Abstract
Polyglutamine (polyQ) spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs) comprise a group of autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorders caused by (CAG/CAA)n expansions. The elongated stretches of adjacent glutamines alter the conformation of the native proteins inducing neurotoxicity, and subsequent motor and neurological symptoms. Although the etiology and neuropathology of most polyQ SCAs have been extensively studied, only a limited selection of therapies is available. Previous studies on SCA1 demonstrated that ATXN1L, a human duplicated gene of the disease-associated ATXN1, alleviated neuropathology in mice models. Other SCA-associated genes have paralogs (i.e., copies at different chromosomal locations derived from duplication of the parental gene), but their functional relevance and potential role in disease pathogenesis remain unexplored. Here, we review the protein homology, expression pattern, and molecular functions of paralogs in seven polyQ dominant ataxias—SCA1, SCA2, MJD/SCA3, SCA6, SCA7, SCA17, and DRPLA. Besides ATXN1L, we highlight ATXN2L, ATXN3L, CACNA1B, ATXN7L1, ATXN7L2, TBPL2, and RERE as promising functional candidates to play a role in the neuropathology of the respective SCA, along with the parental gene. Although most of these duplicates lack the (CAG/CAA)n region, if functionally redundant, they may compensate for a partial loss-of-function or dysfunction of the wild-type genes in SCAs. We aim to draw attention to the hypothesis that paralogs of disease-associated genes may underlie the complex neuropathology of dominant ataxias and potentiate new therapeutic strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Microsatellite repeats in dominant spinocerebellar ataxias
Short tandem repeats (STRs or microsatellites) consist of short sequence motifs (1–6 bp) contiguously repeated at a given locus, estimated to constitute at least 3% of the human genome (Shortt et al. 2020). STRs are intrinsically unstable and more prone to mutations than other parts of the genome (Ellegren 2000), occurring mostly alterations in the number of repeated units (contractions or expansions). These alterations can happen via slipped-strand mispairing during DNA replication, recombination events (unequal crossing over or gene conversion), or incorrect repair of DNA strand-breakage (Gemayel et al. 2010). STRs occur both in coding and noncoding regions of the genome but those that fall within coding sequences are limited to trinucleotide repeats, often CAG or GCN encoding for polyglutamine (polyQ) and polyalanine (polyA) amino acid tracts, respectively. On the other hand, repetitive loci in the noncoding genome may encompass regulatory elements (Sawaya et al. 2013; Fotsing et al. 2019) and function as expression regulators through the modulation of DNA methylation, alternative splicing, and transcription factor binding (Gemayel et al. 2010). In both coding and noncoding regions, large expansions (typically more modest in length in the first) have occurred at some loci over human evolution. These expansions, after reaching a given locus-specific threshold, trigger cytotoxicity through diverse mechanisms leading to disease (Hannan 2018; Depienne and Mandel 2021).
To date, more than 40 repeat expansion disorders have been discovered to primarily affect the nervous system, including 13 spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs). In this group of disorders, the length and nucleotide composition of the STR motif differs according to the causative gene: SCA1, SCA2, Machado-Joseph disease (MJD)/SCA3, SCA6-8, SCA10, SCA12, SCA17, SCA31, SCA36, SCA37, dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA), and the recently identified SCA27B (Klockgether et al. 2019; Pellerin et al. 2023). From these repeat-associated SCAs, seven are caused by (CAG)n tracts, which together with Huntington’s disease and spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy make a total of nine polyQ-associated diseases (Hannan 2018; Paulson 2018). Genes involved in polyQ SCAs are ataxin 1 (ATXN1; SCA1), ataxin 2 (ATXN2; SCA2), ataxin 3 (ATXN3; MJD/SCA3), calcium voltage-gated channel subunit α1A (CACNA1A; SCA6), ataxin 7 (ATXN7; SCA7), TATA-box binding protein (TBP; SCA17) and atrophin 1 (ATN1; DRPLA) (Table 1). Additionally, SCA12 is also a CAG disorder but the expanded repeat is located in the untranslated region of the gene, typically not encoding polyQ tract proteins (Paulson 2018). In the case of SCA8, the bidirectional transcription of CTG*CAG repeat expanded transcripts in two overlapping genes, ataxin 8 opposite strand and ataxin 8 (ATXN8OS/ATXN8), produces a CTG-expanded antisense non-coding RNA and a pathogenic polyQ protein (Moseley et al. 2006). Moreover, an alternative repeat-associated non-AUG translation may contribute to the pathogenesis of SCA8 (Zu et al. 2011). Thereafter, SCA2 and SCA7 have been found to present bidirectional transcription, along with Huntington’s disease. The ATXN2 (CAG)n was found to be bidirectionally transcribed into an antisense (CUG)n (ATXN2-AS) transcript in both unaffected and SCA2 affected brain tissues. However, both normal and expanded ATXN2-AS RNAs do not seem to be translated by non-AUG translation (Li et al. 2016a). In ATXN7, one alternative promoter (intron 5′ to exon 3) has been found to transcribe the spinocerebellar ataxia 7 antisense noncoding transcript 1 (SCAANT1). Notably, the SCAANT1 and ATXN7 have a synergist transcriptional regulation, which is dysregulated by polyQ expansions (Sopher et al. 2011). Very recently, a novel subtype of SCA caused by a (CAG)n expansions in the THAP domain containing 11 gene has been described in two families (Tan et al. 2023).
Unfortunately, the pathological mechanisms underlying SCAs remain poorly understood and only a few therapeutic approaches have been proposed to mitigate disease symptomatology (Klockgether et al. 2019). The abnormal polyQ expanded proteins increase the propensity for aggregation and misfolding processes, tending to reduce the interaction with usual binding partners and/or recruit other susceptible proteins into inactive cytoplasmic or nuclear inclusions. Consequently, these polyQ expansions cause a loss of function effect perturbing protein and RNA homeostasis in a specific manner dependent on the native protein function (Paulson et al. 2017; Lieberman et al. 2019) (Figs. 1 and 2). In contrast, these polyQ-expanded motifs can produce both expanded proteins and RNAs that promote abnormal interactions, i.e., a gain of function mostly characterized by RNA toxicity, aberrant alternative splicing, repeat-associated non-AUG translation, and proteinopathy (Lieberman et al. 2019). In some cases, the native protein intermingles with the polyQ expanded form (e.g., SCA1, MJD/SCA3) contributing to the aggregation process and loss of function effect, suggesting that a partial loss of function mechanism contributes to disease progression (Crespo-Barreto et al. 2010; Zeng et al. 2018). Moreover, in some SCAs, both the abnormal repeat expansions and single nucleotide variants appear to cause ataxia-like symptoms (e.g., SCA6) with both gain of function and loss of function mechanisms underlying the observed phenotypes, emphasizing the complexity of SCAs etiology (Pietrobon 2002; Indelicato and Boesch 2021). The main challenge in developing treatments for SCAs is their genetic diversity and clinical variability. Studies have successfully reported the use of gene silencing strategies as therapies for some SCAs presenting a toxic gain of function mechanism (Bushart et al. 2016; McIntosh et al. 2021). Other strategies involve finding convergent mechanisms within multiple SCAs. Since many cerebellar ataxias seem to be caused by a process of protein aggregation, a promising treatment approach would implicate compounds that promote the redirection of protein aggregates to the proteasome, actively stimulating their degradation (Bushart et al. 2016; Klockgether et al. 2019).
