Abstract
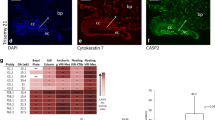
The balance between cell death and cell proliferation and its regulation are essential features of many physiological processes and are particularly important in fetal morphogenesis and adult tissue homeostasis. Apoptosis is a type of cell suicide that is activated in two main ways: through a receptor-mediated pathway or through a mitochondrial pathway. We have investigated the immunohistochemical distribution of proteins belonging to these two pathways in human placenta during gestation by comparing their expression levels between the first and third trimester of gestation. In the first trimester, the receptor-mediated pathway prevails over the mitochondrial pathway with a moderate/intense expression of its three components, viz., Fas ligand (FasL), Fas, and caspase-8, and weak positivity of anti-apoptotic FLIP, these proteins being mainly localized in the cytotrophoblast compartment. In the third trimester of gestation, there is an increased expression of mitochondrial pathway proteins, viz., Apaf-1 and caspase-9. We have also investigated the expression level of caspase-3, the primary effector caspase of both pathways, and have observed that it is moderately expressed during gestation, being mainly localized in the cytotrophoblast during the first trimester and in both placental compartments during the third trimester of gestation. Thus, both pathways actively function in human placenta to execute cell death. By means of immunoelectron microscopy, we have further shown that, in human placenta, the two proteins of the mitochondrial pathway together with caspase-3 are localized both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus. In particular, Apaf-1 and caspase-9 are distributed near to the nuclear envelope suggesting an important role for these two proteins in disrupting the nuclear–cytoplasmic barrier.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alnemri ES, Livington DJ, Nicholson DW, Salvesen G, Thornberry NA, Wong WW, Yuan J (1996) Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 87:171
Bernirschke K, Kaufmann P (2000) Pathology of the human placenta, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X (1999) Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:269–290
Cain K, Bratton SB, Langlais C, Walker G, Brown DG, Sun XM, Cohen GM (2000) Apaf-1 oligomerizes into biologically active approximately 700-kDa and inactive approximately 1.4-MDa apoptosome complexes. J Biol Chem 275:6067–6070
Costantini P, Bruey J-M, Castedo M, Métivier D, Loeffler M, Susin SA, Ravagnan L, Zampami N, Garrido C, Kroemer G (2002) Pre-processed caspase-9 contained in mitochondria participates in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 9:82–88
Cross JC, Werb Z, Fisher SJ (1994) Implantation and the placenta: key pieces of the development puzzle. Science 266:1508–1518
Cryns V, Yuan J (1998) Proteases to die for. Genes Dev 12:1551–1570
De Falco M, De Luca L, Acanfora F, Cavallotti I, Cottone G, Laforgia V, De Luca B, Baldi A, De Luca A (2001) Alteration of the Bcl2:Bax ratio in the placenta as pregnancy proceeds. Histochem J 33:421–425
De Falco M, Fedele V, Cobellis L, Mastrogiacomo A, Leone S, Giraldi D, De Luca L, Laforgia V, De Luca A (2004) Pattern of expression of cyclin D1/cdk4 complex in human placenta during gestation. Cell Tissue Res (in press)
De Luca A, De Falco M, Severino A, Campioni M, Santini D, Baldi F, Paggi MG, Baldi A (2003) Distribution of the serine protease HtrA1 in normal human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 51:1279–1284
De Luca A, De Falco M, Fedele V, Cobellis L, Mastrogiacomo A, Laforgia V, Tuduce IL, Paggi MG, Baldi A (2004) The serine protease HtrA1 is upregulated in human placenta during pregnancy. J Histochem Cytochem (in press)
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM, Kaufmann SH (1999) Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates, and functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem 68:383–424
