Abstract
The eukaryotic Golgi apparatus is characterized by a stack of flattened cisternae that are surrounded by transport vesicles. The organization and function of the Golgi require Golgi matrix proteins, including GRASPs and golgins, which exist primarily as fiber-like bridges between Golgi cisternae or between cisternae and vesicles. In this review, we highlight recent findings on Golgi matrix proteins, including their roles in maintaining the Golgi structure, vesicle tethering, and novel, unexpected functions. These new discoveries further our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that maintain the structure and the function of the Golgi, as well as its relationship with other cellular organelles such as the centrosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane organelle that functions as the hub in the secretory pathway in almost all eukaryotic cells, including those of animals, plants and fungi (Dacks 2011). It is comprised of stacks of flattened cisternal membranes, which are surrounded by transport vesicles (Ladinsky et al. 1999). In vertebrates, Golgi stacks are connected by tubules to form a ribbon-like structure that localizes adjacent to the nucleus; in contrast, the Golgi stacks are dispersed throughout the cytoplasm in flies, plants and fungi (Ladinsky et al. 1999; Rambourg and Clermont 1990). Despite its structured organization, the Golgi is a highly dynamic organelle that undergoes rapid disassembly/reassembly throughout cell cycle progression, upon experimental manipulation, and during massive flows of cargo proteins or membranes. The unique morphology and dynamics of the Golgi apparatus have prompted numerous studies aimed at understanding the underlying mechanisms of Golgi structure formation and function. Early electron-microscopy studies demonstrated inter-cisternal connections between Golgi cisternae (Franke et al. 1972; Franke and Scheer 1972; Mollenhauer 1965; Mollenhauer and Morre 1998). These inter-cisternal connections are comprised of proteins that mediate cisternal stacking, because mild proteolysis removes these connections and results in Golgi unstacking (Cluett and Brown 1992). In addition, thin fibers have been observed to connect transport vesicles with Golgi cisternae via high resolution electron microscopy (EM) (Orci et al. 1998). EM studies have also demonstrated a “ribosome exclusion zone” surrounding the Golgi apparatus, suggestive of a protein network that extends into the cytoplasm (Lowe 2011; Shorter and Warren 2002). In 1994, Warren and colleagues isolated a detergent and salt-resistant protein complex, thus introducing the concept of “Golgi matrix” proteins (Slusarewicz et al. 1994). The first identified component of the Golgi matrix was GM130 (Nakamura et al. 1995), an extended rod-like protein that localized to the cis-Golgi (Alvarez et al. 2001). Numerous Golgi matrix proteins have been discovered since then, including Golgi reassembly stacking proteins (GRASPs) and golgins, which are vital for maintaining the Golgi structural organization and regulating protein trafficking through the Golgi stack (Table 1). Treatment with brefeldin A (BFA), a fungal metabolite that inactivates the small GTPase ADP-ribosylation factor-1 (ARF1), blocks the assembly of COPI-coated vesicles and redistributes Golgi enzymes and golgins harboring a transmembrane domain into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via tubular connections between the Golgi and the ER (Bascom et al. 1999; Klausner et al. 1992; Orci et al. 1991). However, some peripheral Golgi matrix proteins, including GM130 and GRASPs, remain in small Golgi tubulovesicular remnants distinct from the ER, which could reform a perinuclear ribbon-like structure (Seemann et al. 2000a), suggesting a requirement for Golgi matrix proteins in maintaining Golgi structure and identity. To perform these functions, the Golgi matrix proteins must be highly dynamic to adapt to the rapid morphological changes of the Golgi during cell cycle progression, during massive cargo flow, or upon experimental treatment. Several peripheral Golgi matrix proteins can undergo rapid exchange between the membrane-associated pool and the cytoplasm revealed by live cell imaging (Ward et al. 2001). The mechanisms that target or dissociate those proteins to or from particular subdomains of the Golgi membrane remain unclear.
Because of the important roles of these Golgi matrix proteins, several review articles have focused on these proteins (Lupashin and Sztul 2005; Ramirez and Lowe 2009; Short et al. 2005). In recent years, new interacting proteins and functions of Golgi matrix proteins have been reported. Several Golgi-localized proteins have been identified and categorized as golgins because they contain predicted coiled-coil domains. In this article, we discuss recent progress in this field.
Golgi reassembly stacking proteins (GRASPs)
GRASPs in Golgi stack and ribbon formation
GRASPs, including GRASP65 and GRASP55, were originally identified as Golgi stacking factors in an in vitro assay that reconstituted the cell cycle-regulated Golgi disassembly and reassembly process. Antibodies against GRASP proteins block the reformation of Golgi stacks, but not the regrowth of Golgi cisternae (Barr et al. 1997; Shorter et al. 1999). Both GRASP65 and GRASP55 are peripheral membrane proteins that attach to the Golgi membrane via an N-terminal myristic acid. GRASP65 localizes to the cis-Golgi cisternae, whereas GRASP55 localizes to the medial/trans-Golgi cisternae (Barr et al. 1997; Shorter et al. 1999). Their peripheral association with the Golgi membrane has been demonstrated to allow rapid exchange between the membrane-associated pool and cytoplasmic pool (Ward et al. 2001), which is consistent with the dynamic characteristics of the Golgi and accommodates the cisternal maturation model (Losev et al. 2006; Matsuura-Tokita et al. 2006). However, there were some inconsistencies in the literature concerning the involvement of GRASPs in Golgi stack formation in vivo. Microinjection of GRASP65 antibodies into mitotic cells was reported to inhibit Golgi reassembly in the post-mitotic daughter cells (Wang et al. 2003). Initial RNA interference experiments confirmed the role of GRASP65 in cisternal stacking, wherein GRASP65 depletion led to a reduction in the number of cisternae in the stacks (Sutterlin et al. 2005). However, it was also reported that GRASP65 or GRASP55 depletion did not affect Golgi stack formation but resulted in Golgi ribbon unlinking (Feinstein and Linstedt 2008; Puthenveedu et al. 2006) or defective cell division (Sutterlin et al. 2005). A recent study using systematic electron microscopy illustrated that depletion of either GRASP65 or GRASP55 caused a reduction in the number of cisternae per stack, whereas simultaneous depletion of both GRASP65 and GRASP55 resulted in severe Golgi unstacking in 80% of HeLa cells, which was partially rescued by the expression of either GRASP (Tang et al. 2010; Xiang and Wang 2010). These results strongly indicate that GRASPs play complementary and essential roles in Golgi cisternal stacking in vertebrates (Xiang and Wang 2010) (Fig. 1a). Whether GRASP proteins mediate Golgi stacking in other organisms remains elusive. In addition to the Golgi, GRASP homologs in budding yeast and flies also localize to the ER exit sites (Behnia et al. 2007; Kondylis et al. 2005; Levi et al. 2010). Depletion of the sole GRASP homolog dGRASP in Drosophila S2 cells affected Golgi stacks in approximately 30% of cells, whereas cooperative depletion of dGRASP and dGM130 converted Golgi stacks to clusters of vesicles, tubules and single cisternae (Kondylis et al. 2005). Furthermore, the presence of a GRASP homolog does not dictate the presence of Golgi stacks. For example, S. cerevisiae has a GRASP homolog, but the Golgi cisternae remain as isolated discs, indicative of other GRASP functions in budding yeast (Levi et al. 2010). In contrast, plant cells have Golgi stacks but lack GRASP homologs, suggesting the presence of unrelated factors mediating cisternal stacking in plant cells (Vinke et al. 2011). Taken together, GRASPs may have gained a stacking function during evolution.