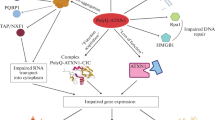
Model for SCA1 neuropathology and ATXN1/ATXN1L functional redundancy. ATXN1 has at least two distinct associated protein complexes in vivo: CIC-ATXN1 and ATXN1-RBM17. In the ATXN1 protein, it is believed that the AXH, SAR and UHM domains are interaction motifs for the transcriptional regulator CIC, ATXN1L and the RNA splicing factor RBM17, respectively. The CIC-ATXN1 complex details a synergistic relationship between the transcriptional repressor CIC, ATXN1, and ATXN1L to drive transcription repression. ATXN1–RBM17 modulates mRNA splicing through the phosphorylation state of ATXN1, but the polyQ-expanded ATXN1 favours the formation of RBM17-containing complexes contributing to SCA1 by means of a gain-of-function. At the same time, polyQ-expansions decreases the formation of ATXN1-CIC complexes, resulting in a partial loss-of-function. This event possibly results from CIC degradation by the E3-ligase TRIM25 and caspase 14-3-3 due to the lack of stabilization by ATXN1L in the complex. The mechanism causing the reduction of ATXN1L levels in SCA1 is still unknown. In SCA1 mice models, this functional overlap between ATXN1 and ATXN1L in the CIC-ATXN1 complex was demonstrated to partially rescue the polyQ-expanded ATXN1 function, contributing to pathology suppression. The increased ATXN1L levels competed with polyQ-expanded ATXN1 and normal ATXN1 (to a lesser extent) for association with CIC: decreasing the levels of polyQ-expanded ATXN1-containing CIC aggregates, promoting ATXN1 nuclear aggregation, and restoring the transcriptional function. In addition, ATXN1 and ATXN1L both interact with components of the co-repressor SMRT-HDAC3 complex but the polyQ-expanded ATXN1 seem to sequester SMRT components into nuclear inclusions (probably also affecting HDAC3 function as seen in MJD/SCA3). Thus, a functional rescue may be also possible in the context of the SMRT/HDAC3 transcription complex. UHM, U2AF homology domain. polyQ expansion (represented as Q in red). Pol II, RNA polymerase II (in dark yellow). Ub, ubiquitin (in black). P, phosphorylation (in yellow)
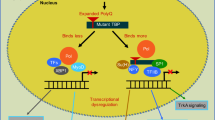
Molecular functions affected by expanded polyQ proteins in SCA2, SCA3, SCA6, SCA7, SCA17, and DRPLA. a ATXN2 interact directly or indirectly with numerous proteins implicated in RNA metabolism, as well as RNA itself, to regulate translation and stress granule/P-body formation. One hypothesis is that the polyQ-expanded ATXN2 inhibits its native interactions, impairing RNA metabolism and autophagy; thereby contributing to SCA2 pathogenesis. The exact mechanisms behind the alterations in RNA metabolism and stress granule/P-body formation in SCA2 remain unknown. Previous studies indicated that reduction of ATXN2 or STAU1, an interactor of ATXN2 and modulator of stress granules, was able to decrease aggregation of polyQ-expanded ATXN2 and improve motor behaviour in mice—suggesting that ATXN2L could also improve symptomatology in SCA2. b ATXN3 binds and cleaves polyubiquitin chains and has been implicated in ubiquitin-dependent protein quality control pathways (e.g., proteasome). Its paralog, ATXN3L Josephin domain revealed a higher deubiquitinase activity (+ +) possibly exhibiting functional redundancy. In MJD/SCA3, the polyQ-expanded ATXN3 seems to inhibit its deubiquitin activity and disrupt cellular proteostasis. Besides, it also can affect its DNA binding function and form nuclear inclusions with its transcription-related interactors (HDAC3, SMRT), impairing transcription repression. c CACNA1A gene encodes a bicistronic mRNA that produces two proteins: the membrane-localized α1A subunit of the Cav2.1 channel and the transcription factor α1ACT. The polyQ-expanded CACNA1A leads to toxicity through impaired α1ACT-mediated transcription (decrease expression of gene targets—TAF1, GRN, BTG1 and PMCA2), as well as through altered Cav2.1 channel properties. CACNA1B and CACNA1E genes also encode Cav2 channels that could partially replace Cav2.1 function in SCA6. d ATXN7 is a component of the SAGA transcription complex. PolyQ-expanded ATXN7 forms nuclear aggregates that are thought to sequester other components of the DUBm (ATXN7L3, ENY2, UPS22) such that the complex can no longer remove ubiquitin from its substrates. Even GCN5 histone acetyltransferase from the SAGA complex is sequestered into polyQ-expanded ATXN7 inclusions. Its paralog ATXN7L3B seems to also interact with ENY2 of the DUBm, however it seems to only function to limit SAGA activity by competing with ATXN7L3 (inactive SAGA). ATXN7L1 and ATXN7L2 have highly conserved domains with ATXN7 that appear to play interchangeable role in SAGA DUBm, however no studies characterized these proteins functions or interactions. Interestingly, co-overexpression of ATXN7L3 and ENY2 suppressed the formation of polyQ-expanded ATXN7 aggregates. e TBP is a transcription factor from the TFIID complex. The TBPL1 paralog does not bind to the TATA box as TBP, instead it relies on TCT motifs to repress transcription. In SCA17, the polyQ-expanded TBP impairs the DNA-binding and transactivation activity (targets—NF-γ, TFIIB, SP1, XBP1, MYOD) and exacerbates the formation of nuclear inclusions that reduce the TFIID complex availability for the transcription initiation process. As opposed to TBPL1, TBPL2 contains a highly conserved core domain and common interactors with TBP, constituting a promising candidate to compensate for TBP loss of function in SCA17. f ATN1 seems to work as a transcriptional co-repressor inhibiting transcription factors, but its function is not yet well understood. In DRPLA, the polyQ-expanded ATN1 was found to generate inclusions, in the cytoplasm and nucleus, which appear to disrupt ATN1 native protein–protein interactions. Also, polyQ-expanded ATN1 present abnormal ubiquitination, phosphorylation and cleavage in patients. The paralog RERE is thought to also be involved in transcription regulation and/or DNA binding, showing the ability to recruit histone deacetylases and serve as a transcriptional corepressor. In addition, RERE was proposed to be involved in caspase-mediated cell death (PML and BAX, promyelocytic leukemia oncogenic domains). Interestingly, RERE seems to directly interact with ATN1 partly via conserved RE motifs and form heterodimers, which can be related to the high tendency of this protein to aggregate with polyQ-expanded ATN1, likely depleting RERE protein in DRPLA patients. Still, not much information is known regarding these proteins nor DRPLA pathological mechanisms. TFs, transcription factors. TAFs, TBP-associated factors. HDAC, histone deacetylase. polyQ expansion (represented as Q in red). Pol II, RNA polymerase II (in dark yellow). Ub, ubiquitin (in black). A, acetylation (in yellow). P, phosphorylation (in yellow)
Paralog genes in humans
The current understanding of the SCA pathophysiological mechanisms may be improved through the analysis of paralogs, i.e., gene copies at different chromosomal locations that are derived from the duplication of a parental gene (Koonin 2005). Previous analyses of the human genome have predicted that at least 15% of human genes are duplicates (Li et al. 2001). These copies can arise from either DNA or RNA-based duplications. In the first case, parts of genes (i.e., segmental duplication or small-scale duplication) can be copied via unequal crossing over and transposable elements, though the exact mechanisms are unknown. In the second case, RNA-based duplication (retrotransposition/retroduplication) can arise through the insertion of reverse transcribed mRNAs into the genome (Kaessmann 2010). It was first thought that retrotransposition events would consistently lead to inactive pseudogenes, i.e., nonfunctional exonic sequences that cannot be expressed (Mighell et al. 2000). Still, retrogenes may become functional after the acquisition or evolution of regulatory elements to drive their expression (Casola and Betrán 2017).
Immediately after gene duplication, paralogs are expected to present complete functional redundancy, facilitating evolutionary change, but subsequently most degenerate and become pseudogenes by the accumulation of loss of function mutations (i.e., pseudogenization/non-functionalization) (Innan and Kondrashov 2010). Exceptionally, paralogs accumulate mutations that can be fixed in a population and give rise to new advantageous functional properties (i.e., neofunctionalization), or even partially conserve the ancestral function through gene-dosage amplification or subfunctionalization (duplication–degeneration–complementation model). The subfunctionalization process may reflect both neutral drift with complementary loss of function mutations between the paralogs making them indispensable for the ancestral function and adaptive evolution. Indeed, the ancestor function can become partitioned between the paralogs, and each may evolve toward the optimization of the retained function. The presence of duplicate genes with overlapping roles may relax/modify the selection pressure of the parental gene, while retaining a certain degree of functional overlap through long periods in evolution (Innan and Kondrashov 2010).
Consequently, paralogs may functionally compensate for the loss of function of parental genes in monogenic diseases and mask the phenotypic effects of their deleterious mutations (Kafri et al. 2006; Hsiao and Vitkup 2008). This would explain why disease-associated genes frequently have redundant paralogs which are conserved through generations (Dickerson and Robertson 2012; Chen et al. 2013). Therefore, investigating the relations between parental genes and their paralogs by an evolutionary approach would be crucial to expand our view on the functional relevance of these gene duplicates. Genomic evidence may elucidate about the rates of evolution and selective constraints among paralogs throughout reconstructed phylogenies. This way, it would be possible to identify the sites and/or regions of these genes that are under stronger selective constraint in humans. Nevertheless, as an initial exploration on this topic, frequency of genetic variants of the parental gene and its copies can be compared to hint their functional redundancy (gnomAD database; constraint metrics in Supplementary Table).
Functional description of polyQ SCA-associated paralogs
SCA1: ATXN1 gene
ATXN1 (6p22.3) is a gene involved in transcriptional repression by interacting with several transcription regulators, e.g., SMRT-HDAC3 repression complex, RBM17 splicing factor, and capicua (CIC) repressor complex (Tsai et al. 2004; Lam et al. 2006; Tong et al. 2011; Kim et al. 2014) (Fig. 1). The polyQ-expanded ATXN1 seems to promote the formation of abnormal protein interactions and nuclear toxic aggregates that perturb its capacity to regulate gene expression (Tejwani et al. 2021).
Previous research refers to the existence of one ATXN1 paralog frequently called ataxin 1 like (ATXN1L) or brother of ataxin 1 (BOAT; 16q22.2) (Mizutani et al. 2005; Bowman et al. 2007), which likely originated from a DNA-based duplication mechanism (Table 2). ATXN1L transcripts were widely detected in human cell lines and tissues, with the highest expression levels found in the cerebellum and the cerebral cortex (Mizutani et al. 2005). Interestingly, ATXN1L was proposed as a candidate gene in an ataxic patient with early cerebellar dysfunction (Monies et al. 2017), as well as a regulator of hematopoietic stem cells quiescence/proliferation (Kahle et al. 2013). Still, ATXN1L function remains poorly understood. At the protein level, ATXN1 and ATXN1L are highly conserved, especially at the ATXN1 and HMG-box protein 1 interacting (AXH) domains (66% homology), showing a global homology of 23–33% (Mizutani et al. 2005; Carlson et al. 2009; Vauti et al. 2021) (Fig. 3a). Thus, based on their structural similarity and tissue expression patterns, it was hypothesized that ATXN1 and ATXN1L are likely to participate in related biological pathways (Bowman et al. 2007). These homologous proteins were shown to interact with each other and share some binding partners, including the transcriptional repressor CIC (Lam et al. 2006), SMRT-HDAC3 complex (Tsai et al. 2004; Mizutani et al. 2005), and a SMRT-associating transcription factor from the Notch pathway (CBF1) (Tong et al. 2011). Indeed, ATXN1L was demonstrated to inhibit NOL3 and PYDC1 expression via HDAC3 and CIC complexes, respectively, mediating apoptosis and pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes (Cai et al. 2022; Xu et al. 2022). Moreover, ATXN1L-CIC transcriptional repressor was found to regulate the expression of ETS-domain transcription factors, which modulated drug resistance in RAS-mutant cancers (Wang et al. 2017).
