Abstract
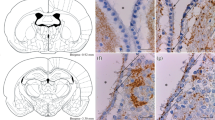
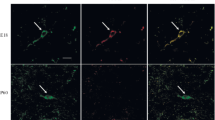
Dopamine receptors have been found in certain populations of non-neuronal cells in the brain, viz., discrete areas of ciliated ependyma and the ependymal cells of the choroid plexus. We have studied the presence of both tyrosine-hydroxylase-immunoreactive nerve fibers and dopamine receptors in the subcommissural organ (SCO), an ependymal brain gland that is located in the roof of the third ventricle and that secretes, into the cerebrospinal fluid, glycoproteins that aggregate to form Reissner’s fiber (RF). Antibodies against D2, D3, D4, and D5 dopamine receptors were used in immunoblots of bovine striatum, fresh SCO, and organ-cultured SCO, and in immunocytochemistry of the bovine, rat, and mouse SCO. Only a few tyrosine-hydroxylase fibers appeared to reach the SCO. However, virtually all the secretory ependymal and hypendymal cells of the SCO immunoreacted with antibodies against D2, D4, and D5 receptors, with the last-mentioned rendering the strongest reaction, especially at the ventricular cell pole of the secretory ependymocytes, suggesting that dopamine might reach the SCO via the cerebrospinal fluid. The antibodies against the four subtypes of receptors revealed corresponding bands in immunoblots of striatum and fresh SCO. Although the cultured SCO displayed dopamine receptors, dopamine had no apparent effect on the expression of the SCO-spondin gene/protein or on the release of RF-glycoproteins (SCO-spondin included) by SCO explants, suggesting that dopamine affects the function(s) of the SCO differently from the secretion of RF-glycoproteins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiso M, Shigematsu K, Kebabian JW, Potter WZ, Cruciani RA, Saavedra JM (1987) Dopamine D1 receptor in rat brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study with 125I-SCH 23982. Brain Res 408:281–285
Bal A, Bachelot T, Savasta M, Manier M, Verna JM, Benabid AL, Feuerstein C (1994) Evidence for dopamine D2 receptor mRNA expression by striatal astrocytes in culture: in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction studies. Mol Brain Res 23:204–212
Balaban CD, Schuerger RJ, Severs WB (1994) Evidence for a noradrenergic projection to the subcommissural organ. Neurosci Lett 180:209–213
Bergson C, Mrzljak L, Lidow MS, Goldman-Rakic PS, Levenson R (1995) Characterization of subtype-specific antibodies to the human D5 dopamine receptor: studies in primate brain and transfected mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:3468–3472
Biedermann B, Fröhlich E, Grosche J, Wagner HJ, Reichenbach A (1995) Mammalian Müller (glial) cells express functional D2 dopamine receptors. Neuroreport 6:609–612
Bongarzone ER, Howard SG, Schonmann V, Campagnoni AT (1998) Identification of the dopamine D3 receptor in oligodendrocyte precursors: potential role in regulating differentiation and myelin formation. J Neurosci 18:5344–5353
Bouchaud C (1979) Evidence for a multiple innervation of subcommissural ependymocytes in the rat. Neurosci Lett 12:253–258
Bouchaud C, Bosler O (1986) The circumventricular organs of the mammalian brain with special reference to monoaminergic innervation. Int Rev Cytol 105:283–327
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bunzow JR, Van Tol HH, Grandy DK, Albert P, Salon J, Christie M, Machida CA, Neve KA, Civelli O (1988) Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature 336:783–787
Caprile T, Hein S, Rodríguez S, Montecinos H, Rodríguez E (2003) Reissner fiber binds and transports away monoamines present in the cerebrospinal fluid. Mol Brain Res 110:177–192
Chan-Palay V (1976) Serotonin axons in the supra- and subependymal plexuses and in the leptomeninges; their roles in local alterations of cerebrospinal fluid and vasomotor activity. Brain Res 102:103–130
Chazot PL, Doherty AJ, Strange PG (1993) Antisera specific for D2 dopamine receptors. Biochem J 289:789–794
Estivill-Torrús G, Cifuentes M, Grondona JM, Miranda E, Bermúdez-Silva FJ, Fernández-Llebrez P, Pérez J (1998) Quantification of the secretory glycoproteins of the subcommissural organ by a sensitive sandwich ELISA with a polyclonal antibody and a set of monoclonal antibodies against the bovine Reissner’s fiber. Cell Tissue Res 249:407–413
Fernández-Llebrez P, Miranda E, Estivill-Torrús G, Cifuentes M, Grondona JM, López-Ávalos MD, Pérez-Martín M, Pérez J (2001) Analysis and quantification of the secretory products of the subcommissural organ by use of monoclonal antibodies. Microsc Res Tech 52:510–519