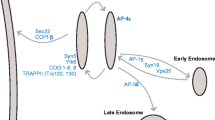
A schematic of new features of Golgi matrix proteins. a GRASP65 and GRASP55, two homologous proteins localized to the cis and medial-to-trans Golgi cisternae, respectively, mediate cisternal stacking by forming cell cycle-regulated oligomers. The depletion of GRASP65 and GRASP55 causes disassembly of the Golgi stacks. b GMAP-210, a cis-Golgi localized golgin, is composed of a 38 aa N-terminal ALPS motif, a C-terminal GRAB domain and six coiled-coil domains. The ALPS motif binds to highly curved membranes, whereas the GRAB domain binds to a flat membrane, which is stabilized by Arf-GTP. This novel structure suggests that GMAP-210 asymmetrically tethers the flat and curved membranes. Reprinted and modified from Drin et al. (2008) with permission from the journal publisher. c A model of GCC185 transferring from a vesicle to the Golgi membrane. Left A cytosolic GCC185 dimer is first recruited to the Rab9-bearing vesicles and interacts with Golgi-bound GCC185 via an unknown protein (X), which is followed by SNARE pairing (not shown). Middle GCC185 is targeted to the Golgi membranes by an interaction with Rab6, which may also promote Arl1 binding to the GRIP domain of GCC185. Right Golgi-anchored GCC185 interacts with CLASP, which promotes microtubule assembly at the Golgi apparatus. Inset: the model of Rab6 and Arl1 bound to the GCC185 Rab-binding domain (RBD) and GRIP domain, respectively. Reprinted and modified from Burguete et al. 008) with permission from the journal publisher. d GM130, a cis Golgi-localized coiled-coil protein originally found in the GM130-p115-giantin complex that is involved in ER-to-Golgi trafficking, interacts with AKAP450, which recruits γ-tubulin to the Golgi apparatus and participates in the organization of non-centrosomal microtubules that are critical for leading edge transport and directed migration (Efimov et al. 2007; Rivero et al. 2009)
How do GRASP proteins mediate Golgi stack formation? The vertebrate GRASP proteins form homodimers that further oligomerize via the N-terminal PDZ domain. These oligomers can cross-link magnetic dynal beads in vitro or mitochondria in vivo (Sengupta et al. 2009; Tang et al. 2010; Wang et al. 2003, 2005; Xiang and Wang 2010). This property provides a possible mechanism for GRASP proteins to link Golgi membranes into stacks (Fig. 1a) (Lowe 2011; Wang 2008). GRASP65 also interacts with GM130, which is required for GRASP65 membrane association (Barr et al. 1998). In combination with the N-myristoylation, GRASP65 is dual-anchored onto the membrane in an orientation that favors trans-oligomerization (Bachert and Linstedt 2011). The Golgi undergoes cell cycle-dependent disassembly and reassembly. Accordingly, the Golgi stacking factors, GRASP65 and GRASP55, are also subjected to cell cycle-dependent regulation. GRASP65 is sequentially phosphorylated by Cdk1 and Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) at the onset of mitosis (Lin et al. 2000; Preisinger et al. 2005; Wang et al. 2003), whereas GRASP55 is mitotically phosphorylated by ERK2 and Cdk1 (Jesch et al. 2001; Xiang and Wang 2010). Phosphorylation of the GRASPs disrupts their oligomerization and prevents cisternal stacking (Tang et al. 2010; Wang et al. 2003, 2005; Xiang and Wang 2010). GRASP dephosphorylation is required for post-mitotic Golgi stack formation (Wang 2008). GRASP65 is dephosphorylated by PP2A after mitosis (Tang et al. 2008), whereas the enzyme that dephosphorylates GRASP55 remains to be identified. A similar mechanism may also regulate Golgi membrane remodeling in interphase cells. For example, the expression of a non-phosphorylatable GRASP65 mutant inhibited the reorientation of the Golgi toward the leading edge in a wound-healing assay (Bisel et al. 2008). These results demonstrate that GRASPs stack Golgi cisternal membranes by forming phosphorylation-regulated trans-oligomers (Lowe 2011; Vinke et al. 2011; Wang and Seemann 2011).
Similarly, GRASP65 and GRASP55 trans-oligomers can also link Golgi stacks into a ribbon. Depletion of either GRASP65 or GRASP55 converted the Golgi ribbon into separated stacks, as shown by fluorescence and electron microscopy. FRAP (fluorescence recovery after photobleaching) experiments suggested that GRASP65 and GRASP55 are required for the lateral fusion of Golgi cisternae (Feinstein and Linstedt 2008; Puthenveedu et al. 2006). Additionally, the expression of GRASPs on the outer member of mitochondria was shown to lead to mitochondrial aggregation (Bachert and Linstedt 2011; Sengupta et al. 2009), indicating that either GRASP65 or GRASP55 alone is sufficient to link Golgi stacks into a ribbon. Because Golgi ribbon formation occurs only in vertebrates, even though GRASP homologs are found in yeast and invertebrates, the role of GRASP in ribbon formation, which is similar to its role in stacking, may have been gained during evolution.
New functions of the GRASP proteins
In addition to Golgi structure formation, GRASPs have been reported to participate in various cellular processes, including specific cargo transport, unconventional and noncanonical secretion, apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, microtubule organization and cell migration (Vinke et al. 2011). GRASP65 and GRASP55 are involved in specific cargo transport and enzyme retention by binding to their cytosolic domains. Both GRASP65 and GRASP55 interact with the p24 cargo receptor family, which is required for the efficient retention of the p24 cargo receptors in the Golgi apparatus (Barr et al. 2001). GRASP55 interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-α) via its first PDZ domain, and this interaction is required for TGF-α transport (Kuo et al. 2000). GRASP65 and GRASP55 also interact via their PDZ domains with a specific class of cargo bearing a C-terminal valine, such as CD8a and Frizzled 4, and are required sequentially for their efficient transport to the plasma membranes through the Golgi (D'Angelo et al. 2009). All these proteins contain a di-valine motif in their cytosolic tail that interacts with the PDZ domain of the GRASP proteins. Taken together, GRASPs may function as the cargo receptors or chaperones for a specific class of cargo proteins. In the budding yeast, the GRASP65 ortholog Grh1 contributes to the ER-to-Golgi traffic (Behnia et al. 2007).
Recently, a novel function for GRASPs in unconventional secretion has been reported. Depletion of the putative GRASP ortholog in Dictyostelium discoideum (Kinseth et al. 2007) or in Pichia pastoris (Duran et al. 2010; Manjithaya et al. 2010) inhibited the secretion of AcbA, a 10-kDa polypeptide that lacks an apparent signal sequence. In Dictyostelium, AcbA was found in vesicles that were subjected to fusion with the plasma membrane, and GRASP was functioning at a later step, leading to the docking/fusion of these vesicles at the cell surface (Cabral et al. 2010). In addition, the Rabouille group demonstrated that during Drosophila epithelial remodeling, proteins involved in cell adhesion and junction formation, including the alpha subunits of integrin, were transported to the plasma membrane in a noncanonical secretory pathway that bypassed the Golgi. Surprisingly, the sole Drosophila ortholog of GRASP, dGRASP, localizes to the plasma membrane in these cells, which is required for the deposition of integrins (Schotman et al. 2008). The precise role of GRASP in unconventional and noncanonical secretion remains elusive, and a similar role for GRASPs in mammalian cells has not been reported.
During apoptosis, the Golgi apparatus is fragmented into dispersed clusters of tubulovesicular membranes, and several Golgi matrix proteins are cleaved by caspases (Hicks and Machamer 2005). GRASP65 cleavage by caspase 3 has been demonstrated to be required for the Golgi fragmentation during apoptosis. Expression of a caspase-resistant GRASP65 mutant partially preserved cisternal stacking and inhibited the breakdown of the Golgi ribbon (Lane et al. 2002). In addition, overexpression of the C-terminal half of GRASP65 inhibited Golgi fragmentation and delayed apoptosis in neurons (Nakagomi et al. 2007). GRASP65 depletion resulted in aberrant spindle formation that may cause apoptosis (Sutterlin et al. 2005), although similar observations have not been reported by other groups (Puthenveedu et al. 2006; Tang et al. 2010; Xiang and Wang 2010). The caspase cleavage sites on GRASP65 are at the C-terminal serine-proline rich (SPR) domain and are not conserved between GRASP65 and GRASP55.
Recently, GRASP65 and GRASP55 have been implicated in cell cycle control. Microinjection of an antibody against the C-terminus of GRASP65 inhibited Golgi fragmentation and delayed mitotic entry. However, when the Golgi was fragmented prior to the injection, the mitotic block was alleviated (Sutterlin et al. 2002), suggestive of a G2/M checkpoint function for Golgi ribbon fragmentation. The expression of the GRASP domain of GRASP65 or phosphorylation-defective GRASP65 and GRASP55 also inhibited mitotic progression (Duran et al. 2008; Sutterlin et al. 2005; Yoshimura et al. 2005). Expression of these mutants inhibited mitotic Golgi unstacking and ribbon unlinking (Feinstein and Linstedt 2008; Sengupta et al. 2009; Tang et al. 2010; Wang et al. 2005), suggesting a direct association between the Golgi structure, or its disassembly at the onset of mitosis, and cell cycle progression. Interestingly, the expression of C-terminal peptide (amino acids 351–454) of GRASP55, which are not directly involved in Golgi structure formation, also inhibited Golgi fragmentation and mitotic entry (Duran et al. 2008). GRASP proteins, which are regulated by and interact with mitotic kinases, may govern cell cycle progression by modulating the mitotic kinase activity and localization (Colanzi and Corda 2007; Preisinger et al. 2005).
Golgi and centrosome reorient toward the leading edge of stimulated cells to allow the cell to migrate, the reorientation is abrogated by a non-phosphorylatable GRASP65 mutant (Bisel et al. 2008). Golgi membrane fragmentation alleviated the block, indicating that the centrosome reorientation depends on the remodeling of the Golgi (Bisel et al. 2008). Additionally, Golgi remodeling in interphase cells may occur by a similar mechanism as the phosphorylation of GRASP proteins in mitosis. Furthermore, depletion of GRASP65 led to aberrant spindle formation during cell division (Sutterlin et al. 2005), suggesting that GRASP65 may also regulate centrosome localization in mitotic cells.
Recent discoveries on golgins as membrane tethers
Golgins are a family of Golgi-associated coiled-coil proteins that are necessary for vesicle docking and Golgi integrity (Barr and Short 2003; Ramirez and Lowe 2009; Satoh et al. 2005; Short et al. 2005; Waters and Pfeffer 1999). Most golgins are peripheral proteins that are anchored on the Golgi membrane by one end and are predicted to exhibit an extended configuration due to their coiled-coil domains, which makes them excellent candidates for tethering membranes over relatively long distances. In addition, flexible regions between the predicted coiled-coil domains allow golgins to undergo conformational changes, which may be needed to position two membranes close enough for fusion (Barr and Short 2003). Many golgins interact with Rab family small GTPases (Sinka et al. 2008). These interactions may recruit golgins to specific subcompartments of the Golgi stack, or regulate their functions. Rabs cycle between the GDP-bound inactive and GTP-bound active forms, wherein the latter becomes membrane-associated and recruits interacting proteins termed effectors. Therefore, Rabs could regulate specific vesicle docking events by controlling the association of tethering factors with specific membranes. Moreover, Rabs may recruit multiple effectors to a specific site in a cooperative manner to allow for sequential or efficient vesicle docking events (Barr and Short 2003). Tethering normally leads to membrane fusion, such as in membrane trafficking, post-mitotic Golgi cisternal formation, and ribbon formation (Malsam et al. 2005; Pfeffer 2010), but may exhibit additional functions in special cases. For example, the tethering factor p115 is temporarily required in the early steps of stacking during post-mitotic Golgi stack formation (Shorter and Warren 1999). Several insights into golgins as membrane tethers are listed below.
