:46–51
Clark EA, King WG, Brugge JS et al (1998) Integrin-mediated signals regulated by members of the rho family of GTPases. J Cell Biol 142:573–586
Clark RAF, An J-Q, Greiling D et al (2003) Fibroblast migration on fibronectin requires three distinct functional domains. J Invest Dermatol 121:695–705. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12484.x
Connelly JT, Gautrot JE, Trappmann B et al (2010) Actin and serum response factor transduce physical cues from the microenvironment to regulate epidermal stem cell fate decisions. Nat Cell Biol 12:711–718. doi:10.1038/ncb2074
Costa P, Gautrot JE, Connelly JT (2014) Directing cell migration using micropatterned and dynamically adhesive polymer brushes. Acta Biomater. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2014.01.029
De S, Razorenova O, McCabe NP et al (2005) VEGF-integrin interplay controls tumor growth and vascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:7589–7594. doi:10.1073/pnas.0502935102
deHart GW, Healy KE, Jones JCR (2003) The role of alpha3beta1 integrin in determining the supramolecular organization of laminin-5 in the extracellular matrix of keratinocytes. Exp Cell Res 283:67–79
Desmoulière A, Chaponnier C, Gabbiani G (2005) Tissue repair, contraction, and the myofibroblast. Wound Repair Regen 13:7–12. doi:10.1111/j.1067-1927.2005.130102.x
DiPersio CM, Hodivala-Dilke KM, Jaenisch R et al (1997) alpha3beta1 Integrin is required for normal development of the epidermal basement membrane. J Cell Biol 137:729–742
DiPersio CM, Van der Neut R, Georges-Labouesse E et al (2000) alpha3beta1 and alpha6beta4 integrin receptors for laminin-5 are not essential for epidermal morphogenesis and homeostasis during skin development. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 17):3051–3062
Dowling J, Yu QC, Fuchs E (1996) Beta4 integrin is required for hemidesmosome formation, cell adhesion and cell survival. J Cell Biol 134:559–572
Edwards R, Harding KG (2004) Bacteria and wound healing. Curr Opin Infect Dis 17:91–96
Elosegui-Artola A, Bazellières E, Allen MD et al (2014) Rigidity sensing and adaptation through regulation of integrin types. Nat Mater 13:631–637. doi:10.1038/nmat3960
Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE (2006) Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126:677–689. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.044
Evans ND, Oreffo ROC, Healy E et al (2013) Epithelial mechanobiology, skin wound healing, and the stem cell niche. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 28:397–409. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.04.023
Frye M, Gardner C, Li ER et al (2003) Evidence that Myc activation depletes the epidermal stem cell compartment by modulating adhesive interactions with the local microenvironment. Development 130:2793–2808
Gaggioli C, Hooper S, Hidalgo-Carcedo C et al (2007) Fibroblast-led collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for RhoGTPases in leading and following cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:1392–1400. doi:10.1038/ncb1658
Gailit J, Clark RA (1996) Studies in vitro on the role of alpha v and beta 1 integrins in the adhesion of human dermal fibroblasts to provisional matrix proteins fibronectin, vitronectin, and fibrinogen. J Invest Dermatol 106:102–108
Gailit J, Clarke C, Newman D et al (1997) Human fibroblasts bind directly to fibrinogen at RGD sites through integrin alpha(v)beta3. Exp Cell Res 232:118–126. doi:10.1006/excr.1997.3512
Gandarillas A, Watt FM (1995) Changes in expression of members of the fos and jun families and myc network during terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes. Oncogene 11:1403–1407
Gardner H, Broberg A, Pozzi A et al (1999) Absence of integrin alpha1beta1 in the mouse causes loss of feedback regulation of collagen synthesis in normal and wounded dermis. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 3):263–272
Georges-Labouesse E, Messaddeq N, Yehia G et al (1996) Absence of integrin alpha 6 leads to epidermolysis bullosa and neonatal death in mice. Nat Genet 13:370–373
Geuijen CAW, Sonnenberg A (2002) Dynamics of the alpha6beta4 integrin in keratinocytes. Mol Biol Cell 13:3845–3858. doi:10.1091/mbc.02-01-0601
Giangreco A, Goldie SJ, Failla V, et al. (2010) Human skin aging is associated with reduced expression of the stem cell markers beta1 integrin and MCSP. J Invest Dermatol 30:604–608