Gamrani H, Belin MF, Aguera M, Calas A, Pujol JF (1981) Radioautographic evidence for an innervation of the subcommissural organ by GABA-containing nerve fibres. J Neurocytol 10:411–424
Ghiani P, Uva B, Vallarino M, Mandich A, Masini MA (1988) Angiotensin II specific receptors in subcommissural organ. Neurosci Lett 85:212–216
Giordano J, Harting PR (1987) In vivo labeling indicates that CSF serotonin activates the 5-HT1c receptor on the apical surface of the choroid plexus epithelium. Neuroscience 22:223
Gobron S, Monnerie H, Meiniel R, Creveaux I, Lehmann W, Lamalle D, Dastugue B, Meiniel A (1996) SCO-spondin: a new member of the thrombospondin family secreted by the subcommissural organ is a candidate in the modulation of neuronal aggregation. J Cell Sci 109:1053–1061
Gobron S, Creveaux I, Meiniel R, Didier R, Herbet A, Bamdad M, El Bitar F, Dastugue B, Meiniel A (2000) Subcommissural organ/Reissner’s fiber complex: characterization of SCO-spondin, a glycoprotein with potent activity on neurite outgrowth. Glia 32:177–191
Hansson E, Ronnback L (1988) Interaction between catecholamines and vasoactive intestinal peptide in cultured astrocytes. Neuropharmacology 27:295–300
Hess J, Sterba G (1973) Studies concerning the function of the complex subcommissural organ-liquor fibre: the binding ability of the liquor fibre to pyrocatechin derivatives and its functional aspects. Brain Res 58:303–312
Howard S, Landry C, Fisher R, Bezouglaia O, Handley V, Campagnoni A (1998) Postnatal localization and morphogenesis of cells expressing the dopaminergic D2 receptor gene in rat brain: expression in non-neuronal cells. J Comp Neurol 391:87–98
Jarvie KR, Niznik HB, Seeman P (1988) Dopamine D2 receptor binding subunits of Mr congruent to 140,000 and 94,000 in brain: deglycosylation yields a common unit of Mr congruent to 44,000. Mol Pharmacol 34:91–97
Jiménez AJ, Fernández-Llebrez P, Pérez-Fígares JM (2001) Neural input and neural control of the subcommissural organ. Microsc Res Tech 52:520–533
Karpa KD, Lin R, Kabbani N, Levenson R (2000) The dopamine D3 receptor interacts with itself and the truncated D3 splice variant d3nf: D3-D3nf interaction causes mislocalization of D3 receptors. Mol Pharmacol 58:677–683
Khan ZU, Gutiérrez A, Martín R, Peñafiel A, Rivera A, Calle A de la (1998) Differential regional and cellular distribution of dopamine D2-like receptors: an immunocytochemical study of subtype-specific antibodies in rat and human brain. J Comp Neurol 402:353–371
Khan ZU, Gutiérrez A, Martín R, Peñafiel A, Rivera A, Calle A de la (2000) Dopamine D5 receptors of rat and human brain. Neuroscience 100:689–699
Khan ZU, Koulen P, Rubinstein M, Grandy DK, Goldman-Rakic PS (2001) An astroglia-linked dopamine D2-receptor action in prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1964–1969
Léger L, Degueurce A, Lundberg JJ, Pujol JF, Møllgard K (1983) Origin and influence of the serotoninergic innervation of the subcommissural organ in the rat. Neuroscience 10:411–423
Lindvall-Axelsson M, Mathew C, Nilsson C, Owman C (1988) Effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the rate of cerebrospinal fluid production in rabbit. Exp Neurol 99:362–368
Meiniel A (2001) SCO-spondin, a glycoprotein of the subcommissural organ/Reissner’s fiber complex: evidence of a potent activity on neuronal development in primary cell cultures. Microsc Res Tech 52:484–495
Meiniel A, Meiniel R, Didier R, Creveaux I, Gobron S, Monnerie H, Dastugue B (1996) The subcommissural organ and Reissner’s fiber complex. An enigma in the central nervous system? Prog Histochem Cytochem 30:1–66
Mignini F, Bronzetti E, Felici L, Ricci A, Sabbatini M, Tayebati SK, Amenta F (2000) Dopamine receptor immunohistochemistry in the rat choroid plexus. J Auton Pharmacol 20:325–332
Miranda E, Almonacid JA, Rodríguez S, Pérez J, Hein S, Cifuentes M, Fernández-Llebrez P, Rodríguez EM (2001) Searching for specific binding sites of the secretory glycoproteins of the subcommissural organ. Microsc Res Tech 52:541–551
Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998) Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 78:189–225
Møllgard K, Lundberg JJ, Wiklund L, Lachenmayer L, Baumgarten HG (1978) Morphologic consequences of serotonin neurotoxin administration: neuron-target cell interaction in the rat subcommissural organ. Ann N Y Acad Sci 305:262–288
Monnerie H, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Dastugue B, Meiniel A (1995) Reissner’s fibre supports the survival of chick cortical neurons in primary mixed cultures. Cell Tissue Res 282:81–91