The GM130-p115-giantin tether in anterograde protein transport
The first isolated Golgi matrix protein, GM130, contains 6 predicted coiled-coil domains and is predominantly found in the central region of the cis cisternae (Alvarez et al. 2001; Nakamura et al. 1995). GM130 forms a stable complex with GRASP65, and this interaction is required for correct localization of GRASP65 (Barr et al. 1998). Both GM130 and GRASPs remain in tubulovesicular remnants distinct from the ER when cells are treated with BFA (Seemann et al. 2000a). GM130 is required for the fusion of COPII vesicles with cis-Golgi cisternae, a process that is regulated by the Rab1 GTPase (Moyer et al. 2001). GM130 also interacts with p115, a golgin that interacts with a specialized set of COPII vesicle-associated SNAREs (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors), which promotes the targeting of COPII vesicles to the Golgi membranes (Allan et al. 2000). p115 also binds giantin on the COPI vesicles and promotes their docking (Malsam et al. 2005; Sonnichsen et al. 1998). Although the GM130-p115-giantin complex is currently one of the best-studied tethering complexes, unanswered questions persist. For example, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor trafficking is defective at non-permissive temperatures (>39.5°C) in CHO IdlG cells that lack detectable GM130, but receptor trafficking is normal at permissive temperatures (Vasile et al. 2003). How a lack of GM130 function is overcome at the permissive temperatures remains unknown.
CASP and golgin-84 in retrograde trafficking
CASP is one of a few golgins that contains a transmembrane domain. CASP was initially demonstrated to play a role in the secretory pathway, where the depletion of its Saccharomyces cerevisiae homolog, COY1, restored normal growth to cells lacking the Golgi SNARE Gos1p (Gillingham et al. 2002). CASP interacts with golgin-84, which is concentrated at the lateral rims of the Golgi stack (Diao et al. 2003). Both CASP and golgin-84 are transported to the ER upon BFA treatment (Bascom et al. 1999; Gillingham et al. 2002; Satoh et al. 2003). Unlike the GM130-p115-giantin tether that binds COPI vesicles containing the p24 cargo receptor family protein and anterograde cargo, the CASP-golgin-84 complex binds retrograde transport vesicles containing Golgi enzymes, suggesting that the two sets of tethering factors recruit different subpopulations of COPI vesicles and confirming vesicle tethering specificity (Malsam et al. 2005).
GMAP210 tethers curved membranes to flat membranes
GMAP-210 is a cis Golgi-localized golgin that is recruited to the Golgi via the interaction with Arf1GTP through its C-terminal GRIP-related ARF-binding (GRAB) domain (Cardenas et al. 2009). Overexpression of GMAP-210 blocked ER-to-Golgi trafficking and resulted in Golgi fragmentation (Gillingham et al. 2004; Rios et al. 2004). Similar to GM130, GMAP-210 remains in Golgi remnants after BFA treatment (Rios et al. 2004). Perhaps the most striking insight into GMAP-210 concerns its biological properties responsible for membrane tethering. A structural study of GMAP-210 revealed that its two ends bind membranes of different curvatures. The amphipathic ArfGAP1 Lipid Packing Sensor (ALPS) motif at the distal N-terminus preferentially binds to highly curved vesicle membranes, whereas the C-terminal attaches to flat membranes, such as Golgi cisternal membranes, through Arf1GTP (Drin et al. 2008) (Fig. 1b). The structural characteristics support the idea that GMAP-210 tethers curved membranes of tubules and vesicles to flat membranes such as the Golgi cisternae, which is confirmed by in vitro assays (Drin et al. 2007). It is also consistent with the electron microscopy observation of thin fibers between transport vesicles and Golgi cisternae. In vivo studies also suggest that GMAP210 may tether periphery Golgi elements to flat cisternae (Cardenas et al. 2009). The tethering function of GMAP-210 may be regulated by Rab GTPases. Similar to all golgins studied to date, GMAP-210 binds Rab GTPases (Sinka et al. 2008), which allows dynamic regulation of GMAP-210-mediated vesicle tethering.
GMAP-210 also targets the cilia component IFT20 to the cis-Golgi, likely through the interaction with the coiled-coil domains, and this function may be independent of the tethering function of GMAP-210. GMAP-210 deficiency resulted in shorter primary cilia and reduced membrane protein polycystin-2 levels in cilia, suggesting that GMAP-210 and IFT20 function together in sorting membrane components to primary cilia. GMAP-210-deficient mice die at birth due to heart and lung defects (Follit et al. 2008), which may result from the incorrect sorting of membrane components. In an independent report, the depletion of GMAP-210 caused skeletal dysplasia in mice (Smits et al. 2010).
TMF/ARA160
TMF/ARA160 was isolated as an HIV-1 TATA element modulatory factor (TMF) and has also been characterized as a coactivator (ARA160) for the androgen receptor (Mori and Kato 2002). It was later recognized as a golgin that binds Golgi membranes through the interaction with Rab6, wherein depletion of TMF/ARA160 caused modest Golgi fragmentation in Normal rat kidney (NRK) cells (Fridmann-Sirkis et al. 2004). All TMF/ARA160 homologs, conserved among yeast, flies, and humans, harbor predicted coiled-coil domains (Fridmann-Sirkis et al. 2004). TMF/ARA160 was shown to colocalize with giantin, but not with ERGIC53, GM130, mannosidase II, golgin-97, or TGN46, by immunofluorescence microscopy. The TMF/ARA160 signal encased the Rab6-positive Golgi structures. Even after a 10-min BFA treatment, TMF/ARA160 colocalized with Rab6 on tubular structures. Immunoperoxidase electron microscopy revealed that TMF/ARA160 is concentrated at the budding structures localized at the tips of cisternae. Because vesicle budding occurs at the rims of cisternae, the localization of TMF/ARF160 indicates that it may function as a tethering factor in vesicle transport. Consistently, TMF/ARA160 depletion displaced GalNAc-T2 N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-2 (GalNAc-T2) from the Golgi or blocked the retrograde transport of endocytosed Shiga toxin from early/recycling endosomes to the trans-Golgi network (Yamane et al. 2007). These phenotypes indicate that TMF/ARA160 may function as a tethering factor in retrograde vesicle transport.
GCC88, GCC185 and GRIP-domain-containing golgins
In addition to Rabs, other small GTPases may also regulate the targeting and function of golgins. For example, the GRIP domain-containing golgins interact with ARF-like GTPases Arl1 and Arl3 via the GRIP domain. The GRIP domain was originally identified as a C-terminal domain of about 50 amino acids that is conserved across a group of Golgi-localized coiled-coiled proteins. It is characterized by an invariant tyrosine at position 4 and a phenylalanine/tyrosine at position 12 (Kjer-Nielsen et al. 1999; Munro and Nichols 1999). Initially, GRIP domains were identified in golgin-245 and golgin-97, which localize to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) (Luke et al. 2005; Munro and Nichols 1999). Subsequently, two additional golgins, GCC88 and GCC185, were shown to bind to the TGN via their GRIP domains (Luke et al. 2003). GRIP domain-containing golgins are released after approximately 15 min of treatment with BFA when the Golgi disassembles (Jackson 2003), suggesting that the golgin membrane association depends on an intact Golgi structure but not on the Arl proteins, which are direct targets of BFA. Overexpression of GCC88 resulted in large electron-dense structures extending from the trans-Golgi, suggesting a role for GCC88 in TGN organization. GCC185 contains 5–6 predicted coiled-coil domains that allow interaction with multiple small GTPases. In addition to Arl1, GCC185 is also associated with 14 Rab GTPases in a yeast two-hybrid experiment, and its interactions with Rab1, Rab6 and Rab9 have been confirmed biochemically (Burguete et al. 2008; Hayes et al. 2009). A recent study has shown that two small GTPases cooperate to target GCC185 onto the membrane. First, GCC185 is recruited to the Golgi via its interaction with Rab6, which recognizes a two-fold symmetric surface on a coiled-coil domain immediately adjacent to a C-terminal GRIP domain (Burguete et al. 2008). The binding of Rab6 promotes the association of Arl1 with the GRIP domain, and the two small GTPases dual anchor GCC185 onto the Golgi membrane. Because the core domain of Rab6 can be 105 Å from the membrane surface due to the hyper-variable domain that consists of 34 amino acids, an interaction with Rab6 may allow an extended configuration of GCC185 and facilitate its function as a tethering factor (Fig. 1c).