Faleiro L, Lazebnik Y (2000) Caspases disrupt the nuclear–cytoplasmic barrier. J Cell Biol 151:951–959
Finkel E (2001) The mitochondrion: is it the central to apoptosis? Science 292:727–730
Formigli L, Papucci L, Tani A, Schiavone N, Tempestini A, Orlandini GE, Capaccioli S, Orlandini SZ (2000) Aponecrosis: morphological and biochemical exploration of a syncretic process of cell death sharing apoptosis and necrosis. J Cell Physiol 182:41–49
Hammer A, Blaschitz A, Daxbock C, Walcher W, Dohr G (1999) Fas and Fas-ligand are expressed in the utero-placental unit of first trimester pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol 41:41–51
Huppertz B, Frank H-G, Kingdom JCP, Reister F, Kaufmann P (1998) Villous cytotrophoblast regulation of the syncytial apoptotic cascade in the human placenta. Histochem Cell Biol 110:495–508
Huppertz B, Frank HG, Reister F, Kingdom J, Korr H, Kaufmann P (1999a) Apoptosis cascade progresses during turnover of human trophoblast: analysis of villous cytotrophoblast and syncytial fragments in vitro. Lab Invest 79:1687–1702
Huppertz B, Frank HG, Kaufmann P (1999b) The apoptosis cascade-morphological and immunohistochemical methods for its visualization. Anat Embryol 200:1–18
Huppertz B, Kingdom J, Caniggia I, Desoye G, Black S, Korr H, Kaufmann P (2003) Hypoxia favours necrotic versus apoptotic shedding of placental syncytiotrophoblast into the maternal circulation. Placenta 24:181–190
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schroter M, Burns K, Mattmann C, Rimoldi D, French LE, Tschopp J (1997) Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 388:190–195
Ishizaki Y, Jacobson MD, Raff MC (1998) A role for caspases in lens fiber differentiation. J Cell Biol 140:153–158
Kerr JFR, Gobè GC, Winterford CM, Harmon BV (1995) Anatomical methods in cell death. Methods Cell Biol 46:1–27
Kohler C, Hakansson A, Svanborg C, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (1999) Protease activation in apoptosis induced by MAL. Exp Cell Res 249:260–268
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Scheurich P, Wajant H (2001) NF-κB inducers up-regulated cFLIP, a cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21:3964–3973
Kuwana T, Smith JJ, Muzio M, Dixit V, Newmeyer DD, Kornbluth S (1998) Apoptosis induction by caspase-8 is amplified through the mitochondrial release of cytochrome c. J Biol Chem 273:16589–16594
Lea RG, Riley SC, Antipatis C, Hannah L, Ashworth CJ, Clark DA, Critchley HOD (1999) Cytokines and the regulation of apoptosis in reproductive tissues: a review. Am J Reprod Immunol 42:100–109
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91:479–489
Liu XS, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang XD (1997) DFF, a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. Cell 89:175–184
Medema JP, Scaffidi C, Kischkel FC, Shevchenko A, Mann M, Krammer PH, Peter ME (1997) FLICE is activated by association with the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). EMBO J 16:2794–2804
Morioka K, Tone S, Mukaida M, Takano-Ohmuro H (1998) The apoptotic and nonapoptotic nature of the terminal differentiation of erythroid cells. Exp Cell Res 240:206–217
Nelson DM (1996) Apoptotic changes occur in syncytiotrophoblast of human placental villi where fibrin type fibrinoid is deposited at discontinuities in the villous trophoblast. Placenta 17:387–391
Nicholson DW (1999) Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ 6:1028–1042
Nie G-Y, Hampton A, Li Y, Findlay JK, Salamonsen LA (2003) Identification and cloning of two isoforms of human high-temperature requirement factor A3 (HtrA), characterization of its genomic structure and comparison of its tissue distribution with HtrA1 and HtrA2. Biochem J 371:39–48
Polak JM, Van Noorden S (1987) An introduction to immunocytochemistry: current techniques and problems. Microscopy handbook 11 (revised edition). Oxford University Press, Oxford
