Abstract
Myosin-Va is a Ca2+/calmodulin-regulated unconventional myosin involved in the transport of vesicles, membranous organelles, and macromolecular complexes composed of proteins and mRNA. The cellular localization of myosin-Va has been described in great detail in several vertebrate cell types, including neurons, melanocytes, lymphocytes, auditory tissues, and a number of cultured cells. Here, we provide an immunohistochemical view of the tissue distribution of myosin-Va in the major endocrine organs. Myosin-Va is highly expressed in the pineal and pituitary glands and in specific cell populations of other endocrine glands, especially the parafollicular cells of the thyroid, the principal cells of the parathyroid, the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla, and a subpopulation of interstitial testicular cells. Weak to moderate staining has been detected in steroidogenic cells of the adrenal cortex, ovary, and Leydig cells. Myosin-Va has also been localized to non-endocrine cells, such as the germ cells of the seminiferous epithelium and maturing oocytes and in the intercalated ducts of the exocrine pancreas. These data provide the first systematic description of myosin-Va localization in the major endocrine organs of rat.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hussain SM (2006) The pinealocytes of the human pineal gland: a light and electron microscopic study. Folia Morphol 65:181–187
Au JS, Huang JD (2002) A tissue-specific exon of myosin Va is responsible for selective cargo binding in melanocytes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 53:89–102
Bizario JC, Castro FA, Sousa JF, Fernandes RN, Damião AD, Oliveira MK, Palma PV, Larson RE, Voltarelli JC, Espreafico EM (2002) Myosin-V colocalizes with MHC class II in blood mononuclear cells and is up-regulated by T-lymphocyte activation. J Leukoc Biol 71:195–204
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bridgman PC (1999) Myosin-Va movements in normal and dilute-lethal axons provide support for a dual filament motor complex. J Cell Biol 146:1045–1060
Burghardt B, Elkaer ML, Kwon TH, Rácz GZ, Varga G, Steward MC, Nielsen S (2003) Distribution of aquaporin water channels AQP1 and AQP5 in the ductal system of the human pancreas. Gut 52:1008–1016
Buttow NC, Zucoloto S, Espreafico EM, Gama P, Alvares EP (2003) Substance P enhances neuronal area and epithelial cell proliferation after colon denervation in rats. Dig Dis Sci 48:2069–2076
Cao TT, Chang W, Masters SE, Mooseker MS (2004) Myosin-Va binds to and mechanochemically couples microtubules to actin filaments. Mol Biol Cell 15:151–161
Cheney RE (1998) Purification and assay of myosin V. Methods Enzymol 298:3–18
Coelho MV, Larson RE (1993) Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of the tail domain of myosin-V, a calmodulin-binding myosin in vertebrate brain. Braz J Med Biol Res 26:465–472
Costa MC, Mani F, Santoro W Jr, Espreafico EM, Larson RE (1999) Brain myosin-V, a calmodulin-carrying myosin, binds to calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and activates its kinase activity. J Biol Chem 274:15811–15819
DePina AS, Langford GM (1999) Vesicle transport: the role of actin filaments and myosin motors. Microsc Res Tech 47:93–106
Desnos C, Huet S, Fanget I, Chapuis C, Böttiger C, Racine V, Sibarita JB, Henry JP, Darchen F (2007) Myosin Va mediates docking of secretory granules at the plasma membrane. J Neurosci 27:10636–10645
Drengk AC, Kajiwara JK, Garcia SB, Carmo VS, Larson RE, Zucoloto S, Espreafico EM (2000) Immunolocalisation of myosin-V in the enteric nervous system of the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst 78:109–112
Espindola FS, Espreafico EM, Coelho MV, Martins AR, Costa FR, Mooseker MS, Larson RE (1992) Biochemical and immunological characterization of p190-calmodulin complex from vertebrate brain: a novel calmodulin-binding myosin. J Cell Biol 118:359–368