Monnerie H, Dastugue B, Meiniel A (1997) In vitro differentiation of chick spinal cord neurons in the presence of Reissner’s fibre, an ependymal brain secretion. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 102:167–176
Monnerie H, Dastugue B, Meiniel A (1998) Effect of synthetic peptides derived from SCO-spondin conserved domains on chick cortical and spinal-cord neurons in cell cultures. Cell Tissue Res 293:407–418
Naumann W (1986) Immunohistochemical investigations on the ontogenesis of the subcommissural organ. Acta Histochem Suppl 33:265–272
Ng GY, O’Dowd BF, Lee SP, Chung HT, Brann MR, Seeman P, George SR (1996) Dopamine D2 receptor dimers and receptor-blocking peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 227:200–204
Nicklaus KJ, McGonigle P, Molinoff PB (1988) [3H]SCH 23390 labels both dopamine-1 and 5-hydroxytryptamine1c receptors in the choroid plexus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:343–348
Nilsson C, Fahrenkrug J, Lindvall-Axelsson M, Owman C (1991) Epithelial cells purified from choroid plexus have receptors for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Brain Res 542:241–247
Nualart F, Hein S, Rodríguez EM, Oksche A (1991) Identification and partial characterization of the secretory glycoproteins of the bovine subcommissural organ-Reissner’s fiber complex. Evidence for the existence of two precursor forms. Mol Brain Res 11:227–238
Nürnberger F, Schöniger S (2001) Presence and functional significance of neuropeptide and neurotransmitter receptors in subcommissural organ cells. Microsc Res Tech 52:534–540
Oksche A (1961) Vergleichende Untersuchungen über die sekretorische Aktivität des Subkommissuralorgans und den Gliacharakter seiner Zellen. Z Zellforsch 54:549–612
Oksche A, Rodríguez EM, Fernández-Llebrez P (1993) The subcommissural organ: an ependymal brain gland. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Olsson R (1993) Reissner’s fiber mechanisms: some common denominators. In: Oksche A, Rodríguez EM, Fernández-Llebrez P (eds) The subcommissural organ: an ependymal brain gland. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 33–39
Pérez J, Garrido O, Cifuentes M, Alonso FJ, Estivill-Torrús G, Eller G, Nualart F, López-Ávalos MD, Fernández-Llebrez P, Rodríguez EM (1996) Bovine Reissner’s fiber (RF) and the central canal of the spinal cord: an immunocytochemical study using a set of monoclonal antibodies against the RF-glycoproteins. Cell Tissue Res 286:33–42
Reuss B, Unsicker K (2000) Survival and differentiation of dopaminergic mesencephalic neurons are promoted by dopamine-mediated induction of FGF-2 in striatal astroglial cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 16:781–792
Richter HG, Muñoz RI, Millan CS, Guinazu MF, Yulis CR, Rodríguez EM (2001) The floor plate cells from bovines express the mRNA encoding for SCO-spondin and its translation products. Mol Brain Res 93:137–147
Rios M, Ojeda S, Velasquez LA, Maisey K, Croxatto HB (2001) A segment and epithelium specific messenger ribonucleic acid fragment up-regulated by estradiol in the rat oviduct. Biol Res 34:15–21
Rodríguez S, Caprile T (2001) Functional aspects of the subcommissural organ-Reissner’s fiber complex with emphasis in the clearance of brain monoamines. Microsc Res Tech 52:564–572
Rodríguez EM, Oksche A, Hein S, Rodríguez S, Yulis R (1984) Comparative immunocytochemical study of the subcommissural organ. Cell Tissue Res 237:427–441
Rodríguez EM, Oksche A, Hein S, Yulis CR (1992) Cell biology of the subcommissural organ. Int Rev Cytol 135:39–121
Rodríguez EM, Jara P, Richter H, Montecinos H, Flandes B, Wiegand R, Oksche A (1993) Evidence of the release of CSF-soluble secretory material from the subcommissural organ, with particular reference to the situation in human. In: Oksche A, Rodríguez EM, Fernández-Llebrez P (eds) The subcommissural organ: an ependymal brain gland. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 121–131
Rodríguez EM, Rodríguez S, Hein S (1998) The subcommissural organ. Microsc Res Tech 41:98–123
Rodríguez S, Vio K, Wagner C, Barria M, Navarrete EH, Ramírez VD, Perez-Fígares JM, Rodríguez EM (1999) Changes in the cerebrospinal-fluid monoamines in rats with an immunoneutralization of the subcommissural organ-Reissner’s fiber complex by maternal delivery of antibodies. Exp Brain Res 128:278–290
Roland BL, Li KX, Funder JW (1995) Hybridization histochemical localization of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in rat brain. Endocrinology 136:4697–4700
Ruckebusch M, Sutra JF (1984) On the significance of monoamines and their metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid of the sheep. J Physiol (Lond) 348:457–469