Domain architecture of polyQ SCA-associated proteins and their paralogs. In each case, a polyQ stretch is depicted at the approximate position (red triangle). a Both ATXN1 and ATXN1L contain the ataxin 1 and AXH domains, along with SAR regions. The AXH domain in both proteins is necessary for the interaction with CIC transcription repressor complex. Moreover, ATXN1 features a UHM motif to interact with the splicing factor RBM17 and a phosphorylation-dependent binding motif for the chaperone 14-3-3 near the C-terminus of the protein. b Both ATXN2 homologs contain Lsm and LsmAD domains for binding to RNA, and a PAM2 to interact with PABP and TDP43 transcription-related proteins. c ATXN3 long isoform contains an N-terminal catalytic Josephin domain and three UIM motifs, while ATXN3L has only two ubiquitin-binding sites like the shorter isoform of ATXN3. Interestingly, ATXN3L also contains a polyQ tract, but unlike ATXN3 it does not appear to expand, showing several interruptions (depicted in a small red triangle). d CACNA1A encodes for two proteins: Cav2.1 voltage-gated calcium channel (full-length) and transcription factor α1ACT (C-terminal fragment) by using a bicistronic mRNA with an internal ribosomal entry site. CACNA1A along with CACNA1B and CACNA1E contain four conserved homologous domains (I–IV), each with six transmembrane segments, and IQ/IQ-associated to bind to CaM. The two paralogs additionally present EF-hand domains responsible for calcium binding. e ATXN7 and its paralogs contain a ZnF domain SCA7 essential for ATXN7 association to DUBm from STAGA (excluding ATXN3LB). ATXN7L3 shows another ZnF/SGF11 domain that plays an important role in the DUB activity and DNA-binding. f All TBP homologs consist of two TBP domains to bind to a DNA sequence called TATA-box. g ATN1 protein only contains two atrophin 1 domains while its paralog RERE (long isoform; -L) includes four specific domains in the N-terminal (BAH, ELM2, SANT, and ZnF/GATA) besides atrophin 1 domain, possibly conferring specific properties. RERE-S isoform simply consist of the atrophin 1 N-terminal domain. UHM, U2AF homology domain. UIM, ubiquitin interacting motifs. IQ, IQ-like CaM interaction domain. CaM, Calmodulin. Amino acid numbering is based on Uniprot accession numbers P54253 (ATXN1), P0C7T5 (ATXN1L), Q99700 (ATXN2), Q8WWM7 (ATXN2L), P54252 (ATXN3), Q9H3M9 (ATXN3L), O00555 (CACNA1A), Q00975 (CACNA1B), Q15878 (CACNA1E), O15265 (ATXN7), Q9ULK2 (ATXN7L1), Q5T6C5 (ATXN7L2), Q14CW9 (ATXN7L3), Q96GX2 (ATXN7L3B), P20226 (TBP), P62380 (TBPL1), Q6SJ96 (TBPL2), P54259 (ATN1), RERE-L(Q9P2R6), and RERE-S (Q9P2R6-2)
Among all the identified interactors, the synergistic relationship described between ATXN1, ATXN1L, and CIC (CIC-ATXN1 complex) is of particular interest because these are the only interactors whose protein levels are significantly reduced in SCA1 models (Mizutani et al. 2005; Lam et al. 2006). In fact, both ATXN1 and ATXN1L knock-out (KO) resulted in early perinatal lethality and several developmental abnormalities in mice, but when comparing to the double KO model, ATXN1 seemed to partially compensate for the loss of ATXN1L function (Lee et al. 2011). ATXN1 polyQ-expansion was demonstrated to alter protein conformation, leading to abnormal interactions (Lim et al. 2006, 2008; Rocha et al. 2019) and functional defects in the CIC-ATXN1 complex, probably due to an apparent reciprocal functional relationship (Lam et al. 2006; Fryer et al. 2011; Wong et al. 2018) (Fig. 1). ATXN1L levels were positively associated with both the CIC expression (Crespo-Barreto et al. 2010; Wang et al. 2017; Wong et al. 2018) and the aggregation of polyQ-expanded ATXN1 (Lam et al. 2006), indicating an apparent relation between the complex formation and SCA1 pathology. Interestingly, ATXN1-CIC interaction was shown to be critical for SCA1 pathogenesis in Purkinje cells, while its ablation partially improved the neurological phenotype in mice (gain of function mechanism) (Rousseaux et al. 2018; Coffin et al. 2023). Moreover, in SCA1 the polyQ-expanded ATXN1 (Ser776 phosphorylation by PKA) favours the formation of RBM17-containing complexes (related to mRNA splicing), inspiring a gain of function mechanism (Kim et al. 2014) (Fig. 1). In fact, in vivo inhibition of ATXN1 Ser776 phosphorylation enhanced degradation of ATXN1 and delayed the onset of ataxia in SCA1 mice (Pérez Ortiz et al. 2018). Several studies in Drosophila and mouse models support the hypothesis of interchangeability between ATXN1L and ATXN1 in the CIC-ATXN1 complex and SCA1 pathology. These findings mostly support that ATXN1L is able to modulate the cytotoxicity of polyQ-expanded ATXN1 and suppress SCA1 symptomatology by reducing the spontaneous formation of expanded ATXN1-CIC complexes and/or compensating for ATXN1 native function by competing for the interaction with CIC (Mizutani et al. 2005; Bowman et al. 2007; Crespo-Barreto et al. 2010; Carrell et al. 2022). Indeed, CIC is polyubiquitinated and degraded by the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM25 in the absence of ATXN1L stabilization, manifesting the dominant role of ATXN1L (Wong et al. 2020). Also, the targeting of ATXN1 (self-association region, SAR; Fig. 3a) by ATXN1L could be suppressing SCA1 cytotoxicity (Mizutani et al. 2005) (Fig. 1). Simultaneously, this implies that SCA1 is induced by the formation of toxic hypermorphic complexes that subsequently affect the transcriptional repression activity of the ATXN1-CIC complex, including ATXN1L (Lasagna-Reeves et al. 2015; Lu et al. 2017; Rousseaux et al. 2018).
SCA2: ATXN2 gene
ATXN2 (12q24.12) encodes for a protein involved in mRNA degradation, stability, and translation by modulating the PABP protein, 3′ untranslated regions (Lee et al. 2018), and stress granule and P-body formation (Nonhoff et al. 2007). The polyQ-expanded ATXN2 causes toxic accumulation of cytoplasmic protein aggregates, inhibiting its native interactions and causing transcription/translation dysregulation (Egorova and Bezprozvanny 2019) (Fig. 2a).
The paralog ataxin 2 like (ATXN2L or A2RP; 16p11.2), possibly derived from an ATXN2 DNA-based duplication event (Table 2), encodes a protein with 50% homology. These paralog proteins present highly similar functional domains [like-sm (Lsm), like-Sm-associated domain (LsmAD), and PABP interacting motif (PAM2); Fig. 3b], and two known common interactors with ATXN2: PABP and DDX6 (Figueroa and Pulst 2003; Jiménez-López and Guzmán 2014) (Fig. 2a). In terms of expression, this paralog was found to be mainly detected in testis (Meunier et al. 2002), with a weak but widespread expression in human adult brain (mostly in the cerebellum) (Figueroa and Pulst 2003). Both ATXN2 and ATXN2L present a proline-rich domain, a conserved region responsible for mediating the direct interaction with SH3 motifs, located in components of the growth factor receptor endocytosis apparatus (Nonis et al. 2008; Lin et al. 2019). ATXN2L was found to be in a complex along PABP, DDX6 and ATXN2 in stress granules and associated with nuclear splicing machinery, suggesting functional redundancy (Kaehler et al. 2012) (Fig. 2a). Besides, ATXN2L was shown to play a major role in the in vitro formation of cytoplasmic granules and P-bodies in mammalian cells, suggesting that it could be important for the nucleation step of stress granules (Kaehler et al. 2012). This functional difference could result from differential methylation applied to ATXN2 and ATXN2L by PRMT1 and/or differences in the C-terminal region, since ATXN2L comprises a sequence absent in ATXN2 that shows homology to a protein family involved in P-body formation (Kaehler et al. 2012, 2015). Still, the implications of ATXN2L promoting the formation of stress granules remain unclear. Recently, a protein–protein interaction network analysis of genes affected by rare and/or potentially pathogenic variants in a member of a large SCA1 family suggested the interaction of ATXN1 with ATXN3, ATXN7, and ATXN2L. This study proposed that genetic variation in ATXN2L may play an additive role and exacerbate the neuropathology already driven by the abnormal intermediate polyQ-expanded ATXN1 (Morello et al. 2020). Studies demonstrated that an ATXN2 KO mouse model is associated with a metabolic syndrome, involving hypercholesterolemia and diabetes mellitus, possibly related with a post-transcriptional effect of ATXN2 on the insulin receptor expression in liver and in cerebellum (Lastres-Becker et al. 2008). On the other hand, ATXN2L absence triggered mid-gestational embryonic lethality in homozygous KO mice, but no consequent dysregulation was seen for ATXN2 (Key et al. 2020). These findings reinforce the crucial role of ATXN2L for RNA metabolism and translation, leaving in open ATXN2L and ATXN2 parallel contribution to SCA2.