Espindola FS, Suter DM, Partata LB, Cao T, Wolenski JS, Cheney RE, King SM, Mooseker MS (2000) The light chain composition of chicken brain myosin-Va: calmodulin, myosin-II essential light chains, and 8-kDa dynein light chain/PIN. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 47:269–281
Espreafico EM, Cheney RE, Matteoli M, Nascimento AA, De Camilli PV, Larson RE, Mooseker MS (1992) Primary structure and cellular localization of chicken brain myosin-V (p190), an unconventional myosin with calmodulin light chains. J Cell Biol 119:1541–1557
Espreafico EM, Coling DE, Tsakraklides V, Krogh K, Wolenski JS, Kalinec G, Kachar B (1998) Localization of myosin-V in the centrosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:8636–8641
Evans LL, Hammer J, Bridgman PC (1997) Subcellular localization of myosin V in nerve growth cones and outgrowth from dilute-lethal neurons. J Cell Sci 110:439–449
Evans LL, Lee AJ, Bridgman PC, Mooseker MS (1998) Vesicle-associated brain myosin-V can be activated to catalyze actin-based transport. J Cell Sci 111:2055–2066
Govindan B, Bowser R, Novick P (1995) The role of Myo2, a yeast class V myosin, in vesicular transport. J Cell Biol 128:1055–1068
Heintzelman MB, Hasson T, Mooseker MS (1994) Multiple unconventional myosin domains of the intestinal brush border cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci 107:3535–3543
Huang JD, Cope MJ, Mermall V, Strobel MC, Kendrick-Jones J, Russell LB, Mooseker MS, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1998) Molecular genetic dissection of mouse unconventional myosin-Va: head region mutations. Genetics 148:1951–1961
Johnston GC, Prendergast JA, Singer RA (1991) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae MYO2 gene encodes an essential myosin for vectorial transport of vesicles. J Cell Biol 113:539–551
Karcher RL, Roland JT, Zappacosta F, Huddleston MJ, Annan RS, Carr SA, Gelfand VI (2001) Cell cycle regulation of myosin-V by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Science 293:1317–1320
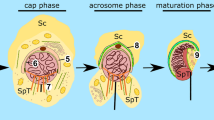
Kierszenbaum AL, Tres LL (2004) The acrosome-acroplaxome-manchette complex and the shaping of the spermatid head. Arch Histol Cytol 67:271–284
Kierszenbaum AL, Rivkin E, Tres LL (2003) The actin-based motor myosin Va is a component of the acroplaxome, an acrosome-nuclear envelope junctional plate, and of manchette-associated vesicles. Cytogenet Genome Res 103:337–344
Ko TL, Chien CL, Lu KS (2005) The expression of alpha-internexin and peripherin in the developing mouse pineal gland. J Biomed Sci 12:777–789
Laemmli UK, Favre M (1973) Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol 80:575–599
Langford GM (2002) Myosin-V, a versatile motor for short-range vesicle transport. Traffic 3:859–865
Lapierre LA, Goldenring JR (2005) Interactions of myosin Vb with Rab11 family members and cargoes traversing the plasma membrane recycling system. Methods Enzymol 403:715–723
Larson RE, Pitta DE, Ferro JA (1988) A novel 190 kDa calmodulin-binding protein associated with brain actomyosin. Braz J Med Biol Res 21:213–217
Larson RE, Espindola FS, Espreafico EM (1990) Calmodulin-binding proteins and calcium/calmodulin-regulated enzyme activities associated with brain actomyosin. J Neurochem 54:1288–1294
Lobo MV, Arenas MI, Alonso FJ, Gomez G, Bazán E, Paíno CL, Fernández E, Fraile B, Paniagua R, Moyano A, Caso E (2004) Nestin, a neuroectodermal stem cell marker molecule, is expressed in Leydig cells of the human testis and in some specific cell types from human testicular tumours. Cell Tissue Res 316:369–376
McGurk L, Tzolovsky G, Spears N, Bownes M (2006) The temporal and spatial expression pattern of myosin Va, Vb and VI in the mouse ovary. Gene Expr Patterns 6:900–907
McLean IW, Nakane PK (1974) Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 22:1077–1083
Mercer JA, Seperack PK, Strobel MC, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1991) Novel myosin heavy chain encoded by murine dilute coat colour locus. Nature 349:709–713
