Abstract
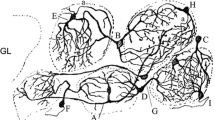
The structure of a new cell type, termed the medullary neuron (MN) because of its intimate association with the rostral migratory stream (RMS) in the bulbar core, is described in the adult rat olfactory bulb. The MN is a triangular or polygonal interneuron whose soma lies between the cellular clusters of the RMS or, less frequently, among the neuron progenitors therein. MNs are easily distinguished from adjacent cells by their large size and differentiated structure. Two MN subtypes have been categorized by the Golgi technique: spiny pyramidal neurons and aspiny neurons. Both MN subtypes bear a large dendritic field impinged upon by axons in the core bulbar white matter. A set of collaterals from the adjacent axons appears to terminate on the MN dendrites. The MN axon passes in close apposition to adjacent neuron progenitors in the RMS. MNs are immunoreactive with antisera raised against gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate decarboxylase 65/67. Electron-microscopic observations confirm that MNs correspond to fully differentiated, mature neurons. MNs seem to be highly conserved among macrosmatic species as they occur in Nissl-stained brain sections from mouse, guinea pig, and hedgehog. Although the functional role of MNs remains to be determined, we suggest that MNs represent a cellular interface between endogenous olfactory activity and the differentiation of new neurons generated during adulthood.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J (1969) Autoradiographic and histological studies of posnatal neurogenesis. IV. Cell proliferation and migration in the anterior forebrain, with special reference to persisting neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 137:433–458
Behar TN, Li YX, Tran HT, Ma W, Deunlap V, Scott C, Maric D, Maric I, Schaffner AE, Serafini R, Smith SV, Somogyi R, Bautrin JY, Wen XL, Xian H (1996) GABAergic cells and signals in the CNS development. Perspect Dev Neurobiol 5:305–322
Behar TN, Schaffner AE, Scott CA, O´Connell C, Barker JL (1998) Differential response of cortical plate and ventricular zone cells to GABA as migration stimulus. J Neurosci 18:6378–6387
Blanes T (1898) Sobre algunos puntos dudosos de la estructura del bulbo olfatorio. Rev Trim Microgr 3:99–127
DeCastro F (1920) Algunas observaciones sobre la histogénesis de la neuroglia en el tallo olfativo. Trab Lab Invest Biol 18:83–108
Doetsch F, García-Verdugo JM, Álvarez-Buylla A (1997) Cellular composition and three-dimensional organization of the subventricular germinal zone in the adult mammal brain. J Neurosci 17:5046–5061
Eyre MD, Antal M, Nusser Z (2008) Distinct deep short-axon cell subtypes of the main olfactory bulb provide novel intrabulbar and extrabulbar GABAergic connections. J Neurosci 28:8217–8229
Farrant M, Nusser Z (2005) Variations on an inhibitory theme: phasic and tonic activation of GABAa receptors. Nat Neurosci 6:215-229
Jankovski A, Sotelo C (1996) Subventricular zone-olfactory bulb migratory pathway in the adult mouse: cellular composition and specificity as determined by heterochronic and heterotopic transplantation. J Comp Neurol 371:376–396
Kelsch W, Lin Ch-L, Mosley CP, Lois C (2009) A critical period for activity-dependent synaptic development during olfactory bulb adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci 29:11852–11858
Larriva-Sahd J (2006) A histological and cytological study of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis of the adult rat. II. Oval nucleus: extrinsic inputs, cell types, and neuronal modules. J Comp Neurol 497:772–807
Larriva–Sahd J (2008) The accessory olfactory bulb in the adult rat: a cytological study of its cell types, neuropil, neuronal modules, and interactions with the main olfactory system. J Comp Neurol 510:309–350
Lledo PM, Merkle FT, Álvarez-Buylla A (2008) Origin and function of olfactory bulb interneuron diversity. Cell 31:392–400
Lohman AHM (1963) The anterior olfactory lobe of the guinea pig. Acta Anat 45:9–109
Lohman AHM, Mentink GM (1969) The lateral olfactory tract and the anterior commissure, and the cells of the olfactory bulb. Brain Res 12:396–413
López-Mascaraque L, De Carlos JA, Valverde F (1986) Structure of the olfactory bulb of the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus): description of cell types in the granule layer. J Comp Neurol 253:135–152
LoTurco JJ, Owens DF, Heath MJ, Davis MB, Kriegstein AR (1995) GABA and glutamate depolarize cortical progenitor cells and inhibit DNA synthesis. Neuron 15:1287–1298
Macrides F, Davis BJ (1983) Chemical neuroanatomy. In: Emson PC (ed) The olfactory bulb. Raven, New York, pp 391–426
Mandarion N, Jourdan F, Didier A (2003) Deprivation of sensory inputs to the olfactory bulb up-regulates cell death and proliferation in the subventricular zone of adult mice. Neurosci 119:507–516
McDonald AJ (1982) Neurons in the lateral and basolateral amygdaloid nuclei: a Golgi study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 212:293–312
Peters A, Palay SL, Webster F (1976) The fine structure of the nervous system: the neurons and supporting cells. Saunders, Philadelphia
Petreanu LT, Álvarez-Buylla A (2002) Maturation and death of adult-born olfactory bulb granule neurons: role of olfaction. J Neurosci 22:6106–6113
Platel JC, Lacar B, Bordey A (2007) GABA and glutamate signaling: homeostatic control of adult forebrain neurogenesis. J Mol Histol 38:303–311
Pressler RT, Strowbridge BW (2006) Blanes cells mediate persistent feedforward inhibition onto granule cells in the olfactory bulb. Neuron 49:889–904
Price JL (1974) An autoradiographic study of complementary laminar patterns of termination of afferent fibers to the olfactory cortex. J Comp Neurol 150:87–108
Ramón y Cajal S (1904) Corteza olfativa, textura del sistema nervioso central del hombre y los vertebrados, vol 2. Librería Nicolás Moya, Madrid
Reyher CKH, Schwerdtfeger WK, Baumgarten HG (1988) Interbulbar axonal collateralization and morphology of anterior olfactory neurons in the rat. Brain Res Bull 20:549–560
Schoenfeld TA, Macrides F (1984) Topographic organization of connections between the main olfactory bulb pars externa of the anterior olfactory nucleus in the hamster. J Comp Neurol 227:121–135
Scott JW, McDonald JK, Pemberton JL (1987) Short axon cells of the rat olfactory bulb display NADPH-diaphorase activity, neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity, and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity. J Comp Neurol 260:378–391
Valverde F (1965) Studies of the pyriform lobe. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass.
Wang DD, Kruger DD, Bordey A (2003) GABA depolarizes neuronal progenitors of the posnatal subventricular zone via GABAA receptor activation. J Physiol (Lond) 550:785–800
Whitman MC, Greer CA (2007) Adult generated neurons exhibit diverse developmental fates. Dev Neurobiol 67:1079–1093
Yan Z, Tan J, Qin C, Lu Y, Ding C, Luo M (2008) Precise circuitry links bilaterally symmetric olfactory maps. Neuron 58:613–624
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Gema Martínez Cabrera and Lourdes Palma for their valuable technical help and to Dr. Dorothy Pless for her careful revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paredes, R.G., Larriva-Sahd, J. Medullary neurons in the core white matter of the olfactory bulb: a new cell type. Cell Tissue Res 339, 281–295 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0910-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0910-y