A recent study indicated that reduction of ATXN2 or STAU1, a interactor of ATXN2 and modulator of stress granules, was able to decrease aggregation of polyQ-expanded ATXN2 and improve motor behaviour in transgenic mice (Paul et al. 2018) (Fig. 2a). Thus, ATXN2L could also have a similar effect since it is known to regulate stress granules. Further research will help to unravel if ATXN2L can eventually remediate ATXN2 native functions and/or interactions, as well as be involved in SCA2 pathogenesis.
MJD/SCA3: ATXN3 gene
ATXN3 (14q32.12) has been associated with transcription regulation by binding to DNA and interacting with several transcription-related factors (e.g., CBP, P300 histone acetyltransferase, HDAC3, and SMRT) (Li et al. 2002; Evert et al. 2006), and also with proteostasis via ubiquitin–proteasome system (Burnett et al. 2003; Burnett and Pittman 2005). The polyQ-expanded ATXN3 causes conformational changes that promote intraneuronal nuclear inclusions and cytotoxicity, which inhibit its function (deubiquitinase and DNA binding) and native protein interactions (Da Silva et al. 2019). Also, these nuclear aggregates hinder transcription related proteins such as HDAC3 and CBP, impairing transcription repression (McCampbell et al. 2000; Evert et al. 2006) (Fig. 2b).
ATXN3 has two paralogs identified: ataxin 3 like (ATXN3L; Xp22.2) that probably resulted from a recent retrotransposition event in primates (Scheel et al. 2003; Vlasschaert et al. 2017; Sousa e Silva et al. 2023) and LOC100132280 (herein called ataxin 3 like 2, ATXN3L2; 8q23.2), which reveals a premature stop codon that likely produces an inactive processed pseudogene (Table 2). The fact that ATXN3L2 is most likely not translated into protein does not rule out the hypothesis of ATXN3L2 mRNA playing a role in gene expression regulation. Nevertheless, as little is known about the possible role of ATXN3L2 and the presence of its transcript in the brain, we will further focus on the known function and interactions of ATXN3L with its parental gene.
ATXN3L and ATXN3 showed similar Josephin domains with a high degree of sequence identity (85%) (Weeks et al. 2011), suggesting that both proteins might play similar functions (Fig. 3c). ATXN3L also contains a (CAG)n tract but unlike ATXN3 it does not appear to expand, showing several GAA interruptions encoding for glutamic acid (Weeks et al. 2011). ATXN3 and ATXN3L have shown different expression patterns (with the retrogene mainly present in testis) and distinct ubiquitin recognition modes, which may be physiologically relevant (Weeks et al. 2011; Sousa e Silva et al. 2023). Nevertheless, in vitro experiments demonstrated that both ATXN3 and ATXN3L can cleave Lys-48-linked and Lys-63-linked polyubiquitin chains, with the Josephin domain of ATXN3L revealing higher deubiquitinase activity and functional redundancy (Fig. 2b). Intriguingly, three mutations (S12F, R59L, and T60A; called triple mutation) occurring in ATXN3 were found to almost equalize the corresponding deubiquitinase activity of ATXN3L, proposing that ATXN3 was subjected to evolutionary constraints (Weeks et al. 2011). In addition, ATXN3 KO animal models (mouse and C. elegans) had no overt phenotype mainly showing alterations in the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway (Rodrigues et al. 2007; Schmitt et al. 2007), which could probably be reverted by ATXN3L.
So far, the role of ATXN3L remains poorly characterized, but some studies have suggested a potential role in cell proliferation and migration possibly by preventing the degradation of proteins like KLF5 (Buus et al. 2009; Ge et al. 2015), also being possibly involved in premature ovarian failure by promoting oocyte maturation (Lee et al. 2020). Interestingly, ATXN3L was linked to sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, but its relation remain unclear (Gómez-Ramos et al. 2015). In addition, ATXN3L seems to regulate directly or indirectly PTEN transcription, similar to ATXN3 and Josephin domain containing 1 (JOSD1) proteins, possibly indicating a conserved function in the Josephin domain-containing proteins (Sacco et al. 2014).
SCA6: CACNA1A gene
CACNA1A (19p13.13) is involved in neuronal signal transmission in neurons presynaptic terminals, encoding for the pore-forming α1A subunit of P/Q type calcium voltage-gated channels (Cav) 2.1, mainly expressed in the cerebellum (specially in Purkinje cells) (Catterall 2000; Catterall et al. 2005). The polyQ-expanded CACNA1A increases the formation of mainly cytoplasmic protein inclusions, reduces Ca2+ influx into Purkinje cells in vitro, and impairs transcriptional dysregulation possibly leading to neurodegeneration (Giunti et al. 2015) (Fig. 2c). CACNA1A is also known to induce episodic ataxia type 2, suggesting that even missense variants in crucial protein domains can cause ataxia-related symptoms (Indelicato and Boesch 2021). In fact, KO mice display severe ataxia and develop absence seizures (Jun et al. 1999; Fletcher et al. 2001) similarly to some mouse strains with missense mutations, which suffer from ataxia and seizures, showing reduced P/Q type currents in Purkinje cells (Pietrobon 2002). Moreover, conditional KO mouse with a postnatal deletion of CACNA1A in Purkinje cells do not initially present ataxia and absence epilepsy but instead develop them during adulthood (Mark et al. 2011), which propose these disorders arise from defects beginning in late infancy—an opportunity window for therapy.
Interestingly, CACNA1A is a bicistronic gene, which means a single transcript can give rise to two independent proteins: (a) the α1A subunit of the Cav2.1 channel has a short and a long splice transcripts but only the latter contains the CAG repeat, and (b) the α1ACT transcription factor which shares the C-terminal sequence of the α1A subunit due to an internal ribosome entry site element (Du et al. 2013) (Figs. 2c and 3d). Thus, two different proteins contain a polyQ tract, the long splice transcript of the α1A channel subunit and the transcription factor α1ACT, both selectively expressed in cerebellar Purkinje cells (Bavassano et al. 2017; Du et al. 2019; Govek and Hatten 2019). In particular, the polyQ-expanded α1ACT leads to ataxia and cerebellar atrophy in SCA transgenic mice, being essential for neonatal neuronal development and neurite outgrowth, since it lacks transcription factor function (TAF1, GRN, BTG1 and PMCA2 target genes; Fig. 2c) and causes cell death (Du et al. 2013, 2019). Moreover, α1ACT transcription factor was also impaired in α1A/Cav2.1 homozygous KO mice, though the expression of normal α1ACT in Purkinje cells leads to a slight phenotypic improvement, they still remain non-viable past the neonatal period (Du et al. 2013). Interestingly, decreased expression of α1ACT but increased expression of Cav2.1 was observed in patient-derived Purkinje cells (Ishida et al. 2016) (Fig. 2c).
Although 26 CACNA1A paralogs are annotated in the human genome, only CACNA1B-I and CACNA1S genes also encode pore-forming α1 subunits of Ca2 + voltage-gated channels (Cav1, Cav2, or Cav3) (Catterall et al. 2005; Heyes et al. 2015). Sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 1–11 (SCN1A-11A) genes encode for α subunits of sodium voltage-gated channels (Nav1.1–1.9), excepting SCN7A (Nax), which has lost its voltage-gated function and rapidly evolved as a signal transducer of extracellular Na+ ions (De Lera and Kraus 2015; Dolivo et al. 2021). Sodium leak channel, non-selective (NALCN) gene encodes a channel that regulates the resting membrane potential and neuronal excitability as part of a complex including G protein-coupled receptors (Cochet-Bissuel et al. 2014). Two pore segment channel 1 and 2 (TPCN1 and TPCN2) genes encode for channels responsible for the acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP)‐mediated calcium release within the endo-lysosomal system (Pitt et al. 2016). Finally, cation channel sperm associated 1–4 (CATSPER1-4) genes were first identified based on sequence similarity to the Cav1.3 channel and encode for channels with a crucial role in sperm physiology and fertility (Shukla et al. 2012). Even though SCNA, NALCN, TPCN and CATSPER groups of paralogs have distinct functions and properties related to ion channels, only the closely related CACNA1 gene family (with 10 homologs, duplicated in vertebrates) can show similar physiological functions (Lagman et al. 2013; Abascal et al. 2015). In particular, genes classified inside each family of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels are evolutionarily closer (Pietrobon 2002; Catterall et al. 2005), making CACNA1B and CACNA1E good candidates to explore functional redundancy since they also belong to the Cav2 subfamily (Figs. 2c and 3d; Table 2).