Mermall V, Bonafé N, Jones L, Sellers JR, Cooley L, Mooseker MS (2005) Drosophila myosin V is required for larval development and spermatid individualization. Dev Biol 286:238–255
Miller KE, Sheetz MP (2000) Characterization of myosin V binding to brain vesicles. J Biol Chem 275:2598–2606
Nagashima K, Torii S, Yi Z, Igarashi M, Okamoto K, Takeuchi T, Izumi T (2002) Melanophilin directly links Rab27a and myosin-Va through its distinct coiled-coil regions. FEBS Lett 517:233–238
Nascimento AA, Cheney RE, Tauhata SB, Larson RE, Mooseker MS (1996) Enzymatic characterization and functional domain mapping of brain myosin-V. J Biol Chem 271:17561–17569
Nascimento AA, Amaral RG, Bizario JC, Larson RE, Espreafico EM (1997) Subcellular localization of myosin-V in the B16 melanoma cells, a wild-type cell line for the dilute gene. Mol Biol Cell 8:1971–1988
O’Shaughnessy PJ, Baker PJ, Johnston H (2005) Neuroendocrine regulation of Leydig cell development. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1061:109–119
Prekeris R, Terrian DM (1997) Brain myosin V is a synaptic vesicle-associated motor protein: evidence for a Ca2+-dependent interaction with the synaptobrevin-synaptophysin complex. J Cell Biol 137:1589–1601
Provance DW Jr, Wei M, Ipe V, Mercer JA (1996) Cultured melanocytes from dilute mutant mice exhibit dendritic morphology and altered melanosome distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14554–14558
Reck-Peterson SL, Provance DW Jr, Mooseker MS, Mercer JA (2000) Class V myosins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1496:36–51
Reis DN, Souza M, Mineo J, Espindola FS (2001) Myosin V and iNOS expression is enhanced in J774 murine macrophages treated with IFN-gamma. Braz J Med Biol Res 34:221–226
Rodriguez OC, Cheney RE (2002) Human myosin-Vc is a novel class V myosin expressed in epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 115:991–1004
Rogers SL, Karcher RL, Roland JT, Minin AA, Steffen W, Gelfand VI (1999) Regulation of melanosome movement in the cell cycle by reversible association with myosin V. J Cell Biol 146:1265–1276
Rosé SD, Lejen T, Casaletti L, Larson RE, Pene TD, Trifaró J-M (2003) Myosins II and V in chromaffin cells: myosin V is a chromaffin vesicle molecular motor involved in secretion. J Neurochem 85:287–298
Rudolf R, Kogel T, Kuznetsov SA, Salm T, Schlicker O, Hellwig A, Hammer JA 3rd, Gerdes HH (2003) Myosin-Va facilitates the distribution of secretory granules in the F-actin rich cortex of PC12 cells. J Cell Sci 116:1339–1348
Seperack PK, Mercer JA, Strobel MC, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1995) Retroviral sequences located within an intron of the dilute gene alter dilute expression in a tissue-specific manner. EMBO J 14:2326–2332
Suter DM, Espindola FS, Lin CH, Forscher P, Mooseker MS (2000) Localization of unconventional myosins V and VI in neuronal growth cones. J Neurobiol 42:370–382
Swiatecka-Urban A, Talebian L, Kanno E, Moreau-Marquis S, Coutermarsh B, Hansen K, Karlson KH, Barnaby R, Cheney RE, Langford GM, Fukuda M, Stanton BA (2007) Myosin Vb is required for trafficking of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in Rab11a-specific apical recycling endosomes in polarized human airway epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 28:23725–23736
Tabb JS, Molyneaux BJ, Cohen DL, Kuznetsov SA, Langford GM (1998) Transport of ER vesicles on actin filaments in neurons by myosin V. J Cell Sci 111:3221–3234
Takagishi Y, Murata Y (2006) Myosin Va mutation in rats is an animal model for the human hereditary neurological disease, Griscelli syndrome type 1. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1086:66–80
Tolmachova T, Anders R, Stinchcombe J, Bossi G, Griffiths GM, Huxley C, Seabra MC (2004) A general role for Rab27a in secretory cells. Mol Biol Cell 15:332–344