Poulaki V, Mitsiades CS, Kotoula V, Tseleni-Balafouta S, Ashkenazi A, Koutras DA, Mitsiades N (2002) Regulation of Apo2L/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in thyroid carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 161:643–654
Rao RV, Castro-Obregon S, Frankowski H, Schuler M, Stoka V, Rio G del, Bredesen DE, Ellerby HM (2002) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program—an Apaf-1 independent intrinsic pathway. J Biol Chem 277:21836–21842
Ratts VS, Tao XJ, Webster CB, Swanson PE, Smith SD, Brownbill P, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Tilly JL, Nelson DM (2000) Expression of BCL-2, BAX and BAK in the trophoblast layer of the term human placenta: a unique model of apoptosis within a syncytium. Placenta 21:361–366
Ritter PM, Marti A, Blanc C, Baltzer A, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Jaggi R (2000) Nuclear localization of procaspase-9 and processing by a caspase-3-like activity in mammary epithelial cells. Eur J Cell Biol 79:358–364
Ruiz-Vela A, Gonzalez de Buitrago G, Martinez-A C (2002) Nuclear Apaf-1 and cytochrome c redistribution following stress-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett 517:133–138
Saleh A, Srinivasula SM, Acharya S, Fishel R, Alnemri ES (1999) Cytochrome c and dATP-mediated oligomerization of Apaf-1 is a prerequisite for procaspase-9 activation. J Biol Chem 274:17941–17945
Santiago B, Galindo M, Palao G, Pablos JL (2004) Intracellular regulation of Fas-induced apoptosis in human fibroblasts by extracellular factors and cycloheximide. J Immunol 172:560–566
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, Debatin KM, Krammer PH, Peter ME (1998) Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J 17:1675–1687
Smith SC, Baker PN, Symonds EM (1997) Placental apoptosis in normal human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 177:57–65
Stennicke HR, Deveraux QL, Humke EW, Reed JC, Dixit VM, Salvesen GS (1999) Caspase-9 can be activated without proteolytic processing. J Biol Chem 274:8359–8362
Thome M, Tschopp J (2001) Regulation of lymphocyte proliferation and death by FLIP. Nat Rev Immunol 1:50–58
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281:1312–1316
Villa P, Kaufmann SC, Earnshaw WC (1997) Caspases and caspase inhibitors. Trends Biochem Sci 22:388–392
Wajant H, Haas E, Scwenzer R, Muhlenbeck F, Kreuz S, Schubert G, Grell M, Smith C, Scheurich P (2000) Inhibition of death receptor-mediated gene induction by a cycloheximide-sensitive factor occurs at the level of or upstream of Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD). J Biol Chem 275:24357–24366
Yasuhara N, Eguchi Y, Tachibana T, Imamoto N, Yoneda Y, Tsujimoto Y (1997) Essential role of active nuclear transport in apoptosis. Genes Cells 2:55–64
Yusuf K, Smith SD, Sadovsky Y, Nelson DM (2002) Trophoblast differentiation modulates the activity of caspases in primary cultures of term human trophoblasts. Pediatr Res 52:411–415
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X, Wang X (1999) Activation of the apoptotic endonuclease DFF40 (caspase-activated DNase or nuclease). Oligomerization and direct interaction with histone H1. J Biol Chem 274:11549–11556
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Pia Furno for editing the manuscript, Mr. Giuseppe Falcone for his contribution to the image elaboration, and Miss Angela Raucci and Miss Nektaria Ndaoula for their contribution in the experimental design.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the University of Naples “Federico II” (V.L.); the Second University of Naples; Regione Campania Funds AIRC (A.D.L.) and I.S.S.C.O (President H.E. Kaiser)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Falco, M., Fedele, V., Cobellis, L. et al. Immunohistochemical distribution of proteins belonging to the receptor-mediated and the mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in human placenta during gestation. Cell Tissue Res 318, 599–608 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0969-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0969-4