CACNA1B (9q34.3) encodes for another pore-forming α1B subunit of the pre-synaptic neuronal Cav2.2 channel of N-type, responsible for the generation of high voltage-activated Ca2+ current with moderate voltage-dependent inactivation (Catterall et al. 2005). CACNA1B has been found to mostly participate in neuronal processes related to neuronal growth, synaptic function, and development (Heyes et al. 2015). In fact, CACNA1B is widely distributed throughout the central and peripheral nervous system (Westenbroek et al. 1992; Wheeler et al. 1994) while CACNA1A was reported to be particularly prevalent in the cerebellum (Ophoff et al. 1996). Previous studies reported a functional overlap between CACNA1A and CACNA1B, both being responsible for most of the glutamatergic neurotransmission in hippocampal synapses (Cao et al. 2004). Interestingly, CACNA1B coordination with CACNA1A seems to be crucial to control synaptic transmission throughout the nervous system. CACNA1B is thought to be crucial for neurotransmission in the early postnatal period as it is replaced by CACNA1A in mature synapses during neurodevelopment (Scholz and Miller 1995; Gorman et al. 2019), highlighting that the contribution of the two homologs is time specific (Iwasaki et al. 2000). In addition, both CACNA1A and CACNA1B mRNAs are regulated by the Nova-2 splicing factor, which preferentially selects certain isoforms (e24a over e31a splicing isoform) to be expressed in the brain (Allen et al. 2010). A study demonstrated that homozygous CACNA1B KO mice only showed mild phenotype (sympathetic nerve dysfunction) when a lethal effect was expected (Ino et al. 2001). However, later CACNA1B was shown to be essential for correct neurodevelopment and predicted to be highly intolerant to loss of function variants, as demonstrated by debilitating symptoms such as memory impairment and atypical locomotor activity in homozygous KO mice (Nakagawasai et al. 2010; Gorman et al. 2019). Besides, single nucleotide and copy-number variants involving CACNA1B have been described in individuals with neurovascular disorders and schizophrenia, and implicated in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (Gorman et al. 2019). For instance, a CACNA1B missense variant (c.4166G > A; p.Arg1389His) was reported in a family with adult-onset myoclonus-dystonia and cardiac arrhythmia, which resulted in lower current Cav2.2 channels, emphasizing the functional relevance of this paralog (Groen et al. 2015).
CACNA1E (1q25.3) encodes for the moderate R-type α1E subunit of the Cav2.3 channel, generating Ca2+ current with fast voltage-dependent inactivation (Catterall et al. 2005), known for its role in synaptic plasticity (Dietrich et al. 2003; Heyes et al. 2015). Previous studies refer that CACNA1E is especially distributed throughout the central nervous system as CACNA1A (Day et al. 1996; Ophoff et al. 1996; Parajuli et al. 2012). CACNA1E variants have been linked to several neurological disorders, including developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, autism spectrum disorder, and migraine (Helbig et al. 2018; Heyne et al. 2018; Takata et al. 2019; Royer-Bertrand et al. 2021), but has not been established as a disease-causing gene. In contrast with CACNA1B, CACNA1E homozygous KO mice did not reveal any evident neurological symptoms, but showed abnormalities in pain responses due to an attenuation of the inhibitory effect in the descending anti-nociceptive pathway (Saegusa et al. 2000).
SCA7: ATXN7 gene
ATXN7 (3p14.1) encodes for a transcriptional factor comprised in the multiprotein Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase (SAGA) complex, which regulates transcription through its histone-modifying enzymes, histone acetyltransferase GCN5, and ubiquitin-specific protease USP22 (Cornelio-Parra et al. 2021). The ATXN7 protein serves to anchor the SAGA’s deubiquitinase module (DUBm) to the larger core module (Lee et al. 2009; Ellisdon et al. 2010), participate in the regulation of histone acetylation/deubiquitination (Lang et al. 2011), and facilitate the RNA polymerase II recruitment (Bonnet et al. 2014). Moreover, ATXN7 may be involved in microtubule stabilization (Nakamura et al. 2012). The polyQ-expanded ATXN7 seems to recruit other factors like the SAGA’s DUBm proteins [ENY2 transcription and mRNA export factor, USP22, and the paralog ataxin 7 like 3 (ATXN7L3)] into nuclear aggregates. Consequently, these aggregates prevent the adequate formation of DUBm, altering the deubiquitinase activity of SAGA and chromatin state of a subset of genes probably related to retina function (one of the main affected regions in SCA7) (Mohan et al. 2014; Lan et al. 2015; Goswami et al. 2022). Yet, the co-overexpression of ATXN7L3 and ENY2 enabled to mitigate the effect of ATXN7 polyQ inclusions (Lan et al. 2015) (Fig. 2d). Interestingly, HDAC3 was found to physically interact with ATXN7, leading to its increased stability, subcellular localisation and post-translational modifications (Duncan et al. 2013). Besides, HDAC3 was highly expressed in both neurons and glia in the cerebellum of non-transgenic and SCA7 transgenic mice, suggesting a role in SCA7 neuropathology (Duncan et al. 2013).
So far, four paralogs of ATXN7 have been identified: ataxin 7 like 1, 2, 3 and 3B [ATXN7L1 (7q22.3), ATXN7L2 (1p13.3), ATXN7L3 (17q21.31), and ATXN7L3B (12q21.1)] (Helmlinger et al. 2004) (Table 2). ATXN7, ATXN7L1, and ATXN7L2 proteins share three conserved regions, designated as domains I (C2H2 zinc-finger), II (SCA7), and III (C-terminal), revealing a high degree of homology (≥ 50%) that suggests functional redundancy (Fig. 3e). In contrast, ATXN7L3 only shares the first two domains with ATXN7 (≤ 35% homology) and presents a distinct SCA7 domain that probably diverged over evolution to achieve specific functions in the SAGA complex, since it was suggested to be originated from an ancient duplication of ATXN7 (Helmlinger et al. 2004; Bonnet et al. 2010). In concordance, ATXN7L3 was shown to play a central and non-redundant function in the SAGA complex, contrarily to the remaining homologs (Zhao et al. 2008; Lang et al. 2011) (Fig. 2d), weakening the hypothesis of functional overlap between ATXN7 and ATXN7L3. Simultaneously, no alternative human proteins substituting ATXN7L3 function were ever described, which suggests that the loss of ATXN7L3 function would exclusively impair SAGA function (Zhao et al. 2008). ATXN7L3B resulted from the retrotransposition of the ATXN7L3 gene (Table 2), both sharing 74% of identity in their correspondent N-terminal regions (including the ENY2-binding region), thereby suggesting common interactors shared by the two homologs (Li et al. 2016b). However, ATXN7L3B localizes in the cytoplasm and seems to solely interact with ENY2 in the SAGA complex, and unlike the ATXN7L3 DUBm, the ATXN7L3B complex cannot function efficiently in vitro. Therefore, the ATXN7L3B-ENY2 interaction could be limiting SAGA activity by sequestering ENY2 in the cytoplasm and competing with ATXN7L3 (Fig. 2d). Moreover, ATXN7L3 and ATXN7L3B expression levels were found to be inversely correlated, whereas the overexpression of ATXN7L3B induces the decrease of ATXN7L3 expression levels and consequent loss of deubiquitinase activity (Li et al. 2016b). Other functional studies suggested that ATXNL3B behaves as a long noncoding RNA (lnc-SCA7) regulating ATXN7 expression, an interaction that appears to be mediated by miR-124 micro-RNA through a negative feedback loop. It was proposed that polyQ-expanded ATXN7 reduces miR-124 transcription due to impairment of the SAGA complex, affecting the repression of the miRNA’s targets, ATXN7 and ATXN7L3B, which will trigger cytotoxic nuclear inclusions primarily in the retina and the cerebellum (Tan et al. 2014).
ATXN7L3 and ATXN7L3B present lower protein conservation and different individual functions from ATXN7, while ATXN7L1 and ATXN7L2 appear to be more suitable for the functional compensation of the partial loss of the parental gene in SCA7 (Helmlinger et al. 2004; Lang et al. 2011). In fact, ATXN7L1 and ATXN7L2 paralogs resulted from the DNA-based duplication of ATXN7 and take interchangeable roles in the SAGA’s DUBm, possibly being mutually exclusive, i.e., only one of these three homologs can be incorporated into a unique module (Vermeulen et al. 2010; Helmlinger and Tora 2017) (Fig. 2d). Moreover, both ATXN7 and ATXN7L2 incorporated in the STAGA’s DUBm complex appeared to be substituted by ATXN7L1 at later stages of the erythroid cells’ development (Papadopoulos et al. 2015). Still, there is a clear lack of studies exploring ATXN7 paralogs function in SAGA’s DUBm complex and transcriptional regulation, and little is known about their tissue expression.
SCA17: TBP gene
TBP (6q27) encodes for a widely expressed transcription initiation factor that integrates a larger complex along with TBP-associated factors (TAF1-15), constituting the core of the TFIID transcription preinitiation complex (Mishal and Luna-Arias 2022). In SCA17, the polyQ-expanded TBP impairs the DNA-binding and transactivation activity of the native protein and exacerbates the formation of neuronal nuclear inclusions, which reduce the TFIID complex availability for the transcription initiation process (Hsu et al. 2014; Yang et al. 2016) (Fig. 2e).