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Trifaro JM, Gasman S, Gutierrez LM (2008) Cytoskeletal control of vesicle transport and exocytosis in chromaffin cells. Acta Physiol 192:165–172
Tsakraklides V, Krogh K, Wang L, Bizario JC, Larson RE, Espreafico EM, Wolenski JS (1999) Subcellular localization of GFP-myosin-V in live mouse melanocytes. J Cell Sci 112:2853–2865
Tyska MJ, Mooseker MS (2003) Myosin-V motility: these levers were made for walking. Trends Cell Biol 13:447–451
Varadi A, Tsuboi T, Rutter GA (2005) Myosin-Va transports dense core secretory vesicles in pancreatic MIN6 beta-cells. Mol Biol Cell 16:2670–2680
Waselle L, Coppola T, Fukuda M, Iezzi M, El-Amraoui A, Petit C, Regazzi R (2003) Involvement of the Rab27 binding protein Slac2c/MyRIP in insulin exocytosis. Mol Biol Cell 14:4103–4113
Watanabe M, Nomura K, Ohyama A, Ishikawa R, Komiya Y, Hosaka K, Yamauchi E, Taniguchi H, Sasakawa N, Kumakura K, Ushiki T, Sato O, Ikebe M, Igarashi M (2005) Myosin-Va regulates exocytosis through the submicromolar Ca2+-dependent binding of syntaxin-1A. Mol Biol Cell 16:4519–4530
Wu XS, Bowers B, Wei Q, Kocher B, Hammer JA 3rd (1997) Myosin V associates with melanosomes in mouse melanocytes: evidence that myosin V is an organelle motor. J Cell Sci 110:847–859
Wu XS, Rao K, Zhang H, Wang F, Sellers JR, Matesic LE, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Hammer JA 3rd (2002a) Identification of an organelle receptor for myosin-Va. Nat Cell Biol 4:271–278
Wu XS, Wang F, Rao K, Sellers JR, Hammer JA 3rd (2002b) Rab27a is an essential component of melanosome receptor for myosin-Va. Mol Biol Cell 13:1735–1749
Yamamoto H, Matsumoto K, Araki E, Miyamoto E (2003) New aspects of neurotransmitter release and exocytosis: involvement of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of synapsin I in insulin exocytosis. J Pharmacol Sci 93:30–34
Acknowledgments
We are extremely grateful to Ms. Vani Maria Alves Corrêa and Mr. Domingos Soares de Souza Filho for their expertise in tissue sectioning and animal manipulation, respectively, to Mr. Domingos Edmundo Pitta for mastering the technique of polyacrylamide gel production and providing us with the gels, and to Ms. Benedita de Oliveira de Souza and Silvia Regina Andrade for general assistance in our laboratories. We thank the Laboratory of Confocal Microscopy of FMRP-USP, especially the talented microscopists Márcia Sirlene Zardin Graeff and Lenaldo Branco Rocha. We would like to thank Dr. Michela Matteoli and Dr. Michele Solimena for allowing us to use the image shown in Fig. 5a, which they obtained, then in Dr. Pietro De Camilli’s laboratory at Yale University. We also express our gratitude to the Emeritus Professor Dr. Antônio Haddad and Dr. Maria Luisa Paço-Larson at FMRP-USP and to Dr. Marcelo Emílio Beletti at ICBIM-UFU for their excellent teaching of histology and for taking time on many occasions to discuss our histology and immunohistochemistry data with us.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
We thank the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Tecnológico (CNPq), and the Fundação de Apoio ao Ensino, Pesquisa e Assistência do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto (FAEPA) for grants to the laboratories of E.M.E. and R.E.L. We are also grateful to CNPq for a scientific initiation fellowship to R.J.C. and a researcher fellowship to E.M.E and R.E.L. The Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) provided grant support to the laboratory of F.S.E. The Coordenadoria de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Ensino Superior (CAPES) provided doctorate fellowships to I.M.L.G. and master fellowships to L.K.C., A.B.P., and J.P.C.J.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espindola, F.S., Banzi, S.R., Calabria, L.K. et al. Localization of myosin-Va in subpopulations of cells in rat endocrine organs. Cell Tissue Res 333, 263–279 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0630-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0630-8