Ruggiero DA, Regunathan S, Wang H, Milner TA, Reis DJ (1998) Immunocytochemical localization of an imidazoline receptor protein in the central nervous system. Brain Res 780:270–293
Schöbitz K, Garrido O, Heinrichs M, Speer L, Rodríguez EM (1986) Ontogenetical development of the chick and duck subcommissural organ. An immunocytochemical study. Histochemistry 84:31–40
Schöbitz K, González C, Peruzzo B, Yulis CR, Rodríguez EM (2001) Organ culture of the bovine subcommissural organ: evidence for synthesis and release of the secretory material. Microsc Res Tech 52:496–509
Schöniger S, Wehming S, González C, Schöbitz K, Rodríguez E, Oksche A, Yulis CR, Nürnberger F (2001) The dispersed cell culture as model for functional studies of the subcommissural organ: preparation and characterization of the culture system. J Neurosci Methods 107:47–61
Schöniger S, Kopp MD, Schomerus C, Maronde E, Dehghani F, Meiniel A, Rodríguez M, Korf HW, Nürnberger F (2002a) Effects of neuroactive substances on the activity of subcommissural organ cells in dispersed cell and explant cultures. Cell Tissue Res 307:101–114
Schöniger S, Maronde E, Kopp MD, Korf HW, Nürnberger F (2002b) Transcription factor CREB and its stimulus-dependent phosphorylation in cell and explant cultures of the bovine subcommissural organ. Cell Tissue Res 308:131–142
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres MP, Bouthenet ML, Schwartz JC (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature 347:146–151
Sunahara RK, Guan HC, O’Dowd BF, Seeman P, Laurier LG, Ng G, George SR, Torchia J, Van Tol HH, Niznik HB (1991) Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature 350:614–619
Surmeier DJ, Eberwine J, Wilson CJ, Cao Y, Stefani A, Kitai ST (1992) Dopamine receptor subtypes colocalize in rat striatonigral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10178–10182
Ternaux JP, Boireau A, Bourgoin S, Hamon M, Hery F, Glowinski J (1976) In vivo release of 5-HT in the lateral ventricle of the rat: effects of 5-hydroxytryptophan and tryptophan. Brain Res 101:533–548
Torres-Farfan C, Richter HG, Rojas-García P, Vergara M, Forcelledo ML, Valladares LE, Torrealba F, Valenzuela GJ, Seron-Ferre M (2003) mt1 Melatonin receptor in the primate adrenal gland: inhibition of adrenocorticotropin-stimulated cortisol production by melatonin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:450–458
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Vallone D, Picetti R, Borrelli E (2000) Structure and function of dopamine receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:125–132
Van Tol HH, Bunzow JR, Guan HC, Sunahara RK, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Civelli O (1991) Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature 350:610–614
Verkhratsky A, Kettenmann H (1996) Calcium signalling in glial cells. Trends Neurosci 19:346–352
Walker GR, Feather KD, Davis PD, Hines KK (1995) SuperSignalTM CL-HRP: a new enhanced chemiluminescent substrate for the development of the horseradish peroxide label in Western blotting applications. J Natl Inst Health Res 7:76
Wang F, Bergson C, Howard RL, Lidow MS (1997) Differential expression of D1 and D5 dopamine receptors in the fetal primate cerebral wall. Cereb Cortex 7:711–721
Zanassi P, Paolillo M, Montecucco A, Avvedimento EV, Schinelli S (1999) Pharmacological and molecular evidence for dopamine D(1) receptor expression by striatal astrocytes in culture. J Neurosci Res 58:544–552
Zawarynski P, Tallerico T, Seeman P, Lee SP, O’Dowd BF, George SR (1998) Dopamine D2 receptor dimers in human and rat brain. FEBS Lett 441:383–386
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. A. de la Calle and his collaborators, Dr. Z. Khan, Dr. A. Gutiérrez, and Dr. R. Martín, from the Department of Cell Biology, University of Málaga for the gift of the polyclonal antibodies against dopamine receptors. We also wish to thank to E. Moreira for her help with the immunostaining of frozen sections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Financial support was provided by grants PI 030756 and Red CIEN, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain (to J.M.P.F.), and 1030265 from Fondecyt, Chile (to E.M.R.)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomé, M., Jiménez, A.J., Richter, H. et al. The subcommissural organ expresses D2, D3, D4, and D5 dopamine receptors. Cell Tissue Res 317, 65–77 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0900-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0900-z