As a Rab9 effector, GCC185 is required for the recycling of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor (MPR) from endosomes to the TGN. Depletion of GCC185 enhanced the degradation of mannose 6-phosphate receptors and resulted in an accumulation of cargo in peripheral Rab9-positive vesicles (Reddy et al. 2006), suggesting that GCC185 is involved in the docking of late endosome-derived, Rab9-bearing transport vesicles at the TGN. Fusion of these vesicles with the Golgi membranes requires a SNARE complex composed of syntaxin 10, syntaxin 16, Vti1a, and VAMP3, whereas fusion of vesicles containing TGN38/46 required syntaxin 6 but neither syntaxin 10 nor GCC185 (Ganley et al. 2008), indicating two distinct endosome to trans-Golgi transport routes. GCC185 depletion also resulted in a block of shiga toxin trafficking to the Golgi apparatus and an accumulation of shiga toxin in Rab11-positive endosomes (Derby and Gleeson 2007). This result suggests that GCC185 participates in the transport between recycling endosomes and the TGN, although an interaction between GCC185 and Rab11 has not been observed. These discoveries of novel GCC185 function ascribe several new features to golgins: (1) specific Rabs can recruit different effectors, and golgins can also interact with different Rabs via multiple coiled-coil domains and function in different transport events (Burguete et al. 2008; Sinka et al. 2008); (2) the structural study of GCC185 supports the predicted extended configuration of golgins; and (3) tethering confers specificity to vesicle transport, which has been illustrated for CASP (Malsam et al. 2005).
SCYL1BP1, IIGP165 and NECC
Several new golgins have recently been identified, including SCYL1BP1, IIGP165 and NECC, based on their Golgi localization and predicted coiled-coil domains. Their functions remain largely unknown or are distinct from that of original golgins.
SCYL1BP1 was originally identified as a binding partner of N-terminal kinase-like protein (Scyl1) (Di et al. 2003). It contains a large number of charged amino acids and two predicted coiled-coil domains. Scyl1, which persists in the Golgi remnants after BFA treatment, is a Golgi protein that binds the COPI coat and regulates Golgi to ER trafficking (Burman et al. 2010). SCYL1BP1 localizes to the Golgi apparatus via an interaction with Rab6. Although the mechanism remains unclear, genetic studies have demonstrated that loss-of-function mutations in SCYL1BP1 are responsible for the autosomal recessive disorder Gerodermia osteodysplastica, which is characterized by wrinkly skin and osteoporosis (Hennies et al. 2008). It would be intriguing to explore the mechanisms that dictate how the defects in the secretory pathway result in wrinkly skin and osteoporosis, which are aging-related pathologies.
The Ischemia-Inducible Golgin Protein 165 (IIGP165) was cloned from ischemic rat brains and has a predicted molecular weight of 165 kDa. The full-length protein localizes to the Golgi apparatus, whereas the cleaved fragments, produced by serum and glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis, translocate to the nucleus. Cooperating with the protein kinase Akt, IIGP165 protects HeLa cells from serum deprivation-induced apoptosis, which requires Akt-induced IIGP165 phosphorylation (Ran et al. 2007). However, the mechanism by which IIGP165 is targeted to the Golgi membrane and its Golgi-related functions are currently unknown.
NECC1 and NECC2 contain several predicted coiled-coil domains (7 for NECC1, 8 for NECC2) and a short transmembrane domain at their C-termini. Exogenously expressed NECC colocalizes with GM130 and VSVG-ts045 at the Golgi complex and is therefore categorized as a golgin. Both proteins are predominantly expressed in (neuro)endocrine tissues, whereas an alternative NECC1 splicing product, which lacks the TMD, is expressed exclusively in endocrine tissues. The functions of these proteins remain undetermined (Cruz-Garcia et al. 2007).
Recent insights into the roles of Golgi matrix proteins in Golgi and microtubule organization
Although the predominant function of golgins is to tether vesicles to adjacent Golgi membranes during protein transport, evidence from recent studies alludes to broader functions. In addition, new interacting partners have been discovered, and unexpected functions of these Golgi matrix proteins have been characterized, such as Golgi stack and ribbon formation, microtubule organization, signaling and the regulation of apoptosis and the cell cycle (Table 1). In mammalian cells, tens of Golgi stacks are laterally linked to form a ribbon-like structure adjacent to the nucleus. The formation of a Golgi ribbon depends on the Golgi matrix proteins and microtubules. Centrosome-derived microtubules are known to bring Golgi stacks to the pericentrosomal region through microtubule minus-end-directed motor proteins. Recent studies have revealed that the Golgi can also nucleate microtubules by recruiting a pool of γ-tubulin. Additionally, the Golgi-orientated microtubules maintain Golgi stacks in close proximity and facilitate tubular connections between them. Several Golgi matrix proteins have been shown to participate in the assembly of non-centrosomal microtubules. Furthermore, the organization of the Golgi has been shown to affect the position of the centrosome. We would like to discuss the recent discoveries regarding Golgi matrix protein function in Golgi ribbon formation, microtubule organization, and centrosome positioning.
The GRASP65-GM130 complex in Golgi ribbon formation and microtubule organization
Similar to GRASP65 described above, GM130 was reported to participate in Golgi ribbon formation, whereby depletion of GM130 by siRNA caused fragmentation of the Golgi ribbon and aberrant glycosylation of plasma membrane proteins (Puthenveedu et al. 2006). GM130 may contribute to Golgi ribbon formation in two ways. GM130 targets GRASP65 on the rim of cis cisternae, prompting GRASP65 to form oligomers that promote lateral linking of cisternae (Puthenveedu et al. 2006). Additionally, GM130 recruits a γ-tubulin complex to the cis-Golgi via the A-kinase anchoring protein 450 (AKAP450) and nucleates non-centrosomal microtubules (Rivero et al. 2009). These Golgi-originated microtubules arrange Golgi stacks in close proximity and facilitate Golgi ribbon formation (Fig. 1d). In addition to nucleating non-centrosomal microtubules, GM130 controls centrosome organization by binding to a cdc42 GEF, Tuba. GM130 depletion results in abnormal and mispositioned centrosomes that are unable to organize microtubules, which results in defective cell migration in interphase as well as in the multiplication of centrosomes, aberrant multi-polar spindles, and improper mitotic cell division (Kodani et al. 2009; Kodani and Sutterlin 2008).
GMAP-210 links cis-Golgi to the microtubule cytoskeleton
As mentioned previously, GMAP-210 is a cis Golgi-localized golgin that functions in asymmetric membrane tethering. Similar to GM130, GMAP-210 also recruits the γ-tubulin complex to the cis-Golgi membrane and facilitates the formation of the Golgi ribbon (Linstedt 2004). Depletion of GMAP-210 causes Golgi ribbon unlinking and inhibited directional cell migration (Yadav et al. 2009). Multiple Golgi matrix proteins mediate the recruitment of the γ-tubulin complex to the Golgi, whether these proteins cooperate in the assembly of non-centrosomal microtubules is currently unknown.
GCC185 interacts with CLASP and promotes microtubule polymerization from the TGN
Unlike GRASP65, GM130, and GMAP210 that localize to cis-Golgi, GCC185 localizes to the TGN. In addition to its function in membrane tethering, GCC185 interacts with CLASP, a microtubule plus-end binding protein that selectively coats the non-centrosomal-originated microtubules (Fig. 1c). These Golgi-emanating microtubules preferentially orient toward the leading edge in motile cells and contribute to asymmetric cargo transport. CLASP coats and stabilizes microtubule seeds at the early stages of growth. Because GCC185 recruits CLASP to TGN, depletion of CLASP or GCC185 impairs microtubule assembly at the Golgi but not those originating from centrosomes (Efimov et al. 2007). Depletion of GCC185 also causes Golgi ribbon unlinking (Derby et al. 2007; Reddy et al. 2006), although it is unclear whether GCC185 is directly involved in maintaining Golgi integrity or whether the observed effect is caused by the alteration of the microtubule cytoskeleton.
Bicaudal-D and microtubule-dependent transport
Bicaudal-D is a novel golgin that interacts with Rab6 on the trans-Golgi membranes. Human Bicaudal-D contains 3 coiled-coil domains, and the highly conserved 3rd coiled-coil domain interacts with Rab6 (Matanis et al. 2002). Bicaudal-D dissociates from the Golgi membrane upon BFA treatment (Hoogenraad et al. 2001). Unlike other Golgi matrix proteins discussed above, Bicaudal-D interacts with the dynein–dynactin complex associated with microtubules (Hoogenraad et al. 2001). The N-terminus of bicaudal-D binds to the dynein motor and induces microtubule minus-end-directed movement independent of cargo content (Hoogenraad et al. 2003), whereas the C-terminus determines cargo specificity. The overexpression of the Bicaudal-D1 N-terminus inhibited the microtubule minus-end-directed distribution of organelles (Matanis et al. 2002). Bicaudal-D may also regulate asymmetric transport. The Drosophila homolog of Bicaudal-D, Bic-D, is required for the apical migration of differentiating photoreceptor (R-cell) precursor nuclei (Houalla et al. 2005). Bic-D is also responsible for ensuring oocyte polarity in Drosophila by regulating the delivery of secretory pathway components, such as the TGF homolog Gurken, to the plasma membrane and organizing microtubule plus-ends at the oocyte posterior (Januschke et al. 2007).