The TBP gene has two known paralogs, TBP like 1 (TBPL1, known as TRF2, TLF, TLP, or TRP) and 2 (TBPL2, also called TBP2/TRF3). TBPL1 (6q23.2) resulted from a DNA-based duplication event of TBP within the same chromosome (Duttke et al. 2014) (Table 2). Despite some similarities observed between the two homologous proteins (C-terminal core; 41% homology), the domains ensuring the interaction with the TATA box do not seem to be preserved in TBPL1 (Rabenstein et al. 1999) (Fig. 3f). In fact, TBPL1 widely drives the transcription of TATA-less genes (e.g., ribosomal protein genes) by relying on polypyrimidine initiator (TCT) motifs (Duttke et al. 2014) (Fig. 2e). Still, TBPL1 seems to be differentially expressed with highest levels in testis resembling TBP (Ohbayashi et al. 1999b; Rabenstein et al. 1999). These homologous genes appear to regulate gene expression in a reciprocal and opposite manner (Rabenstein et al. 1999; Chong et al. 2005) and cannot replace each other’s functional properties (Moore et al. 1999; Teichmann et al. 1999; Dantonel et al. 2000; Kaltenbach et al. 2000). TBPL1 and TBP seem to have evolved for different purposes, possibly regulating the transcription of different sets of genes and intervening at different stages of development (Rabenstein et al. 1999; Müller et al. 2001). One hypothesis is that the distinct N-terminus between the paralogs commit the transcription factors for specific regulatory signals or processes (Bondareva and Schmidt 2003). In fact, TBPL1 seems to be no longer needed for survival in more evolutionarily complex animals such as mice (impairment of spermiogenesis) (Martianov et al. 2001; Zhang et al. 2001), when compared to C. elegans (Dantonel et al. 2000; Kaltenbach et al. 2000) or Xenopus laevis (Veenstra et al. 2000; Jacobi et al. 2007) (defects in gastrulation and embryogenesis). In terms of transcriptional regulation, TBPL1 was considered a negative regulator of transcription, generally functioning as a signal-transducing transcription factor in cell cycle regulation and stress response (Dantonel et al. 2000; Shimada et al. 2003; Kieffer-Kwon et al. 2004; Chong et al. 2005; Tanaka et al. 2007), and directing the gene expression of target genes related to DNA replication and cell proliferation (Hochheimer et al. 2002; Park et al. 2006). Overall, TBPL1 seems unlikely to substitute the parental gene functions as shown by TBPL1 KO in mouse embryonic stem cells (Kwan et al. 2023).
TBPL2 (14q22.3) probably resulted from a vertebrate-specific duplication event of TBP, being absent in lower eukaryotes, such as Drosophila and C. elegans (Persengiev et al. 2003; Bártfai et al. 2004) (Table 2). TBPL2 is a closely related TBP paralog with 95% identity in the C-terminal core (Persengiev et al. 2003; Akhtar and Veenstra 2011), able to bind to TATA promoters (Bártfai et al. 2004) (Figs. 2e, 3f). TBPL2 was reported to be widely expressed in human tissues and cell lines as the parental gene, only showing some differences in the relative amount (Persengiev et al. 2003). However, it has become apparent that TBPL2 is mainly expressed in oocytes and embryos (until the gastrula stage), showing an expression consistently lower than its paralogs (Persengiev et al. 2003; Bártfai et al. 2004; Jallow et al. 2004). Interestingly, TBPL1 and TBPL2 appear to be involved in a distinct processes in mice, being required to ensure adequate transcription during spermiogenesis and oogenesis, respectively (Martianov et al. 2001; Zhang et al. 2001; Gazdag et al. 2007, 2009). Similar to TBPL1, TBPL2 appears to have evolved distinctively according to the species, being involved in oocyte maturation in mice (Müller et al. 2001; Gazdag et al. 2007, 2009) but required for embryonic development in Xenopus laevis and zebrafish (Bártfai et al. 2004; Jallow et al. 2004; Jacobi et al. 2007). In particular, TBPL2 was shown to mediate RNA polymerase II transcription during the meiosis of oocytes in mice, whereas continuously replacing the TBP during the oogenesis (Gazdag et al. 2007, 2009; Akhtar and Veenstra 2009) (Fig. 2e). TBP KO in mice seems lethal at the embryonic blastocyst stage (Martianov et al. 2002; Kwan et al. 2023). TBPL2 KO mice were found to be sterile showing that the substitution of TBP by TBPL2 during the development of oocytes might be crucial for adequate transcription during folliculogenesis (Gazdag et al. 2009). However, the same was not observed in muscle differentiation (Malecova et al. 2016). Xenopus laevis studies also seem to support that TBPL2 can partially restore the transcription of TBP-dependent genes in the absence of TBP in embryonic development. Also, relatively few genes seem to depend on TBP in the embryo, suggesting specific and partially redundant functions (Jallow et al. 2004; Jacobi et al. 2007) that can be studied in SCA17 animal models (Cui et al. 2017).
DRPLA: ATN1 gene
ATN1 (12p13.31) encodes for the atrophin protein, a class of conserved transcriptional co-repressors playing a crucial role in nuclear receptor signalling pathways (Okamura-Oho et al. 1999; Wood et al. 2000; Feng et al. 2004; Zhang et al. 2006; Wang et al. 2008) (Fig. 2f). Also, ATN1 has been propose to interact with cytoskeletal and ubiquitin ligase proteins (Wood et al. 1998; Hou and Sibinga 2009). This gene is present in vertebrates and belongs to the atrophin family of proteins, along with the arginine-glutamic acid dipeptide repeats (RERE) gene and the Drosophila atrophin (Atro) [termed Grunge (Gug)] (Wang and Tsai 2008). The polyQ-expanded ATN1 was found to generate inclusions, both localized in the cytoplasm and nucleus of neuronal cells, which disrupts native protein–protein interactions (Nowak et al. 2023). Another feature of DRPLA was the ubiquitination, abnormal phosphorylation, and cleavage of polyQ-expanded ATN1 (Yazawa et al. 1999; Okamura-Oho et al. 2003; Suzuki et al. 2010) (Fig. 2f). Moreover, the polyQ-expanded ATN1 was suggested to cause a toxic gain of function by inhibiting CBP-dependent transcription, which is essential for neuronal development (Shimohata et al. 2000; Nucifora et al. 2001). Interestingly, ATN1 KO mice were neurologically not affected but the selective knock-down of ATN1 or histone demethylase LSD1 (positively regulates ATN1 expression) in mice was sufficient to cause a premature differentiation and reduction of neural progenitor cells (mostly radial glial cells) (Zhang et al. 2014). Yet, increasing the expression of ATN1 rescued the deficit of neural progenitor cells, suggesting that ATN1 depletion may have consequences in brain development and a LSD1 inhibitor could function as a treatment option for adult-onset DRPLA (Zhang et al. 2014).
In vertebrates, there is only one known ATN1 paralog previously mentioned as part of the atrophin family (Yanagisawa et al. 2000). The RERE gene (1p36.23) is thought to be involved in transcription regulation and/or DNA binding, showing the ability to recruit histone deacetylases and serve as a transcriptional corepressor (Zoltewicz et al. 2004; Wang et al. 2006, 2008; Plaster et al. 2007; Shen et al. 2007) (Table 2; Fig. 2f). The presence of a dipeptide repeat motif-containing arginine-glutamic acid (RE) at its C-terminus gave rise to the designation of RERE, but this gene is also referred to as atrophin 2 (ATN2) or ATN1L. RERE is critical for both mouse and zebrafish development and survival (Zoltewicz et al. 2004; Asai et al. 2006; Plaster et al. 2007; Kim et al. 2013), especially in cerebellar Purkinje cells (Kim and Scott 2014), raising the assumption that ATN1 probably originated from a DNA-based duplication event of RERE. This would also explain why RERE is distributed across metazoans and ATN1 is restricted to vertebrates (Shen and Peterson 2009). In addition, the inability to distinguish ATN1 KO and wild-type mice groups (Shen et al. 2007) further suggests that RERE and ATN1 functions are not equivalent on development. Nevertheless, the homologous genes seem to be post transcriptionally regulated by the same miRNAs (miR-429/miR-200b) (Karres et al. 2007), which may be a conserved mechanism to fine tune their expression and limit histone deacetylases activity [of particular interest in neurodegenerative diseases (Shukla and Tekwani 2020)].
Interestingly, RERE has the particularity to encode for two distinct transcripts: a long form (RERE-L, 1559 amino acids) restricted to the pancreas and testis; and a shorter ubiquitous form (RERE-S, 990 amino acids) expressed at higher levels in the cerebellum, testis, uterus, prostate, skeletal muscle and kidney, similar to ATN1 (Onodera et al. 1995; Yanagisawa et al. 2000; Waerner et al. 2001; Shen et al. 2007). In addition, the presence of RERE transcripts has been predominantly reported to concentrate in the nucleus of cells, with residual levels in the cytoplasm (Yanagisawa et al. 2000; Waerner et al. 2001). Nonetheless, expression levels of RERE are generally lower when compared to ATN1 (Yanagisawa et al. 2000). Contrasting with ATN1, RERE-L presents a high level of homology with the metastasis-associated family of proteins within its additional sequence of 569 amino acids (in comparison with RERE-S) and includes a total of four domains in the N-terminal [bromo-adjacent homology (BAH), EGL-27 and MTA1 homology 2 (ELM2), SWI3/ADA2/N-CoR/TFIII-B (SANT), and ZnF/GATA] mostly involved with proteins implicated in transcriptional regulation, followed by an atrophin 1 related domain (C-terminus region, 67% homology) (Yanagisawa et al. 2000; Bowen et al. 2004; Wang et al. 2006, 2008). RERE-S only contains the atrophin 1 domain, and is transcribed through an internal promoter (Shen et al. 2007) (Fig. 3g). RERE-S protein shares 50.8% identity with ATN1, suggesting highly conserved regions and overlapping functions (Shen and Peterson 2009). However, the atrophin domain generally has two structures: the conserved N-terminal, containing a nuclear localization signal, and a C-terminal interrupted by a nuclear export signal; reinforcing that atrophin-1 function is yet to be understood. Contrarily to ATN1, RERE has functional domains (SANT) that allow its concentration in the nucleus, where it forms nuclear speckles (Yanagisawa et al. 2000; Wang et al. 2006; Shen et al. 2007) and co-localizes with pro-apoptotic proteins (e.g., PML and BAX) in promyelocytic leukemia oncogenic domains (Waerner et al. 2001) (Fig. 2f). Furthermore, RERE was suggested to control caspase-mediated cell death and cell survival (Waerner et al. 2001). In short, ATN1 resembles a truncated form of RERE, the portion of RERE that is missing from ATN1 could account for their functional differences while the conserved region could potentiate a functional overlap.