Gregor M, Osmanagic-Myers S, Burgstaller G et al (2014) Mechanosensing through focal adhesion-anchored intermediate filaments. FASEB J 28:715–729. doi:10.1096/fj.13-231829
Grenache DG, Zhang Z, Wells LE et al (2007) Wound healing in the alpha2beta1 integrin-deficient mouse: altered keratinocyte biology and dysregulated matrix metalloproteinase expression. J Invest Dermatol 127:455–466. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700611
Grinnell F, Billingham RE, Burgess L (1981) Distribution of fibronectin during wound healing in vivo. J Invest Dermatol 76:181–189
Grinnell F, Ho CH, Wysocki A (1992) Degradation of fibronectin and vitronectin in chronic wound fluid: analysis by cell blotting, immunoblotting, and cell adhesion assays. J Invest Dermatol 98:410–416
Grose R, Hutter C, Bloch W et al (2002) A crucial role of beta 1 integrins for keratinocyte migration in vitro and during cutaneous wound repair. Development 129:2303–2315
Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, Longaker MT (2008) Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 453:314–321. doi:10.1038/nature07039
Häkkinen L, Koivisto L, Gardner H et al (2004) Increased expression of beta6-integrin in skin leads to spontaneous development of chronic wounds. Am J Pathol 164:229–242
Hamelers IH, Olivo C, Mertens AE et al (2005) The Rac activator Tiam1 is required for (alpha)3(beta)1-mediated laminin-5 deposition, cell spreading, and cell migration. J Cell Biol 171:871–881. doi:10.1083/jcb.200509172
Harding KG, Morris HL, Patel GK (2002) Healing chronic wounds. BMJ 324:160
Has C, Spartà G, Kiritsi D et al (2012) Integrin α3 mutations with kidney, lung, and skin disease. N Engl J Med 366:1508–1514. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1110813
Herouy Y, Mellios P, Bandemir E et al (2000) Autologous platelet-derived wound healing factor promotes angiogenesis via alphavbeta3-integrin expression in chronic wounds. Int J Mol Med 6:515–519
Herrick SE, Sloan P, McGurk M et al (1992) Sequential changes in histologic pattern and extracellular matrix deposition during the healing of chronic venous ulcers. Am J Pathol 141:1085–1095
Hertle MD, Adams JC, Watt FM (1991) Integrin expression during human epidermal development in vivo and in vitro. Development 112:193–206
Hertle MD, Kubler MD, Leigh IM, Watt FM (1992) Aberrant integrin expression during epidermal wound healing and in psoriatic epidermis. J Clin Invest 89:1892–1901. doi:10.1172/JCI115794
Huang XZ, Wu JF, Cass D et al (1996) Inactivation of the integrin beta 6 subunit gene reveals a role of epithelial integrins in regulating inflammation in the lung and skin. J Cell Biol 133:921–928
Huang X, Griffiths M, Wu J et al (2000) Normal development, wound healing, and adenovirus susceptibility in beta5-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol 20:755–759
Humphries JD, Wang P, Streuli C et al (2007) Vinculin controls focal adhesion formation by direct interactions with talin and actin. J Cell Biol 179:1043–1057. doi:10.1083/jcb.200703036
Hynes RO (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110:673–687
Jackson B, Peyrollier K, Pedersen E et al (2011) RhoA is dispensable for skin development, but crucial for contraction and directed migration of keratinocytes. Mol Biol Cell 22:593–605. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-10-0859
Jones PH, Watt FM (1993) Separation of human epidermal stem cells from transit amplifying cells on the basis of differences in integrin function and expression. Cell 73:713–724
Juhasz I, Murphy GF, Yan HC et al (1993) Regulation of extracellular matrix proteins and integrin cell substratum adhesion receptors on epithelium during cutaneous human wound healing in vivo. Am J Pathol 143:1458–1469
Kim JP, Zhang K, Chen JD et al (1992) Mechanism of human keratinocyte migration on fibronectin: unique roles of RGD site and integrins. J Cell Physiol 151:443–450. doi:10.1002/jcp.1041510303
Kim JP, Zhang K, Chen JD et al (1994) Vitronectin-driven human keratinocyte locomotion is mediated by the alpha v beta 5 integrin receptor. J Biol Chem 269:26926–26932
Kiritsi D, Has C, Bruckner-Tuderman L (2013) Laminin 332 in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Cell Adh Migr 7:135–141