Current understanding of the relationship between the Golgi and the centrosome
The centrosome functions as the major microtubule organization center, and the perinuclear localization of the Golgi and exocytic transport rely on their interactions with centrosome-originated microtubules. However, recent discoveries of Golgi matrix proteins indicate a bidirectional relationship between the Golgi and centrosome. First, several cis-Golgi matrix proteins, such as GM130 and GMAP-210, recruit γ-tubulin and nucleate the assembly of non-centrosomal microtubules (Rios et al. 2004; Rivero et al. 2009). The trans-Golgi matrix protein GCC185 recruits the microtubule plus-end binding protein CLASP to stabilize the initial growth of these non-centrosomal microtubules (Efimov et al. 2007). These Golgi-originated microtubules play important roles in asymmetric transport. Second, Golgi and Golgi matrix proteins regulate centrosome localization. The reorientation of centrosomes in stimulated cells depends on the remodeling of the Golgi and the phosphorylation of GRASP65 (Bisel et al. 2008). GM130 also regulates centrosome positioning via the cdc42 GEF, Tuba (Kodani et al. 2009).
The precise function of the Golgi ribbon is unclear. Several studies have described the basic functions of the Golgi apparatus, such as membrane trafficking and modification of secretory proteins, to be unaffected when the Golgi is fragmented into separate ministacks (Diao et al. 2003; Yadav et al. 2009). Recent studies also suggest that the Golgi ribbon facilitates lateral diffusion of Golgi enzymes and glycosylation of cargo proteins and that Golgi fragmentation due to the depletion of GM130, GRAPS65, or GRASP55 cause glycosylation defects. In addition, the Golgi ribbon is oriented toward the cell surface where exocytosis occurs, such as the leading edges of migrating cells (Bisel et al. 2008). The depletion of Golgi matrix proteins, such as GM130, GMAP-210, and GCC185, interferes with asymmetric transport (Efimov et al. 2007; Rios et al. 2004; Rivero et al. 2009), although it is unclear whether this effect results from Golgi ribbon fragmentation or from the disruption of non-centrosomal microtubules. A very recent study has reported that two signaling pathways influence Golgi morphogenesis to regulate the polarization of neuronal cells via GM130. Specifically, the Stk25 kinase phosphorylates GM130 and promotes condensed Golgi and axon development, while the Reelin-Dab signaling pathway antagonizes the Stk25 pathway, which results in an extended Golgi morphology and dendrite development (Matsuki et al. 2010). GM130 also recruits the mammalian Ste20 kinases YSK1 and MST4 to the Golgi membranes, which are required for directed cell migration (Preisinger et al. 2004), concomitantly with these signaling events. These results suggest an association between protein trafficking, cytoskeleton organization and cell migration.
Golgins in yeast, plants and other species
TbG63 is a golgin that localizes to the Golgi via its C-terminus and interacts with TbRab1A-GTP in the procyclic form of the Trypanosoma brucei parasite. TbG63 is involved in the Golgi architecture or the growth of the parasites in the bloodstream (Ramirez et al. 2008). The Drosophila Lava lamp is a novel golgin that is required for cellularization by promoting dynein-based Golgi motility (Papoulas et al. 2005). In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, in which the Golgi membranes do not form stacks, the GRASP65 orthologue, Grh1, contributes to ER-to-Golgi trafficking (Behnia et al. 2007). Grp1p is the yeast homolog of golgin-160 that may be involved in the ER-to-Golgi transport. Grp1p is localized to the cis-Golgi and is required for its structural organization; the loss of Grp1 leads to a growth defect at higher temperatures,(Kim 2003). Six putative Arabidopsis golgins, GC1 to GC6, have been extensively reviewed by Latijnhouwers et al. (2007). These golgins have similarities to Golgi matrix proteins identified in mammals and yeast, implicating a role for golgins in maintaining the Golgi structure and tethering in plant cells. These studies suggest that the roles for Golgi matrix proteins in Golgi structure formation and protein trafficking are conserved during evolution.
Conclusion
In most eukaryotic cells, the Golgi is composed of flattened cisternae that are arranged in stacks with numerous vesicles in the vicinity. Golgi matrix proteins, including GRASPs and golgins, are important for proper Golgi organization and function. In mammalian cells, recent studies have demonstrated critical roles for GRASP65 and GRASP55 in Golgi stacking, ribbon formation, specific cargo transport, apoptosis and cell cycle control. In D. discoideum, P. pastoris and flies, GRASPs have been shown to play a role in unconventional and noncanonical secretion. Golgins are involved in membrane tethering and are predicted to exhibit an extended configuration due to multiple coiled-coil domains. The most recent structural study on GMAP-210 demonstrates that it can bind to two membranes with different curvatures, which provides a possible mechanism for how vesicles could be tethered to flat Golgi cisternae. Extensive analysis of GCC185 supports the hypothesis that multiple small GTPases can cooperate to regulate the function of golgins and that golgins have an extended configuration on the membranes. The studies with CASP and GCC185 confirm that tethering factors confer specificity to vesicle transport. New functions for golgins have been reported, which may be distinct from the canonical functions of Golgi integrity and vesicle transport. In addition, the relationship between the Golgi and the centrosome has been reassessed. Even though the Golgi stacks are brought to the perinuclear ribbon by centrosome-originated microtubules, the positioning of the centrosome is regulated by Golgi organization and Golgi matrix proteins. Several general conclusions can be made from these studies. Golgi matrix proteins may have broad but redundant functions. The events occurring at the Golgi apparatus may be highly regulated and cargo- and localization-specific. Finally, Golgi-mediated protein trafficking is linked to various cellular processes such as cell cycle progression.
Future studies to further our understanding of the functions of the Golgi matrix proteins are warranted. Purified proteins may be placed into an in vitro assay similar to the system used to demonstrate the function of GMAP-210 in membrane tethering (Drin et al. 2008). Mutations in golgins have been linked to several human diseases; thus, these mutants may be useful tools for determining the functions of the proteins under physiological and pathological conditions. Manipulation of Golgi matrix proteins in multicellular organisms using available transgenic techniques may also provide insight into the function of various matrix proteins in specific tissues and during development. Because Golgi matrix proteins often have broad but redundant functions, a comparative study of a group of related matrix proteins may help understand their functions and relationships. Collaboration between different laboratories is encouraged because testing the functions with different methods, as well as using a variety of model systems, may enhance progress, provide unbiased conclusions, and help to understand the evolution of the secretory pathway.
References
Al-Dosari M, Alkuraya FS (2009) A novel missense mutation in SCYL1BP1 produces geroderma osteodysplastica phenotype indistinguishable from that caused by nullimorphic mutations. Am J Med Genet A 149A:2093–2098
Allan BB, Moyer BD, Balch WE (2000) Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science 289:444–448
Alvarez C, Garcia-Mata R, Hauri HP, Sztul E (2001) The p115-interactive proteins GM130 and giantin participate in endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi traffic. J Biol Chem 276:2693–2700
Alzhanova D, Hruby DE (2007) A host cell membrane protein, golgin-97, is essential for poxvirus morphogenesis. Virology 362:421–427
Bachert C, Linstedt AD (2011) Dual anchoring of the GRASP membrane tether promotes trans pairing. J Biol Chem 285:16294–16301
Barr FA, Short B (2003) Golgins in the structure and dynamics of the Golgi apparatus. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:405–413
Barr FA, Puype M, Vandekerckhove J, Warren G (1997) GRASP65, a protein involved in the stacking of Golgi cisternae. Cell 91:253–262
Barr FA, Nakamura N, Warren G (1998) Mapping the interaction between GRASP65 and GM130, components of a protein complex involved in the stacking of Golgi cisternae. EMBO J 17:3258–3268
Barr FA, Preisinger C, Kopajtich R, Korner R (2001) Golgi matrix proteins interact with p24 cargo receptors and aid their efficient retention in the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol 155:885–891