The previously mentioned RE repeat motifs are one common conserved regions between both homologs, though the precise function of this domain remains unclear (Yanagisawa et al. 2000; Shen and Peterson 2009). Nevertheless, RERE seems to directly interact with ATN1 partly via conserved RE motifs and form heterodimers, which can be related to the high tendency of this protein to aggregate with polyQ-expanded ATN1 (Yanagisawa et al. 2000). Therefore, the neuropathology occurring in DRPLA patients is likely to be accompanied by a depletion of the RERE protein due to this high affinity for the polyQ-expanded ATN1 aggregates. RERE heterozygous variants have been associated with neurodevelopmental disorder with or without anomalies of the brain, eye, or heart, with a loss of RERE function contributing to the development of orofacial clefts (Jordan et al. 2018; Kim et al. 2021). Besides, de novo variants in both ATN1 and RERE seem to perturb the HX-repeat motif of the atrophin 1 domain (Fig. 3g), causing congenital anomalies such as hypotonia, epilepsy and developmental delay (Fregeau et al. 2016; Palmer et al. 2019), which further indicates a link between their functions.
Conclusion and future perspectives
Seven SCAs are classified as polyQ diseases, as they result from the elongation of a glutamine tract, encoded by an expanded CAG repeat in the respective causative gene. So far, the pathological mechanisms underlying SCAs remain poorly understood, with just a few therapeutic approaches described to alleviate disease symptomatology. Cytotoxicity and neurodegeneration seem to occur primarily through a gain of function mechanism since polyQ expansions induce misfolding and aggregation inhibiting their typical interactions and/or promoting abnormal protein networks. Additionally, there has been increasing evidence for a partial loss of function effect responsible for disease-specific features as the biological activities of normal (non-expanded) proteins are partially lost and may be impaired by the polyQ-expanded form. Interestingly, some studies in SCA1 found that ATXN1L, a highly conserved paralog of the disease-associated ATXN1 gene, was able to modulate the cytotoxicity of polyQ-expanded ATXN1 and suppress SCA1 symptomatology. The duplicate ATXN1L was suggested to compensate the ATXN1 native functions in the transcriptional ATXN1-CIC complex. Thus, an opportunity to further explore the etiology, pathological mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets may arise from the study of other SCA-associated paralogs that partially maintained the ancestral function of the respective parental genes over evolution. This may enrich the discussion around this group of SCA-associated genes, which has been studied over decades mostly under a very specific disease-oriented perspective.
Here, we reviewed the currently known similarities between polyQ SCA-associated genes and their human paralogs to ascertain functional redundancy, which would open an avenue to explore the hypothesis of duplicates being able to compensate for the partial loss of function reported in polyQ SCAs. The evolutionary relationships among paralogs may explain the degree of conservation between the parental gene and its duplicates, and elucidate about the potential functional redundancy of the homologous proteins. Future studies will certainly provide functional evidence that can grant us clues on common interactors and pathways regarding these paralogs. In this review, we guided the reader through the example of ATXN1L and its crucial role in SCA1, and next gathered data suggesting potential functional redundancy in additional seven duplicates of SCA-associated genes: ATXN2L, ATXN3L, CACNA1B, ATXN7L1, ATXN7L2, TBPL2, and RERE.
-
ATXN2L is involved in stress granule and RNA metabolism, sharing highly similar protein domains and some common interactors with ATXN2, though little is known about its cellular function or association with SCA2 pathology.
-
ATXN3L has been shown to analogously act as a deubiquitinase and is predicted to bind to the same interactors as ATXN3, suggesting a functional overlap that could restore the partial loss of function in MJD/SCA3. In addition, ATXN3L even presents a non-expanded (CAG)n tract that opens a broad road to explore the evolution and expansion mechanisms underlying the CAG repeats at the parental ATXN3.
-
CACNA1B is closely related to CACNA1A, presenting similar protein structures and synaptic functions, which suggests a high degree of functional overlap within Cav2 channels that may be valuable in the context of SCA6.
-
ATXN7L1 and ATXN7L2 have highly conserved domains and seem to play interchangeable roles with ATXN7 to ensure the adequate operation of the DUB module, as part of the SAGA complex. Nevertheless, there is a clear lack of studies exploring ATXN7 paralogs function in transcriptional regulation and involvement in SCA7 disease.
-
TBPL2 seems to be the most promising paralog to compensate for TBP loss of function, since it contains a highly conserved core domain and common interactors with TBP (whereas TBPL1 does not bind to any TATA box-containing promoter). Still, further studies are needed to clarify the role of TBPL2 in transcription regulation and determine if a compensatory effect would be viable in SCA17.
-
RERE belongs to the same family of proteins as the DRPLA causative protein, ATN1, playing similar roles in transcription repression. ATN1 KO was not linked to any evident phenotype whereas RERE showed to be essential for both development and survival. These findings highly support the relevance of RERE in cellular function and corroborate the functional redundancy hypothesis that could be important in DRPLA.
In this review, we intended to draw attention to the study of duplicate genes in the context of polyQ SCA diseases, but certainly proteins with common domains may also be capable of functional redundancy. For instances, ATXN3 belongs to a family of deubiquitinating enzymes, which in addition to ATXN3L, includes JOSD1 and JOSD2, all sharing a highly conserved catalytic domain. Thus, all should be taken into consideration while exploring the molecular mechanisms of ATXN3 and MJD pathogenesis. However, in functional studies of highly homologous proteins, one limitation researchers may face is the specificity of antibodies to distinguish proteins. The search for monoclonal customized antibodies with epitopes in less conserved regions of the proteins may help to overcome this concern.
In addition, bidirectional transcription of repeat expansions has been proposed to play a role in SCA pathogenesis. Hence, it would be interesting to gain insight on whether the presence of antisense genes for other parental/duplicated genes could affect expression levels of ataxin genes. Further studies on expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) would probably explain variable levels of gene expression underlying these genes, ultimately elucidating some phenotypic variability observed in patients. The presence of possible haplotype effects (as well as interactions between variants, epistasis) could be considered to capture simultaneously the effect of multiple variants. Following these future research directions, it would be worthwhile exploring the potential of these genes that share functional activity to mitigate the effect of non-allele-specific therapeutic approaches on the normal alleles of polyQ SCA-associated genes. Treatments with small interfering RNAs, short hairpin RNAs, microRNAs, and antisense oligonucleotides have been performed in cell models and transgenic rodents in order to reduce exclusively mutant gene levels; however, when an allele-specific approach is not possible, duplicated genes may also be used as targets for therapeutic interventions.
Data availability
Data sharing does not apply to this article as no new data was generated or analysed for this review.