Labat-Robert J, Leutenegger M, Llopis G et al (1984) Plasma and tissue fibronectin in diabetes. Clin Physiol Biochem 2:39–48
Larjava H, Salo T, Haapasalmi K et al (1993) Expression of integrins and basement membrane components by wound keratinocytes. J Clin Invest 92:1425–1435. doi:10.1172/JCI116719
Lawson C, Lim S-T, Uryu S et al (2012) FAK promotes recruitment of talin to nascent adhesions to control cell motility. J Cell Biol 196:223–232. doi:10.1083/jcb.201108078
Levental KR, Yu H, Kass L et al (2009) Matrix Crosslinking Forces Tumor Progression by Enhancing Integrin Signaling. Cell 139:891–906
Li A, Simmons PJ, Kaur P (1998) Identification and isolation of candidate human keratinocyte stem cells based on cell surface phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3902–3907
Liu S, Leask A (2013) Integrin β1 is required for dermal homeostasis. J Invest Dermatol 133:899–906. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.438
Liu S, Xu S, Blumbach K et al (2010) Expression of integrin beta1 by fibroblasts is required for tissue repair in vivo. J Cell Sci 123:3674–3682. doi:10.1242/jcs.070672
Longmate WM, Monichan R, Chu M-L et al (2014) Reduced fibulin-2 contributes to loss of basement membrane integrity and skin blistering in mice lacking integrin α3β1 in the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 134:1609–1617. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.10
Lopez-Rovira T, Silva-Vargas V, Watt FM (2005) Different consequences of beta1 integrin deletion in neonatal and adult mouse epidermis reveal a context-dependent role of integrins in regulating proliferation, differentiation, and intercellular communication. J Invest Dermatol 125:1215–1227
Lorenz K, Grashoff C, Torka R et al (2007) Integrin-linked kinase is required for epidermal and hair follicle morphogenesis. J Cell Biol 177:501–513. doi:10.1083/jcb.200608125
Margadant C, Raymond K, Kreft M et al (2009) Integrin alpha3beta1 inhibits directional migration and wound re-epithelialization in the skin. J Cell Sci 122:278–288. doi:10.1242/jcs.029108
Martin P (1997) Wound healing–aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276:75–81
McBeath R, Pirone DM, Nelson CM et al (2004) Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev Cell 6:483–495
McLean GW, Komiyama NH, Serrels B et al (2004) Specific deletion of focal adhesion kinase suppresses tumor formation and blocks malignant progression. Genes Dev 18:2998–3003. doi:10.1101/gad.316304
Mitchell K, Szekeres C, Milano V et al (2009) Alpha3beta1 integrin in epidermis promotes wound angiogenesis and keratinocyte-to-endothelial-cell crosstalk through the induction of MRP3. J Cell Sci 122:1778–1787. doi:10.1242/jcs.040956
Mitra SK, Hanson DA, Schlaepfer DD (2005) Focal adhesion kinase: in command and control of cell motility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:56–68. doi:10.1038/nrm1549
Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL et al (1982) The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell 31:11–24
Nemes Z, Steinert PM (1999) Bricks and mortar of the epidermal barrier. Exp Mol Med 31:5–19. doi:10.1038/emm.1999.2
Ng MR, Besser A, Danuser G, Brugge JS (2012) Substrate stiffness regulates cadherin-dependent collective migration through myosin-II contractility. J Cell Biol 199:545–563. doi:10.1083/jcb.201207148
Nobes CD, Hall A (1995) Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81:53–62
O’Toole EA, Marinkovich MP, Hoeffler WK et al (1997) Laminin-5 inhibits human keratinocyte migration. Exp Cell Res 233:330–339. doi:10.1006/excr.1997.3586
Osmanagic-Myers S, Gregor M, Walko G et al (2006) Plectin-controlled keratin cytoarchitecture affects MAP kinases involved in cellular stress response and migration. J Cell Biol 174:557–568. doi:10.1083/jcb.200605172
Paszek MJ, Zahir N, Johnson KR et al (2005) Tensional homeostasis and the malignant phenotype. Cancer Cell 8:241–254. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.08.010
Pelham RJ, Wang Y (1997) Cell locomotion and focal adhesions are regulated by substrate flexibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:13661–13665
Peltonen J, Larjava H, Jaakkola S et al (1989) Localization of integrin receptors for fibronectin, collagen, and laminin in human skin. Variable expression in basal and squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest 84:1916–1923. doi:10.1172/JCI114379