Bascom RA, Srinivasan S, Nussbaum RL (1999) Identification and characterization of golgin-84, a novel Golgi integral membrane protein with a cytoplasmic coiled-coil domain. J Biol Chem 274:2953–2962
Behnia R, Barr FA, Flanagan JJ, Barlowe C, Munro S (2007) The yeast orthologue of GRASP65 forms a complex with a coiled-coil protein that contributes to ER to Golgi traffic. J Cell Biol 176:255–261
Bisel B, Wang Y, Wei JH, Xiang Y, Tang D, Miron-Mendoza M, Yoshimura S, Nakamura N, Seemann J (2008) ERK regulates Golgi and centrosome orientation towards the leading edge through GRASP65. J Cell Biol 182:837–843
Bundis F, Neagoe I, Schwappach B, Steinmeyer K (2006) Involvement of Golgin-160 in cell surface transport of renal ROMK channel: co-expression of Golgin-160 increases ROMK currents. Cell Physiol Biochem 17:1–12
Burguete AS, Fenn TD, Brunger AT, Pfeffer SR (2008) Rab and Arl GTPase family members cooperate in the localization of the golgin GCC185. Cell 132:286–298
Burman JL, Hamlin JN, McPherson PS (2010) Scyl1 regulates Golgi morphology. PLoS ONE 5:e9537
Cabral M, Anjard C, Malhotra V, Loomis WF, Kuspa A (2010) Unconventional secretion of AcbA in Dictyostelium discoideum through a vesicular intermediate. Eukaryot Cell 9:1009–1017
Cardenas J, Rivero S, Goud B, Bornens M, Rios RM (2009) Golgi localisation of GMAP210 requires two distinct cis-membrane binding mechanisms. BMC Biol 7:56
Chen Y, Chen PL, Chen CF, Sharp ZD, Lee WH (1999) Thyroid hormone, T3-dependent phosphorylation and translocation of Trip230 from the Golgi complex to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4443–4448
Chiu R, Novikov L, Mukherjee S, Shields D (2002) A caspase cleavage fragment of p115 induces fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus and apoptosis. J Cell Biol 159:637–648
Cluett EB, Brown WJ (1992) Adhesion of Golgi cisternae by proteinaceous interactions: intercisternal bridges as putative adhesive structures. J Cell Sci 103:773–784
Colanzi A, Corda D (2007) Mitosis controls the Golgi and the Golgi controls mitosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:386–393
Cruz-Garcia D, Vazquez-Martinez R, Peinado JR, Anouar Y, Tonon MC, Vaudry H, Castano JP, Malagon MM (2007) Identification and characterization of two novel (neuro)endocrine long coiled-coil proteins. FEBS Lett 581:3149–3156
Dacks J (2011) Golgi evolution. In: Warren G, Rothman JE (eds) The Golgi. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor
D'Angelo G, Prencipe L, Iodice L, Beznoussenko G, Savarese M, Marra P, Di Tullio G, Martire G, De Matteis MA, Bonatti S (2009) GRASP65 and GRASP55 sequentially promote the transport of C-terminal valine bearing cargoes to and through the golgi complex. J Biol Chem 284:34849–34860
Derby MC, Gleeson PA (2007) New insights into membrane trafficking and protein sorting. Int Rev Cytol 261:47–116
Derby MC, Lieu ZZ, Brown D, Stow JL, Goud B, Gleeson PA (2007) The trans-Golgi network golgin, GCC185, is required for endosome-to-Golgi transport and maintenance of Golgi structure. Traffic 8:758–773
Di Y, Li J, Fang J, Xu Z, He X, Zhang F, Ling J, Li X, Xu D, Li L, Li YY, Huo K (2003) Cloning and characterization of a novel gene which encodes a protein interacting with the mitosis-associated kinase-like protein NTKL. J Hum Genet 48:315–321
Diao A, Rahman D, Pappin DJ, Lucocq J, Lowe M (2003) The coiled-coil membrane protein golgin-84 is a novel rab effector required for Golgi ribbon formation. J Cell Biol 160:201–212
Drin G, Casella JF, Gautier R, Boehmer T, Schwartz TU, Antonny B (2007) A general amphipathic alpha-helical motif for sensing membrane curvature. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:138–146
Drin G, Morello V, Casella JF, Gounon P, Antonny B (2008) Asymmetric tethering of flat and curved lipid membranes by a golgin. Science 320:670–673
Duran JM, Kinseth M, Bossard C, Rose DW, Polishchuk R, Wu CC, Yates J, Zimmerman T, Malhotra V (2008) The role of GRASP55 in Golgi fragmentation and entry of cells into mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 19:2579–2587
Duran JM, Anjard C, Stefan C, Loomis WF, Malhotra V (2010) Unconventional secretion of Acb1 is mediated by autophagosomes. J Cell Biol 188:527–536
Efimov A, Kharitonov A, Efimova N, Loncarek J, Miller PM, Andreyeva N, Gleeson P, Galjart N, Maia AR, McLeod IX, Yates JR 3rd, Maiato H, Khodjakov A, Akhmanova A, Kaverina I (2007) Asymmetric CLASP-dependent nucleation of noncentrosomal microtubules at the trans-Golgi network. Dev Cell 12:917–930
Eystathioy T, Jakymiw A, Fujita DJ, Fritzler MJ, Chan EK (2000) Human autoantibodies to a novel Golgi protein golgin-67: high similarity with golgin-95/gm 130 autoantigen. J Autoimmun 14:179–187
Feinstein TN, Linstedt AD (2008) GRASP55 regulates Golgi ribbon formation. Mol Biol Cell 19:2696–2707
Follit JA, San Agustin JT, Xu F, Jonassen JA, Samtani R, Lo CW, Pazour GJ (2008) The Golgin GMAP210/TRIP11 anchors IFT20 to the Golgi complex. PLoS Genet 4:e1000315
Franke WW, Scheer U (1972) Structural details of dictyosomal pores. J Ultrastruct Res 40:132–144
Franke WW, Kartenbeck J, Krien S, VanderWoude WJ, Scheer U, Morre DJ (1972) Inter- and intracisternal elements of the Golgi apparatus. A system of membrane-to-membrane cross-links. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 132:365–380
Fridmann-Sirkis Y, Siniossoglou S, Pelham HR (2004) TMF is a golgin that binds Rab6 and influences Golgi morphology. BMC Cell Biol 5:18
Ganley IG, Espinosa E, Pfeffer SR (2008) A syntaxin 10-SNARE complex distinguishes two distinct transport routes from endosomes to the trans-Golgi in human cells. J Cell Biol 180:159–172
Gillingham AK, Pfeifer AC, Munro S (2002) CASP, the alternatively spliced product of the gene encoding the CCAAT-displacement protein transcription factor, is a Golgi membrane protein related to giantin. Mol Biol Cell 13:3761–3774
Gillingham AK, Tong AH, Boone C, Munro S (2004) The GTPase Arf1p and the ER to Golgi cargo receptor Erv14p cooperate to recruit the golgin Rud3p to the cis-Golgi. J Cell Biol 167:281–292
Hayes GL, Brown FC, Haas AK, Nottingham RM, Barr FA, Pfeffer SR (2009) Multiple Rab GTPase binding sites in GCC185 suggest a model for vesicle tethering at the trans-Golgi. Mol Biol Cell 20:209–217
Hennies HC, Kornak U, Zhang H, Egerer J, Zhang X, Seifert W, Kuhnisch J, Budde B, Natebus M, Brancati F, Wilcox WR, Muller D, Kaplan PB, Rajab A, Zampino G, Fodale V, Dallapiccola B, Newman W, Metcalfe K, Clayton-Smith J, Tassabehji M, Steinmann B, Barr FA, Nurnberg P, Wieacker P, Mundlos S (2008) Gerodermia osteodysplastica is caused by mutations in SCYL1BP1, a Rab-6 interacting golgin. Nat Genet 40:1410–1412
Hicks SW, Machamer CE (2005) Golgi structure in stress sensing and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1744:406–414
Hoogenraad CC, Akhmanova A, Howell SA, Dortland BR, De Zeeuw CI, Willemsen R, Visser P, Grosveld F, Galjart N (2001) Mammalian Golgi-associated Bicaudal-D2 functions in the dynein-dynactin pathway by interacting with these complexes. EMBO J 20:4041–4054
Hoogenraad CC, Wulf P, Schiefermeier N, Stepanova T, Galjart N, Small JV, Grosveld F, De Zeeuw CI, Akhmanova A (2003) Bicaudal D induces selective dynein-mediated microtubule minus end-directed transport. EMBO J 22:6004–6015
Houalla T, Hien Vuong D, Ruan W, Suter B, Rao Y (2005) The Ste20-like kinase misshapen functions together with Bicaudal-D and dynein in driving nuclear migration in the developing Drosophila eye. Mech Dev 122:97–108
Jackson CL (2003) Membrane traffic: Arl GTPases get a GRIP on the Golgi. Curr Biol 13:R174–R176
Jakymiw A, Raharjo E, Rattner JB, Eystathioy T, Chan EK, Fujita DJ (2000) Identification and characterization of a novel Golgi protein, golgin-67. J Biol Chem 275:4137–4144
Januschke J, Nicolas E, Compagnon J, Formstecher E, Goud B, Guichet A (2007) Rab6 and the secretory pathway affect oocyte polarity in Drosophila. Development 134:3419–3425
Jesch SA, Lewis TS, Ahn NG, Linstedt AD (2001) Mitotic phosphorylation of Golgi reassembly stacking protein 55 by mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK2. Mol Biol Cell 12:1811–1817
Jing J, Junutula JR, Wu C, Burden J, Matern H, Peden AA, Prekeris R (2010) FIP1/RCP binding to Golgin-97 regulates retrograde transport from recycling endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. Mol Biol Cell 21:3041–3053
Kim DW (2003) Characterization of Grp1p, a novel cis-Golgi matrix protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:370–378
Kinseth MA, Anjard C, Fuller D, Guizzunti G, Loomis WF, Malhotra V (2007) The Golgi-associated protein GRASP is required for unconventional protein secretion during development. Cell 130:524–534
Kjer-Nielsen L, Teasdale RD, Van Vliet C, Gleeson PA (1999) A novel Golgi-localisation domain shared by a class of coiled-coil peripheral membrane proteins. Curr Biol 9:385–388
Klausner RD, Donaldson JG, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1992) Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol 116:1071–1080
