Abstract
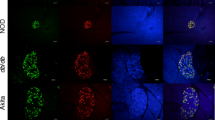
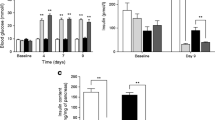
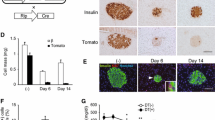
Incretins, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP)-1, have been shown to elevate plasma insulin concentration. The purpose of this study is to investigate the cellular and molecular basis of the beneficial effects of GLP-1. Normal and diabetic male Wistar rats were treated with GLP-1 (50 ng/kg body weight) for 10 weeks. At the end of the experiment, pancreatic tissues were taken for immunohistochemistry, immunoelectron microscopy and real-time polymerase chain reaction studies. Samples of blood were retrieved from the animals for the measurement of enzymes and insulin. The results show that treatment of diabetic rats with GLP-1 caused significant (P < 0.05) reduction in body weight gain and blood glucose level. GLP-1 (10−12–10−6 M) induced significant (P < 0.01) dose-dependent increases in insulin release from the pancreas of normal and diabetic rats compared to basal. Diabetes-induced abnormal liver (aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase) and kidney (blood urea nitrogen and uric acid) parameters were corrected in GLP-1-treated rats compared to controls. GLP-1 treatment induced significant (P < 0.05) elevation in the expression of pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1, heat shock protein-70, glutathione peroxidase, insulin receptor and GLP-1-receptor genes in diabetic animals compared to controls. GLP-1 is present in pancreatic beta cells and significantly (P < 0.05) increased the number of insulin-, glutathione reductase- and catalase-immunoreactive islet cells. The results of this study show that GLP-1 is co-localized with insulin and seems to exert its beneficial effects by increasing cellular concentrations of endogenous antioxidant genes and other genes involved in the maintenance of pancreatic beta cell structure and function.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DPP-4:
-
Dipeptide peptidase-IV
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- EM:
-
Electron microscopic
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- GLP-1r:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSR:
-
Glutathione Reductase
- HSP-70:
-
Heat shock protein-70
- IPGTT:
-
Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RT-PCR:
-
Real time-polymerase chain reaction
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- T1DM:
-
Type 1 DM
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 DM
- UAEU:
-
United Arab Emirates University
References
Adeghate E (1999) Effect of subcutaneous pancreatic tissue transplants on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. I. Morphological studies on normal, diabetic and transplanted pancreatic tissues. Tissue Cell 31:66–72
Adeghate E, Ponery AS (2002) Ghrelin stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas of normal and diabetic rats. J Neuroendocrinol 14:555–560
Adeghate E, Ponery AS (2004) Diabetes mellitus influences the degree of co-localization of calcitonin-gene-related-peptide with insulin and somatostatin in the rat pancreas. Pancreas 29:311–319
Amin A, Lotfy M, Mahmoud-Ghoneim D, Adeghate E, Al-Akhras MA, Al-Saadi M, Al-Rahmoun S, Hameed R (2011) Pancreas-protective effects of chlorella in STZ-induced diabetic animal model: insights into the mechanism. J Diabetes Mellit 1(3):36–45
Aragon G, Younossi ZM (2010) When and how to evaluate mildly elevated liver enzymes in apparently healthy patients. Cleve Clin J Med 77(3):195–204
Baggio LL, Drucker DJ (2007) Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterol 132:2131–2157
Bener A, Zirie M, Janahi IM, Al-Hamaq AO, Musallam M, Wareham NJ (2009) Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and its risk factors in a population-based study of Qatar. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 84(1):99–106
Bouwens L, Rooman I (2005) Regulation of pancreatic beta-cell mass. Physiol Rev 85(4):1255–1270
Bucinskaite V, Tolessa T, Pedersen J, Rydqvist B, Zerihun L, Holst JJ, Hellström PM (2009) Receptor-mediated activation of gastric vagal afferents by glucagon-like peptide-1 in the rat. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:978–978
Bulchandani D, Nachnani J, Eaton C, Hamburg M (2009) Association of Exenatide with liver enzymes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 19(3):114–115
Buse JB, Rosenstock J, Sesti G, Schmidt WE, Montanya E, Brett JH, Zychma M, Blonde L (2009) Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type 2 diabetes: a 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational, open-label trial (LEAD-6). Lancet 374(4):39–47
Buteau J, El-Assaad W, Rhodes CJ, Rosenberg L, Joly E, Prentki M (2004) Glucagon-like peptide-1 prevents beta cell glucolipotoxicity. Diabetologia 47:806–815