Pierschbacher MD, Ruoslahti E (1984) Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature 309:30–33
Pulkkinen L, Rouan F, Bruckner-Tuderman L et al (1998) Novel ITGB4 Mutations in Lethal and Nonlethal Variants of Epidermolysis Bullosa with Pyloric Atresia: Missense versus Nonsense. Am J Hum Genet 63:1376–1387
Raghavan S, Desai RA, Kwon Y et al (2010) Micropatterned dynamically adhesive substrates for cell migration. Langmuir 26:17733–17738. doi:10.1021/la102955m
Ramjaun AR, Hodivala-Dilke K (2009) The role of cell adhesion pathways in angiogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:521–530. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2008.05.030
Ramms L, Fabris G, Windoffer R et al (2013) Keratins as the main component for the mechanical integrity of keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:18513–18518. doi:10.1073/pnas.1313491110
Reffay M, Parrini MC, Cochet-Escartin O et al (2014) Interplay of RhoA and mechanical forces in collective cell migration driven by leader cells. Nat Cell Biol 16:217–223. doi:10.1038/ncb2917
Reichelt J (2007) Mechanotransduction of keratinocytes in culture and in the epidermis. Eur J Cell Biol 86:807–816. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2007.06.004
Reynolds LE, Conti FJ, Silva R et al (2008) alpha3beta1 integrin-controlled Smad7 regulates reepithelialization during wound healing in mice. J Clin Invest 118:965–974. doi:10.1172/JCI33538
Rice RH, Green H (1977) The cornified envelope of terminally differentiated human epidermal keratinocytes consists of cross-linked protein. Cell 11:417–422
Rice RH, Green H (1978) Relation of protein synthesis and transglutaminase activity to formation of the cross-linked envelope during terminal differentiation of the cultured human epidermal keratinocyte. J Cell Biol 76:705–711
Ridley AJ, Hall A (1992) The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell 70:389–399
Riveline D, Zamir E, Balaban NQ et al (2001) Focal contacts as mechanosensors: externally applied local mechanical force induces growth of focal contacts by an mDia1-dependent and ROCK-independent mechanism. J Cell Biol 153:1175–1186
Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD (1986) Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell 44:517–518
Schlaepfer DD, Hunter T (1997) Focal adhesion kinase overexpression enhances ras-dependent integrin signaling to ERK2/mitogen-activated protein kinase through interactions with and activation of c-Src. J Biol Chem 272:13189–13195
Schlaepfer DD, Hanks SK, Hunter T, Van der Geer P (1994) Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 372:786–791
Seltmann K, Fritsch AW, Käs JA, Magin TM (2013) Keratins significantly contribute to cell stiffness and impact invasive behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:18507–18512. doi:10.1073/pnas.1310493110
Sen CK, Gordillo GM, Roy S et al (2009) Human Skin Wounds: A Major and Snowballing Threat to Public Health and the Economy. Wound Repair Regen 17:763–771. doi:10.1111/j.1524-475X.2009.00543.x
Serrano I, Díez-Marqués ML, Rodríguez-Puyol M et al (2012) Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) modulates wound healing through regulation of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Exp Cell Res 318:2470–2481. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.08.001
Siegel DH, Ashton GH, Penagos HG et al (2003) Loss of kindlin-1, a human homolog of the Caenorhabditis elegans actin-extracellular-matrix linker protein UNC-112, causes Kindler syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 73:174–187
Singh P, Chen C, Pal-Ghosh S et al (2009) Loss of integrin alpha9beta1 results in defects in proliferation, causing poor re-epithelialization during cutaneous wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 129:217–228. doi:10.1038/jid.2008.201
Stupack DG, Cheresh DA (2004) Integrins and angiogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol 64:207–238. doi:10.1016/S0070-2153(04)64009-9
Swift ME, Burns AL, Gray KL, DiPietro LA (2001) Age-related alterations in the inflammatory response to dermal injury. J Invest Dermatol 117:1027–1035
Tadokoro S, Shattil SJ, Eto K et al (2003) Talin Binding to Integrin ß Tails: A Final Common Step in Integrin Activation. Science 302:103–106
