Abstract
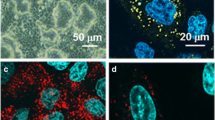
The distribution of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp/MDR1) efflux transporter at mucosal barriers has defined it as a functionally important element in limiting drug absorption into the systemic circulation. However, little is known about the distribution and functionality of P-gp/MDR1 in the human lung. Here, the presence of P-gp/MDR1 was investigated immunohistochemically in distal human lung tissue and at mRNA and protein levels in human alveolar epithelial cells (hAEpC) in primary culture. We studied the presence and activity of P-gp/MDR1 in hAEpC monolayers by Western blotting, by immunofluorescence microscopy and by conducting bi-directional transport studies employing a P-gp substrate (rhodamine 123) with and without a P-gp inhibitor (verapamil). The flux of fluorescein sodium was also examined as a paracellular transport marker. Alveolar tissue specimens showed P-gp localised at the luminal membranes of type I pneumocytes. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction revealed the presence of mRNA encoding for P-gp/MDR1 in freshly isolated (i.e. type II) hAEpC and in monolayers of hAEpC cultured for 8 days (i.e. type I-like morphology). At the protein level, P-gp could be detected in hAEpC monolayers after 8 days in culture but not in freshly isolated type II pneumocytes. The flux of rhodamine 123 across hAEpC monolayers on day 8 in culture exhibited net secretion, which disappeared in the presence of verapamil. Fluorescein sodium fluxes showed no distinct directionality. Our findings indicate that P-gp is functionally active in the human alveolar airspace and that hAEpC monolayers might provide a suitable in vitro model for studying P-gp function mechanistically in the distal human lung.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abulrob AG, Gumbleton M (1999) Transport of phosphatidylcholine in MDR3-negative epithelial cell lines via drug-induced MDR1 P-glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262:121–126
Axiotis CA, Bani D, Bianchi S, Pioli P, Tanini A, Brandi ML (1995) P-glycoprotein is expressed in parathyroid epithelium and is regulated by calcium. Calcif Tissue Int 56:170–174
Bosch I, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Wu RL, Furlong ST, Croop J (1997) Phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine behave as substrates of the human MDR1 P-glycoprotein. Biochemistry 36:5685–5694
Campbell L, Abulrob AN, Kandalaft LE, Plummer S, Hollins AJ, Gibbs A, Gumbleton M (2003) Constitutive expression of P-glycoprotein in normal lung alveolar epithelium and functionality in primary alveolar epithelial cultures. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:441–452
Chen J, Chen Z, Narasaraju T, Jin N, Liu L (2004) Isolation of highly pure alveolar epithelial type I and type II cells from rat lungs. Lab Invest 84:727–735 (Erratum in: Lab Invest 85:1181)
Cordon-Cardo C, O’Brien LP, Boccia J, Casals D, Bertino JR, Melamed MR (1990) Expression of the multidrug resistance gene product (P-glycoprotein) in human normal and tumor tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 38:1277–1287
Demeule M, Jodoin J, Gingras D, Beliveau R (2000) P-glycoprotein is localized in caveolae in resistant cells and in brain capillaries. FEBS Lett 466:219–224
Demeule M, Shedid D, Beaulieu E, Del Maestro RF, Moghrabi A, Ghosn PB, Moumdjian R, Berthelet F, Beliveau R (2001) Expression of multidrug-resistance P-glycoprotein (MDR1) in human brain tumors. Int J Cancer 93:62–66
Demling N, Ehrhardt C, Kasper M, Laue M, Knels L, Rieber EP (2006) Promotion of cell adherence and spreading: a novel function of RAGE, the highly selective differentiation marker of human alveolar epithelial type I cells. Cell Tissue Res 323:475–488
Dobbs LG, Gonzales RF (2002) Isolation and culture of pulmonary alveolar epithelial type II cells. In: Freshney RI, Freshney M (eds) Culture of epithelial cells, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 277–301
Ehrhardt C, Kneuer C, Fiegel J, Hanes J, Schaefer UF, Kim KJ, Lehr CM (2002) Influence of apical fluid volume on the development of functional intercellular junctions in the human epithelial cell line 16HBE14o-: implications for the use of this cell line as an in vitro model for bronchial drug absorption studies. Cell Tissue Res 308:391–400