Caluwaerts S, Lambin S, van Bree R, Peeters H, Vergote I, Verhaeghe J (2007) Diet-induced obesity in gravid rats engenders early hyperadiposity in the offspring. Metabolism 56:1431–1438
Cejkova P, Fojtikova M, Cerna M (2009) Immunomodulatory role of prolactin in diabetes development. Autoimmun Rev 9(1):23–27
Cernea S, Raz I (2011) Therapy in the early stage: incretins. Diabetes Care 34(2):S264–S271
Druker DJ (2005) Therapeutic strategic based on GLP-1 pathway. Adv Stud Med 5(10E):S1069–S1073
Fehmann HC, Hering BJ, Wolf MJ, Brandhorst H, Brandhorst D, Bretzel RG, Federlin K, Göke B (1995) The effects of glucagon-like peptide-I (GLP-I) on hormone secretion from isolated human pancreatic islets. Pancreas 11:196–200
Fisher TL, White MF (2004) Signaling pathways: the benefits of good communication. Curr Biol 14:R1005–R1007
Fujita A, Sasaki H, Ogawa K, Okamoto K, Matsuno S, Matsumoto E, Furuta H, Nishi M, Nakao T, Tsuno T, Taniguchi H, Nanjo K (2005) Increased gene expression of antioxidant enzymes in KKAy diabetic mice but not in STZ diabetic mice. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 69(2):113–119
Garber AJ (2011) Incretin effects on β-cell function, replication, and mass. Diabetes Care 34(2):S258–S263
Gezginci-Oktayoglu S, Bolkent S (2009) Exendin-4 exerts its effects through the NGF/p75NTR system in diabetic mouse pancreas. Biochem Cell Biol 87(4):641–651
Girard J (2008) The incretins: from the concept to their use in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Part A: incretins: concept and physiological functions. Diabetes Metab 34:550–559
Habib AM, Richards P, Rogers GJ, Reimann F, Gribble FM (2013) Co-localisation and secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 and peptide YY from primary cultured human L cells. Diabetologia 56:1413–1416
Hamouchene H, Arlt VM, Giddings I, Phillips DH (2011) Influence of cell cycle on responses of MCF-7 cells to benzo[a]pyrene. BMC Med Genom 12:333
Hare KJ, Vilsbøll T, Asmar M, Deacon CF, Knop FK, Holst JJ (2010) The glucagonostatic and insulinotropic effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 contribute equally to its glucose-lowering action. Diabetes 59:1765–1770
Heller RS, Kieffer TJ, Habener JF (1997) Insulinotropic glucagon-like peptide I receptor expression in glucagon-producing alpha-cells of the rat endocrine pancreas. Diabetes 46(5):785–791
Holst JJ (2008) The physiology and pharmacology of incretins in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab 10:14–21
Hutt DM, Powers ET, Balch WE (2009) The proteostasis boundary in misfolding diseases of membrane traffic. FEBS Lett 583:2639–2646
Islam MS (2010) Calcium signaling in the islets. Adv Exp Med Biol 654:235–259
Kanitkara M, Bhonde RR (2008) Curcumin treatment enhances islet recovery by induction of heat shock response proteins, Hsp70 and heme oxygenase-1, during cryopreservation. Life Sci 82(3–4):182–189
Karaca M, Magnan C, Kargar C (2009) Functional pancreatic beta-cell mass: involvement in type 2 diabetes and therapeutic intervention. Diabetes Metab 35:77–84
Kawahito S, Kitahata H, Oshita S (2009) Problems associated with glucose toxicity: role of hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol 15(33):4137–4142
Kitamura T, Kahn CR, Accili D (2003) Insulin receptor knockout mice. Annu Rev Physiol 65:313–332
Kjems LL, Holst JJ, Vølund A, Madsbad S (2003) The influence of GLP-1 on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: effects on beta-cell sensitivity in type 2 and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes 52:380–386
Kumar PJ, Clark ML (2007) Diabetes mellitus and other disorders of metabolism. In: Kumar PJ, Clark ML (eds) Clinical medicine, 6th edn. Saunders, London, pp 1069–1121
Larsen MO (2009) Beta-cell function and mass in type 2 diabetes. Dan Med J 56:153–164
Leibiger B, Leibiger IB, Moede T, Kemper S, Kulkarni RN, Kahn CR, de Vargas LM, Berggren P-O (2001) Selective insulin signaling through A and B insulin receptors regulates transcription of insulin and glucokinase genes in pancreatic beta cells. Mol Cell 7(3):559–570
Liu Q, Adams L, Broyde A, Fernandez R, Baron AD, Parkes DG (2010) The exenatide analogue AC3174 attenuates hypertension, insulin resistance, and renal dysfunction in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol 9(32):1–10
Lotfy M, Singh J, Rashed H, Tariq S, Zilahi E, Adeghate E (2014) Mechanism of the beneficial and protective effects of exenatide in diabetic rats. J Endocrinol 220(3):291–304
Mayhew TM, Lucocq JM (2011) Multiple-labelling immunoEM using different sizes of colloidal gold: alternative approaches to test for differential distribution and colocalization in subcellular structures. Histochem Cell Biol 135:317–326