Takashima A, Grinnell F (1985) Fibronectin-mediated keratinocyte migration and initiation of fibronectin receptor function in vitro. J Invest Dermatol 85:304–308
Thery M, Racine V, Pepin A et al (2005) The extracellular matrix guides the orientation of the cell division axis. Nat Cell Biol 7:947–953
Theveneau E, Mayor R (2013) Collective cell migration of epithelial and mesenchymal cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1251-7
Thomas GJ, Lewis MP, Whawell SA et al (2001) Expression of the alphavbeta6 integrin promotes migration and invasion in squamous carcinoma cells. J Invest Dermatol 117:67–73. doi:10.1046/j.0022-202x.2001.01379.x
Timpl R (1989) Structure and biological activity of basement membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem 180:487–502
Trappmann B, Gautrot JE, Connelly JT et al (2011) Extracellular-matrix tethering regulates stem-cell fate. Nat Mater 11:642–649. doi:10.1038/nmat3339
Tscharntke M, Pofahl R, Chrostek-Grashoff A et al (2007) Impaired epidermal wound healing in vivo upon inhibition or deletion of Rac1. J Cell Sci 120:1480–1490. doi:10.1242/jcs.03426
Tsutsumi M, Inoue K, Denda S et al (2009) Mechanical-stimulation-evoked calcium waves in proliferating and differentiated human keratinocytes. Cell Tissue Res 338:99–106. doi:10.1007/s00441-009-0848-0
Uriu K, Morelli LG, Oates AC (2014) Interplay between intercellular signaling and cell movement in development. Semin Cell Dev Biol. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.011
Van Dongen SFM, Maiuri P, Marie E et al (2013) Triggering cell adhesion, migration or shape change with a dynamic surface coating. Adv Mater Weinheim 25:1687–1691. doi:10.1002/adma.201204474
Vedula SRK, Hirata H, Nai MH et al (2014) Epithelial bridges maintain tissue integrity during collective cell migration. Nat Mater 13:87–96. doi:10.1038/nmat3814
Vignaud T, Galland R, Tseng Q et al (2012) Reprogramming cell shape with laser nano-patterning. J Cell Sci 125:2134–2140. doi:10.1242/jcs.104901
Watt FM (1983) Involucrin and Other Markers of Keratinocyte Terminal Differentiation. J Investig Dermatol 81:100s–103s
Watt FM (1989) Terminal differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1:1107–1115
Watt FM, Green H (1982) Stratification and terminal differentiation of cultured epidermal cells. Nature 295:434–436
Watt FM, Jordan PW, O’Neill CH (1988) Cell shape controls terminal differentiation of human epidermal keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:5576–5580
Watt FM, Kubler MD, Hotchin NA et al (1993) Regulation of keratinocyte terminal differentiation by integrin-extracellular matrix interactions. J Cell Sci 106(Pt 1):175–182
Weis S, Lee TT, Del Campo A, García AJ (2013) Dynamic cell-adhesive microenvironments and their effect on myogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater 9:8059–8066. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2013.06.019
White SJ, McLean WH (2005) Kindler surprise: mutations in a novel actin-associated protein cause Kindler syndrome. J Dermatol Sci 38:169–175
Wysocki AB, Grinnell F (1990) Fibronectin profiles in normal and chronic wound fluid. Lab Invest 63:825–831
Wysocki AB, Staiano-Coico L, Grinnell F (1993) Wound fluid from chronic leg ulcers contains elevated levels of metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9. J Invest Dermatol 101:64–68
Xiong J-P, Stehle T, Diefenbach B et al (2001) Crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin αVβ3. Science 294:339–345
Yang JT, Rayburn H, Hynes RO (1993) Embryonic mesodermal defects in alpha 5 integrin-deficient mice. Development 119:1093–1105
Yang C, Tibbitt MW, Basta L, Anseth KS (2014) Mechanical memory and dosing influence stem cell fate. Nat Mater 13:645–652. doi:10.1038/nmat3889
Zhao JH, Reiske H, Guan JL (1998) Regulation of the cell cycle by focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol 143:1997–2008
Zhu AJ, Haase I, Watt FM (1999) Signaling via beta1 integrins and mitogen-activated protein kinase determines human epidermal stem cell fate in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:6728–6733
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kenny, F.N., Connelly, J.T. Integrin-mediated adhesion and mechano-sensing in cutaneous wound healing. Cell Tissue Res 360, 571–582 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-2064-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-2064-9