Ehrhardt C, Kim KJ, Lehr CM (2005) Isolation and culture of human alveolar epithelial cells. Methods Mol Med 107:207–216
Ehrhardt C, Collnot EM, Baldes C, Becker U, Laue M, Kim KJ, Lehr CM (2006) Towards an in vitro model of cystic fibrosis small airway epithelium: characterisation of the human bronchial epithelial cell line CFBE41o-. Cell Tissue Res 323:405–415
Elbert KJ, Schafer UF, Schafers HJ, Kim KJ, Lee VH, Lehr CM (1999) Monolayers of human alveolar epithelial cells in primary culture for pulmonary absorption and transport studies. Pharm Res 16:601–608
Florea BI, Cassara ML, Junginger HE, Borchard G (2003) Drug transport and metabolism characteristics of the human airway epithelial cell line Calu-3. J Control Release 87:131–138
Forbes B, Ehrhardt C (2005) Human respiratory epithelial cell culture for drug delivery applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 60:193–205
Foster KA, Oster CG, Mayer MM, Avery ML, Audus KL (1998) Characterization of the A549 cell line as a type II pulmonary epithelial cell model for drug metabolism. Exp Cell Res 243:359–366
Fuchs S, Hollins AJ, Laue M, Schaefer UF, Roemer K, Gumbleton M, Lehr CM (2003) Differentiation of human alveolar epithelial cells in primary culture: morphological characterization and synthesis of caveolin-1 and surfactant protein-C. Cell Tissue Res 311:31–45
Greiner B, Eichelbaum M, Fritz P, Kreichgauer HP, Richter O von, Zundler J, Kroemer HK (1999) The role of intestinal P-glycoprotein in the interaction of digoxin and rifampin. J Clin Invest 104:147–153
Gruenert DC, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH (1995) Culture and transformation of human airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 268:L347–L360
Hamilton KO, Backstrom G, Yazdanian MA, Audus KL (2001) P-glycoprotein efflux pump expression and activity in Calu-3 cells. J Pharm Sci 90:647–658
Higgins CF (1995) Volume-activated chloride currents associated with the multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. J Physiol (Lond) 482:31S–36S
Kennedy BG, Mangini NJ (2002) P-glycoprotein expression in human retinal pigment epithelium. Mol Vis 8:422–430
Kim KJ, Borok Z, Crandall ED (2001) A useful in vitro model for transport studies of alveolar epithelial barrier. Pharm Res 18:253–255
Lechapt-Zalcman E, Hurbain I, Lacave R, Commo F, Urban T, Antoine M, Milleron B, Bernaudin JF (1997) MDR1-Pgp 170 expression in human bronchus. Eur Respir J 10:1837–1843
Manford F, Tronde A, Jeppsson AB, Patel N, Johansson F, Forbes B (2005) Drug permeability in 16HBE14o- airway cell layers correlates with absorption from the isolated perfused rat lung. Eur J Pharm Sci 26:414–420
Mi Q, Cui B, Silva GL, Lantvit D, Lim E, Chai H, You M, Hollingshead MG, Mayo JG, Kinghorn AD, Pezzuto JM, Pervilleine A (2001) A novel tropane alkaloid that reverses the multidrug-resistance phenotype. Cancer Res 261:4030–4037
Patton JS, Fishburn CS, Weers JG (2004) The lungs as a portal of entry for systemic drug delivery. Proc Am Thorac Soc 1:338–344
Steimer A, Haltner E, Lehr CM (2005) Cell culture models of the respiratory tract relevant to pulmonary drug delivery. J Aerosol Med 18:137–182
Stouch TR, Gudmundsson O (2002) Progress in understanding the structure-activity relationships of P-glycoprotein. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:315–328
Wichert P von, Seifart C (2005) The lung, an organ for absorption? Respiration 72:552–558
Wise J, Lechner JF (2002) Normal human bronchial epithelial cell culture. In: Freshney RI, Freshney M (eds) Culture of epithelial cells, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 257–276
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. Susanne Kossek for her skilful technical assistance, Dr. Paul Buckland (Department of Psychological Medicine, Cardiff University) for his help in the PCR studies, and Prof. Kwang-Jin Kim (University of Southern California) for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sibylle Endter is funded by a personal GALENOS Marie-Curie Early Stage Research Training Fellowship (MEST CT-2004-504992).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Endter, S., Becker, U., Daum, N. et al. P-glycoprotein (MDR1) functional activity in human alveolar epithelial cell monolayers. Cell Tissue Res 328, 77–84 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0346-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0346-6