Kodani A, Sutterlin C (2008) The Golgi protein GM130 regulates centrosome morphology and function. Mol Biol Cell 19:745–753
Kodani A, Kristensen I, Huang L, Sutterlin C (2009) GM130-dependent control of Cdc42 activity at the Golgi regulates centrosome organization. Mol Biol Cell 20:1192–1200
Kondylis V, Spoorendonk KM, Rabouille C (2005) dGRASP localization and function in the early exocytic pathway in Drosophila S2 cells. Mol Biol Cell 16:4061–4072
Kuo A, Zhong C, Lane WS, Derynck R (2000) Transmembrane transforming growth factor-alpha tethers to the PDZ domain-containing, Golgi membrane-associated protein p59/GRASP55. EMBO J 19:6427–6439
Ladinsky MS, Mastronarde DN, McIntosh JR, Howell KE, Staehelin LA (1999) Golgi structure in three dimensions: functional insights from the normal rat kidney cell. J Cell Biol 144:1135–1149
Lane JD, Lucocq J, Pryde J, Barr FA, Woodman PG, Allan VJ, Lowe M (2002) Caspase-mediated cleavage of the stacking protein GRASP65 is required for Golgi fragmentation during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 156:495–509
Latijnhouwers M, Gillespie T, Boevink P, Kriechbaumer V, Hawes C, Carvalho CM (2007) Localization and domain characterization of Arabidopsis golgin candidates. J Exp Bot 58:4373–4386
Levi SK, Bhattacharyya D, Strack RL, Austin JR 2nd, Glick BS (2010) The yeast GRASP Grh1 colocalizes with COPII and is dispensable for organizing the secretory pathway. Traffic 11:1168–1179
Lieu ZZ, Derby MC, Teasdale RD, Hart C, Gunn P, Gleeson PA (2007) The golgin GCC88 is required for efficient retrograde transport of cargo from the early endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. Mol Biol Cell 18:4979–4991
Lin CY, Madsen ML, Yarm FR, Jang YJ, Liu X, Erikson RL (2000) Peripheral Golgi protein GRASP65 is a target of mitotic polo-like kinase (Plk) and Cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12589–12594
Linstedt AD (2004) Positioning the Golgi apparatus. Cell 118:271–272
Linstedt AD, Jesch SA, Mehta A, Lee TH, Garcia-Mata R, Nelson DS, Sztul E (2000) Binding relationships of membrane tethering components. The giantin N terminus and the GM130 N terminus compete for binding to the p115 C terminus. J Biol Chem 275:10196–10201
Lock JG, Hammond LA, Houghton F, Gleeson PA, Stow JL (2005) E-cadherin transport from the trans-Golgi network in tubulovesicular carriers is selectively regulated by golgin-97. Traffic 6:1142–1156
Losev E, Reinke CA, Jellen J, Strongin DE, Bevis BJ, Glick BS (2006) Golgi maturation visualized in living yeast. Nature 441:1002–1006
Lowe M (2011) Structural organization of the Golgi apparatus. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23:85–93
Lowe M, Lane JD, Woodman PG, Allan VJ (2004) Caspase-mediated cleavage of syntaxin 5 and giantin accompanies inhibition of secretory traffic during apoptosis. J Cell Sci 117:1139–1150
Lu L, Hong W (2003) Interaction of Arl1-GTP with GRIP domains recruits autoantigens Golgin-97 and Golgin-245/p230 onto the Golgi. Mol Biol Cell 14:3767–3781
Lu L, Tai G, Hong W (2004) Autoantigen Golgin-97, an effector of Arl1 GTPase, participates in traffic from the endosome to the trans-golgi network. Mol Biol Cell 15:4426–4443
Luke MR, Kjer-Nielsen L, Brown DL, Stow JL, Gleeson PA (2003) GRIP domain-mediated targeting of two new coiled-coil proteins, GCC88 and GCC185, to subcompartments of the trans-Golgi network. J Biol Chem 278:4216–4226
Luke MR, Houghton F, Perugini MA, Gleeson PA (2005) The trans-Golgi network GRIP-domain proteins form alpha-helical homodimers. Biochem J 388:835–841
Lupashin V, Sztul E (2005) Golgi tethering factors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1744:325–339
Maag RS, Mancini M, Rosen A, Machamer CE (2005) Caspase-resistant Golgin-160 disrupts apoptosis induced by secretory pathway stress and ligation of death receptors. Mol Biol Cell 16:3019–3027
Malsam J, Satoh A, Pelletier L, Warren G (2005) Golgin tethers define subpopulations of COPI vesicles. Science 307:1095–1098
Mancini M, Machamer CE, Roy S, Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA, Casciola-Rosen LA, Rosen A (2000) Caspase-2 is localized at the Golgi complex and cleaves golgin-160 during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 149:603–612
Manjithaya R, Anjard C, Loomis WF, Subramani S (2010) Unconventional secretion of Pichia pastoris Acb1 is dependent on GRASP protein, peroxisomal functions, and autophagosome formation. J Cell Biol 188:537–546
Matanis T, Akhmanova A, Wulf P, Del Nery E, Weide T, Stepanova T, Galjart N, Grosveld F, Goud B, De Zeeuw CI, Barnekow A, Hoogenraad CC (2002) Bicaudal-D regulates COPI-independent Golgi-ER transport by recruiting the dynein-dynactin motor complex. Nat Cell Biol 4:986–992
Matsuki T, Matthews RT, Cooper JA, Van Der Brug MP, Cookson MR, Hardy JA, Olson EC, Howell BW (2010) Reelin and stk25 have opposing roles in neuronal polarization and dendritic Golgi deployment. Cell 143:826–836
Matsuura-Tokita K, Takeuchi M, Ichihara A, Mikuriya K, Nakano A (2006) Live imaging of yeast Golgi cisternal maturation. Nature 441:1007–1010
Misumi Y, Sohda M, Tashiro A, Sato H, Ikehara Y (2001) An essential cytoplasmic domain for the Golgi localization of coiled- coil proteins with a COOH-terminal membrane anchor. J Biol Chem 276:6867–6873
Mollenhauer HH (1965) An intercisternal structure in the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol 24:504–511
Mollenhauer HH, Morre DJ (1998) The tubular network of the Golgi apparatus. Histochem Cell Biol 109:533–543
Mori K, Kato H (2002) A putative nuclear receptor coactivator (TMF/ARA160) associates with hbrm/hSNF2 alpha and BRG-1/hSNF2 beta and localizes in the Golgi apparatus. FEBS Lett 520:127–132
Moyer BD, Allan BB, Balch WE (2001) Rab1 interaction with a GM130 effector complex regulates COPII Vesicle cis-Golgi tethering. Traffic 2:268–276
Mukherjee S, Shields D (2009) Nuclear import is required for the pro-apoptotic function of the Golgi protein p115. J Biol Chem 284:1709–1717
Munro S, Nichols BJ (1999) The GRIP domain - a novel Golgi-targeting domain found in several coiled-coil proteins. Curr Biol 9:377–380
Nakagomi S, Barsoum MJ, Bossy-Wetzel E, Sutterlin C, Malhotra V, Lipton SA (2007) A Golgi fragmentation pathway in neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 29:221–231
Nakamura N, Rabouille C, Watson R, Nilsson T, Hui N, Slusarewicz P, Kreis TE, Warren G (1995) Characterization of a cis-Golgi matrix protein, GM130. J Cell Biol 131:1715–1726
Nakamura N, Lowe M, Levine TP, Rabouille C, Warren G (1997) The vesicle docking protein p115 binds GM130, a cis-Golgi matrix protein, in a mitotically regulated manner. Cell 89:445–455
Ohta E, Misumi Y, Sohda M, Fujiwara T, Yano A, Ikehara Y (2003) Identification and characterization of GCP16, a novel acylated Golgi protein that interacts with GCP170. J Biol Chem 278:51957–51967
Orci L, Tagaya M, Amherdt M, Perrelet A, Donaldson JG, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Klausner RD, Rothman JE (1991) Brefeldin A, a drug that blocks secretion, prevents the assembly of non-clathrin-coated buds on Golgi cisternae. Cell 64:1183–1195
Orci L, Perrelet A, Rothman JE (1998) Vesicles on strings: morphological evidence for processive transport within the Golgi stack. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2279–2283
Papoulas O, Hays TS, Sisson JC (2005) The golgin Lava lamp mediates dynein-based Golgi movements during Drosophila cellularization. Nat Cell Biol 7:612–618
Pfeffer SR (2010) How the Golgi works: a cisternal progenitor model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19614–19618
Preisinger C, Short B, De Corte V, Bruyneel E, Haas A, Kopajtich R, Gettemans J, Barr FA (2004) YSK1 is activated by the Golgi matrix protein GM130 and plays a role in cell migration through its substrate 14-3-3{zeta}. J Cell Biol 164:1009–1020
Preisinger C, Korner R, Wind M, Lehmann WD, Kopajtich R, Barr FA (2005) Plk1 docking to GRASP65 phosphorylated by Cdk1 suggests a mechanism for Golgi checkpoint signalling. EMBO J 24:753–765
Puthenveedu MA, Bachert C, Puri S, Lanni F, Linstedt AD (2006) GM130 and GRASP65-dependent lateral cisternal fusion allows uniform Golgi-enzyme distribution. Nat Cell Biol 8:238–248
Rambourg A, Clermont Y (1990) Three-dimensional electron microscopy: structure of the Golgi apparatus. Eur J Cell Biol 51:189–200
Ramirez IB, Lowe M (2009) Golgins and GRASPs: holding the Golgi together. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20:770–779
Ramirez IB, De Graffenried CL, Ebersberger I, Yelinek J, He CY, Price A, Warren G (2008) TbG63, a golgin involved in Golgi architecture in Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Sci 121:1538–1546
Ran R, Pan R, Lu A, Xu H, Davis RR, Sharp FR (2007) A novel 165-kDa Golgin protein induced by brain ischemia and phosphorylated by Akt protects against apoptosis. Mol Cell Neurosci 36:392–407
Reddy JV, Burguete AS, Sridevi K, Ganley IG, Nottingham RM, Pfeffer SR (2006) A functional role for the GCC185 golgin in mannose 6-phosphate receptor recycling. Mol Biol Cell 17:4353–4363