Montrose-Rafizadeh C, Wang Y, Janczewski AM, Henderson TE, Egan JM (1997) Overexpression of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor in an insulin-secreting cell line enhances glucose responsiveness. Mol Cell Endocrinol 130(1–2):109–117
Mudaliar S, Henry RR (2010) Effects of incretin hormones on β-cell mass and function, body weight, and hepatic and myocardial function. Am J Med 123(3):S19–S27
Park S, Dong X, Fisher TL, Dunn S, Omer AK, Weir G, White MF (2006) Exendin-4 uses Irs2 signaling to mediate pancreatic beta cell growth and function. J Biol Chem 281(2):1159–1168
Patel SK, Goyal RK, Anand IS, Shah JS, Patel HU, Patel CN (2006) Glucagon like peptide-1: a new therapeutic target for diabetes mellitus. Indian J Pharmacol 38(4):231–237
Perfeitti R, Zhou J, Doyle ME, Egan J (2000) Glucagon-like peptide-1 induces cell proliferation and pancreatic-duodenum homeobox-1 expression and increases endocrine cell mass in the pancreas of old, glucose-intolerant rats. Endocrinol 141(12):4600–4605
Portha B, Tourrel-Cuzin C, Movassat J (2011) Activation of the GLP-1 receptor signalling pathway: a relevant strategy to repair a deficient beta-cell mass. Exp Diabetes Res 2011:376509
Puddu A, Mach F, Nencioni A, Viviani GL, Montecucco F (2013) An emerging role of glucagon-like peptide-1 in preventing advanced-glycation-end-product-mediated damages in diabetes. Mediat Inflamm 2013:591056
Robertson RP, Harmon JS (2007) Pancreatic islet β-cell and oxidative stress: the importance of glutathione peroxidase. FEBS Lett 581:3743–3748
Romaní-Pérez M, Outeiriño-Iglesias V, Gil-Lozano M, González-Matías LC, Mallo F, Vigo E (2013) Pulmonary GLP-1 receptor increases at birth and exogenous GLP-1 receptor agonists augmented surfactant-protein levels in litters from normal and nitrofen-treated pregnant rats. Endocrinol 154(3):1144–1155
Salehi M, Aulinger BA, D’Alessio DA (2008) Targeting β-cell mass in type 2 diabetes: promise and limitations of new drugs based on incretins. Endocr Rev 29(3):367–379
Schwartz EA, Koska J, Mullin MP, Syoufi I, Schwenke DC, Reaven PD (2010) Exenatide suppresses postprandial elevations in lipids and lipoproteins in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance and recent onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 212(1):217–222
Shu T, Zhu Y, Wang H, Lin Y, Ma Z, Han X (2011) AGEs decrease insulin synthesis in pancreatic β-cell by repressing Pdx-1 protein expression at the post-translational level. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18782
Song WJ, Seshadri M, Ashraf U, Mdluli T, Mondal P, Keil M, Azevedo M, Kirschner LS, Stratakis CA, Hussain MA (2011) Snapin mediates incretin action and augments glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Cell Metab 13(3):308–319
Srinivasan K, Ramarao P (2007) Animal models in type 2 diabetes research: an overview. Indian J Med Res 125:451–472
Stanley S, Wynne K, McGowan B, Bloom S (2005) Hormonal regulation of food intake. Physiol Rev 85:1131–1158
Suen PM, Zou C, Zhang YA, Lau TK, Chan J, Yao KM, Leung PS (2008) PDZ-domain containing-2 (PDZD2) is a novel factor that affects the growth and differentiation of human fetal pancreatic progenitor cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:789–803
Townsend T (2000) A decade of diabetes research and development. Int J Diabetes Metab 8:88–92
Vaghasiya JD, Sheth NR, Bhalodia YS, Jivani NP, Shailesh M, Jivani N (2010) Exenatide protects renal ischemia reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 30(4):217–225
Vetter ML, Cardillo S, Rickels MR, Iqbal N (2009) Narrative review: effect of bariatric surgery on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med 150:94–103
Whalley NM, Pritchard LE, Smith DM (2011) White A. Processing of proglucagon to GLP-1 in pancreatic α-cells: is this a paracrine mechanism enabling GLP-1 to act on β-cells? J Endocrinol 211:99–106
Wideman RD, Kieffer TJ (2004) Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide as a regulator of beta cell function and fate. Horm Metab Res 36:782–786
Wong ML, Medrano JF (2005) Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation. BioTech 39:75–85
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by a grant from the United Arab Emirates University.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author contributions
ML, JS and EA planned and wrote the manuscript. HR played a major role in the in vitro study and immunohistochemistry. ST made contribution to the transmission electron microscopy section and EZ played a major role in the gene expression study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lotfy, M., Singh, J., Rashed, H. et al. The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 in the management of diabetes mellitus: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Cell Tissue Res 358, 343–358 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1959-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1959-9