Rejman Lipinski A, Heymann J, Meissner C, Karlas A, Brinkmann V, Meyer TF, Heuer D (2009) Rab6 and Rab11 regulate Chlamydia trachomatis development and golgin-84-dependent Golgi fragmentation. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000615
Rios RM, Sanchis A, Tassin AM, Fedriani C, Bornens M (2004) GMAP-210 recruits gamma-tubulin complexes to cis-Golgi membranes and is required for Golgi ribbon formation. Cell 118:323–335
Rivero S, Cardenas J, Bornens M, Rios RM (2009) Microtubule nucleation at the cis-side of the Golgi apparatus requires AKAP450 and GM130. EMBO J 28:1016–1028
Sapperstein SK, Walter DM, Grosvenor AR, Heuser JE, Waters MG (1995) p115 is a general vesicular transport factor related to the yeast endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport factor Uso1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:522–526
Satoh A, Wang Y, Malsam J, Beard MB, Warren G (2003) Golgin-84 is a rab1 binding partner involved in Golgi structure. Traffic 4:153–161
Satoh A, Malsam J, Warren G (2005) Tethering assays for COPI vesicles mediated by golgins. Methods Enzymol 404:125–134
Sbodio JI, Hicks SW, Simon D, Machamer CE (2006) GCP60 preferentially interacts with a caspase-generated golgin-160 fragment. J Biol Chem 281:27924–27931
Schotman H, Karhinen L, Rabouille C (2008) dGRASP-mediated noncanonical integrin secretion is required for Drosophila epithelial remodeling. Dev Cell 14:171–182
Seemann J, Jokitalo E, Pypaert M, Warren G (2000a) Matrix proteins can generate the higher order architecture of the Golgi apparatus. Nature 407:1022–1026
Seemann J, Jokitalo EJ, Warren G (2000b) The role of the tethering proteins p115 and GM130 in transport through the Golgi apparatus in vivo. Mol Biol Cell 11:635–645
Sengupta D, Truschel S, Bachert C, Linstedt AD (2009) Organelle tethering by a homotypic PDZ interaction underlies formation of the Golgi membrane network. J Cell Biol 186:41–55
Short B, Preisinger C, Korner R, Kopajtich R, Byron O, Barr FA (2001) A GRASP55-rab2 effector complex linking Golgi structure to membrane traffic. J Cell Biol 155:877–883
Short B, Haas A, Barr FA (2005) Golgins and GTPases, giving identity and structure to the Golgi apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1744:383–395
Shorter J, Warren G (1999) A role for the vesicle tethering protein, p115, in the post-mitotic stacking of reassembling golgi cisternae in a cell-free system. J Cell Biol 146:57–70
Shorter J, Warren G (2002) Golgi architecture and inheritance. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:379–420
Shorter J, Watson R, Giannakou ME, Clarke M, Warren G, Barr FA (1999) GRASP55, a second mammalian GRASP protein involved in the stacking of Golgi cisternae in a cell-free system. EMBO J 18:4949–4960
Shorter J, Beard MB, Seemann J, Dirac-Svejstrup AB, Warren G (2002) Sequential tethering of Golgins and catalysis of SNAREpin assembly by the vesicle-tethering protein p115. J Cell Biol 157:45–62
Sinka R, Gillingham AK, Kondylis V, Munro S (2008) Golgi coiled-coil proteins contain multiple binding sites for Rab family G proteins. J Cell Biol 183:607–615
Slusarewicz P, Nilsson T, Hui N, Watson R, Warren G (1994) Isolation of a matrix that binds medial Golgi enzymes. J Cell Biol 124:405–413
Smits P, Bolton AD, Funari V, Hong M, Boyden ED, Lu L, Manning DK, Dwyer ND, Moran JL, Prysak M, Merriman B, Nelson SF, Bonafe L, Superti-Furga A, Ikegawa S, Krakow D, Cohn DH, Kirchhausen T, Warman ML, Beier DR (2010) Lethal skeletal dysplasia in mice and humans lacking the golgin GMAP-210. N Engl J Med 362:206–216
Sohda M, Misumi Y, Yamamoto A, Yano A, Nakamura N, Ikehara Y (2001) Identification and characterization of a novel Golgi protein, GCP60, that interacts with the integral membrane protein giantin. J Biol Chem 276:45298–45306
Sohda M, Misumi Y, Yamamoto A, Nakamura N, Ogata S, Sakisaka S, Hirose S, Ikehara Y, Oda K (2010) Interaction of Golgin-84 with the COG complex mediates the intra-Golgi retrograde transport. Traffic 11:1552–1566
Sonnichsen B, Lowe M, Levine T, Jamsa E, Dirac-Svejstrup B, Warren G (1998) A role for giantin in docking COPI vesicles to Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol 140:1013–1021
Sutterlin C, Hsu P, Mallabiabarrena A, Malhotra V (2002) Fragmentation and dispersal of the pericentriolar Golgi complex is required for entry into mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell 109:359–369
Sutterlin C, Polishchuk R, Pecot M, Malhotra V (2005) The Golgi-associated protein GRASP65 regulates spindle dynamics and is essential for cell division. Mol Biol Cell 16:3211–3222
Takahashi M, Shibata H, Shimakawa M, Miyamoto M, Mukai H, Ono Y (1999) Characterization of a novel giant scaffolding protein, CG-NAP, that anchors multiple signaling enzymes to centrosome and the golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem 274:17267–17274
Tang D, Mar K, Warren G, Wang Y (2008) Molecular mechanism of mitotic Golgi disassembly and reassembly revealed by a defined reconstitution assay. J Biol Chem 283:6085–6094
Tang D, Yuan H, Wang Y (2010) The Role of GRASP65 in Golgi cisternal stacking and cell cycle progression. Traffic 11:827–842
Toki C, Fujiwara T, Sohda M, Hong HS, Misumi Y, Ikehara Y (1997) Identification and characterization of rat 364-kDa Golgi-associated protein recognized by autoantibodies from a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Struct Funct 22:565–577
Van Valkenburgh H, Shern JF, Sharer JD, Zhu X, Kahn RA (2001) ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) and ARF-like 1 (ARL1) have both specific and shared effectors: characterizing ARL1-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 276:22826–22837
Vasile E, Perez T, Nakamura N, Krieger M (2003) Structural integrity of the Golgi is temperature sensitive in conditional-lethal mutants with no detectable GM130. Traffic 4:254–272
Vinke FP, Grieve AG, Rabouille C (2011) The multiple facets of the Golgi reassembly stacking proteins. Biochem J 433:423–433
Walker A, Ward C, Sheldrake TA, Dransfield I, Rossi AG, Pryde JG, Haslett C (2004) Golgi fragmentation during Fas-mediated apoptosis is associated with the rapid loss of GM130. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316:6–11
Wang Y (2008) Golgi apparatus inheritance. In: Mironov A, Pavelka M, Luini A (eds) The Golgi apparatus. State of the art 110 years after Camillo Golgi’s discovery. Springer, New York, pp 580–607
Wang Y, Seemann J (2011) Golgi biogenesis. In: Warren G, Rothman JE (eds) The Golgi book. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Wang Y, Seemann J, Pypaert M, Shorter J, Warren G (2003) A direct role for GRASP65 as a mitotically regulated Golgi stacking factor. EMBO J 22:3279–3290
Wang Y, Satoh A, Warren G (2005) Mapping the functional domains of the Golgi stacking factor GRASP65. J Biol Chem 280:4921–4928
Wanschers BF, Van de Vorstenbosch R, Schlager MA, Splinter D, Akhmanova A, Hoogenraad CC, Wieringa B, Fransen JA (2007) A role for the Rab6B Bicaudal-D1 interaction in retrograde transport in neuronal cells. Exp Cell Res 313:3408–3420
Ward TH, Polishchuk RS, Caplan S, Hirschberg K, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2001) Maintenance of Golgi structure and function depends on the integrity of ER export. J Cell Biol 155:557–570
Waters MG, Pfeffer SR (1999) Membrane tethering in intracellular transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:453–459
Xiang Y, Wang Y (2010) GRASP55 and GRASP65 play complementary and essential roles in Golgi cisternal stacking. J Cell Biol 188:237–251
Yadav S, Puri S, Linstedt AD (2009) A primary role for Golgi positioning in directed secretion, cell polarity, and wound healing. Mol Biol Cell 20:1728–1736
Yamane J, Kubo A, Nakayama K, Yuba-Kubo A, Katsuno T, Tsukita S (2007) Functional involvement of TMF/ARA160 in Rab6-dependent retrograde membrane traffic. Exp Cell Res 313:3472–3485
Yoshimura S, Yoshioka K, Barr FA, Lowe M, Nakayama K, Ohkuma S, Nakamura N (2005) Convergence of cell cycle regulation and growth factor signals on GRASP65. J Biol Chem 280:23048–23056
Zhou Y, Atkins JB, Rompani SB, Bancescu DL, Petersen PH, Tang H, Zou K, Stewart SB, Zhong W (2007) The mammalian Golgi regulates numb signaling in asymmetric cell division by releasing ACBD3 during mitosis. Cell 129:163–178
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank members of the Wang Lab for suggestions and for critical reading of the manuscript. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (GM087364) and the American Cancer Society (RGS-09-278-01-CSM) to Y. Wang and a University of Michigan Rackham Predoctoral Fellowship to Y. Xiang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, Y., Wang, Y. New components of the Golgi matrix. Cell Tissue Res 344, 365–379 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1166-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1166-x