References
Abascal F, Tress ML, Valencia A (2015) The evolutionary fate of alternatively spliced homologous exons after gene duplication. Genome Biol Evol 7:1392–1403. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evv076
Akhtar W, Veenstra GJC (2009) TBP2 is a substitute for TBP in Xenopus oocyte transcription. BMC Biol 7:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-7-45
Akhtar W, Veenstra GJC (2011) TBP-related factors: a paradigm of diversity in transcription initiation. Cell Biosci 1:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-1-23
Allen SE, Darnell RB, Lipscombe D (2010) The neuronal splicing factor Nova controls alternative splicing in N-type and P-type CaV2 calcium channels. Channels 4:483–489. https://doi.org/10.4161/chan.4.6.12868
Araujo J, Breuer P, Dieringer S et al (2011) FOXO4-dependent upregulation of superoxide dismutase-2 in response to oxidative stress is impaired in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3. Hum Mol Genet 20:2928–2941. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr197
Asai Y, Chan DK, Starr CJ et al (2006) Mutation of the atrophin2 gene in the zebrafish disrupts signaling by fibroblast growth factor during development of the inner ear. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:9069–9074. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603453103
Ashkenazi A, Bento CF, Ricketts T et al (2017) Polyglutamine tracts regulate beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Nature 545:108–111. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature2207
Atlas D, Wiser O, Trus M (2001) The voltage-gated Ca2+ channel is the Ca2+ sensor of fast neurotransmitter release. Cell Mol Neurobiol 21:717–731. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015104105262
Bártfai R, Balduf C, Hilton T et al (2004) TBP2, a vertebrate-specific member of the TBP family, is required in embryonic development of zebrafish. Curr Biol 14:593–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2004.03.034
Bavassano C, Eigentler A, Stanika R et al (2017) Bicistronic CACNA1A gene expression in neurons derived from spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 patient-induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 26:1612–1625. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2017.0085
Bolger TA, Zhao X, Cohen TJ et al (2007) The neurodegenerative disease protein ataxin-1 antagonizes the neuronal survival function of myocyte enhancer factor-2. J Biol Chem 282:29186–29192. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M704182200
Bondareva AA, Schmidt EE (2003) Early vertebrate evolution of the TATA-binding protein, TBP. Mol Biol Evol 20:1932–1939. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msg205
Bonnet J, Wang YH, Spedale G et al (2010) The structural plasticity of SCA7 domains defines their differential nucleosome-binding properties. EMBO Rep 11:612–618. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2010.98
Bonnet J, Wang CY, Baptista T et al (2014) The SAGA coactivator complex acts on the whole transcribed genome and is required for RNA polymerase II transcription. Genes Dev 28:1999–2012. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.250225.114
Bowen NJ, Fujita N, Kajita M, Wade PA (2004) Mi-2/NuRD: multiple complexes for many purposes. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Struct Expr 1677:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbaexp.2003.10.010
Bowman AB, Lam YC, Jafar-Nejad P et al (2007) Duplication of Atxn1l suppresses SCA1 neuropathology by decreasing incorporation of polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-1 into native complexes. Nat Genet 39:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1977
Burnett BG, Pittman RN (2005) The polyglutamine neurodegenerative protein ataxin 3 regulates aggresome formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:4330–4335. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407252102
Burnett B, Li F, Pittman RN (2003) The polyglutamine neurodegenerative protein ataxin-3 binds polyubiquitylated proteins and has ubiquitin protease activity. Hum Mol Genet 12:3195–3205. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddg344
Bushart DD, Murphy GG, Shakkottai VG (2016) Precision medicine in spinocerebellar ataxias: treatment based on common mechanisms of disease. Ann Transl Med 4:25. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2016.01.06
Buus R, Faronato M, Hammond DE et al (2009) Deubiquitinase activities required for hepatocyte growth factor-induced scattering of epithelial cells. Curr Biol 19:1463–1466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.040
Čabart P, Murphy S (2001) BRFU, a TFIIB-like Factor, is directly recruited to the TATA-box of polymerase III small nuclear RNA gene promoters through its interaction with TATA-binding protein. J Biol Chem 276:43056–43064. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M108515200
Cai R, Xu Y, Ren Y et al (2022) MicroRNA-136-5p protects cardiomyocytes from coronary microembolization through the inhibition of pyroptosis. Apoptosis 27:206–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01712-5
Cao YQ, Piedras-Rentería ES, Smith GB et al (2004) Presynaptic Ca2+ channels compete for channel type-preferring slots in altered neurotransmission arising from Ca2+ channelopathy. Neuron 43:387–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.07.014
Carlson KM, Melcher L, Lai S et al (2009) Characterization of the zebrafish atxn1/axh gene family. J Neurogenet 23:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1080/01677060802399976
Carrell EM, Keiser MS, Robbins AB, Davidson BL (2022) Combined overexpression of ATXN1L and mutant ATXN1 knockdown by AAV rescue motor phenotypes and gene signatures in SCA1 mice. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 25:333–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2022.04.004
Casola C, Betrán E (2017) The genomic impact of gene retrocopies: what have we learned from comparative genomics, population genomics, and transcriptomic analyses? Genome Biol Evol 9:1351–1373. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evx081
Catterall W (2000) Structure and regulation of voltage-gated ca2+ channels. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:521–555. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.521
Catterall WA, Perez-Reyes E, Snutch TP, Striessnig J (2005) International union of pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels. Pharmacol Rev 57:411–425. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.57.4.6
Chai Y, Wu L, Griffin JD, Paulson HL (2001) The role of protein composition in specifying nuclear inclusion formation in polyglutamine disease. J Biol Chem 276:44889–44897. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M106575200
Chang CH, Scott GK, Baldwin MA, Benz CC (1999) Exon 4-encoded acidic domain in the epithelium-restricted Ets factor, ESX, confers potent transactivating capacity and binds to TATA-binding protein (TBP). Oncogene 18:3682–3695. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202674
Chen HK, Fernandez-Funez P, Acevedo SF et al (2003) Interaction of Akt-phosphorylated ataxin-1 with 14–3-3 mediates neurodegeneration in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Cell 113:457–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00349-0
Chen S, Peng GH, Wang X et al (2004) Interference of Crx-dependent transcription by ataxin-7 involves interaction between th glutamine regions and requires the ataxin-7 carboxy-terminal region for nuclear localization. Hum Mol Genet 13:53–67. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddh005
Chen WH, Zhao XM, van Noort V, Bork P (2013) Human monogenic disease genes have frequently functionally redundant paralogs. PLoS Comput Biol 9:e1003073. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003073
Chong JA, Moran MM, Teichmann M et al (2005) TATA-binding protein (TBP)-like factor (TLF) is a functional regulator of transcription: reciprocal regulation of the neurofibromatosis type 1 and c- fos genes by TLF/TRF2 and TBP. Mol Cell Biol 25:2632–2643. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.25.7.2632-2643.2005
Cochet-Bissuel M, Lory P, Monteil A (2014) The sodium leak channel, NALCN, in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci 8:132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00132
Coffin SL, Durham MA, Nitschke L et al (2023) Disruption of the ATXN1-CIC complex reveals the role of additional nuclear ATXN1 interactors in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Neuron 111:481–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2022.11.016
Cohen-Kutner M, Nachmanni D, Atlas D (2010) CaV2.1 (P/Q channel) interaction with synaptic proteins is essential for depolarization-evoked release. Channels 4:266–277. https://doi.org/10.4161/chan.4.4.12130
Comai L, Zomerdijk JCBM, Beckmann H et al (1994) Reconstitution of transcription factor SL1: exclusive binding of TBP by SL1 or TFIID subunits. Science 266:1966–1972. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7801123
Cornelio-Parra DV, Goswami R, Costanzo K et al (2021) Function and regulation of the Spt-Ada-Gcn5-Acetyltransferase (SAGA) deubiquitinase module. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1864:194630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194630
Crespo-Barreto J, Fryer JD, Shaw CA et al (2010) Partial loss of ataxin-1 function contributes to transcriptional dysregulation in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 pathogenesis. PLoS Genet 6:e1001021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001021
Cui Y, Yang S, Li XJ, Li S (2017) Genetically modified rodent models of SCA17. J Neurosci Res 95:1540–1547. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23984
Da Silva JD, Teixeira-Castro A, Maciel P (2019) From pathogenesis to novel therapeutics for spinocerebellar ataxia type 3: evading potholes on the way to translation. Neurotherapeutics 16:1009–1031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-019-00798-1
Dantonel J, Quintin S, Labouesse M (2000) TBP-like factor is required for embryonic RNA polymerase II transcription in C. elegans expected for a putative transcription factor. Staining 6:715–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00069-1
Davidson JD, Riley B, Burright EN et al (2000) Identification and characterization of an ataxin-1-interacting protein: A1Up, a ubiquitin-like nuclear protein. Hum Mol Genet 9:2305–2312. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.hmg.a018922
Day NC, Shaw PJ, McCormack AL et al (1996) Distribution of α1A, α1B and α1E, voltage-dependent calcium channel subunits in the human hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus. Neuroscience 71:1013–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(95)00514-5
De Lera RM, Kraus RL (2015) Voltage-gated sodium channels: structure, function, pharmacology, and clinical indications. J Med Chem 58:7093–7118. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm501981g
Depienne C, Mandel JL (2021) 30 years of repeat expansion disorders: what have we learned and what are the remaining challenges? Am J Hum Genet 108:764–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.03.011
Dickerson JE, Robertson DL (2012) On the origins of Mendelian disease genes in man: the impact of gene duplication. Mol Biol Evol 29:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr111
Dietrich D, Kirschstein T, Kukley M et al (2003) Functional specialization of presynaptic Cav2.3 Ca2+ channels. Neuron 39:483–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00430-6
Dolivo D, Rodrigues A, Sun L et al (2021) The Nax (SCN7A) channel: an atypical regulator of tissue homeostasis and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 78:5469–5488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03854-2
Du X, Wang J, Zhu H et al (2013) A second cistron in the CACNA1A gene encodes a transcription factor that mediates cerebellar development and SCA6. Cell 154:118–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.059
Du X, Wei C, Hejazi Pastor DP et al (2019) α1ACT is essential for survival and early cerebellar programming in a critical neonatal window. Neuron 102:770-785.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.02.036
Duncan CE, An MC, Papanikolaou T et al (2013) Histone deacetylase-3 interacts with ataxin-7 and is altered in a spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 mouse model. Mol Neurodegener 8:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-8-42
Duttke SHC, Doolittle RF, Wang YL, Kadonaga JT (2014) TRF2 and the evolution of the bilateria. Genes Dev 28:2071–2076. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.250563.114
Egorova PA, Bezprozvanny IB (2019) Molecular mechanisms and therapeutics for spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. Neurotherapeutics 16:1050–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-019-00777-6
Elden AC, Kim HJ, Hart MP et al (2010) Ataxin-2 intermediate-length polyglutamine expansions are associated with increased risk for ALS. Nature 466:1069–1075. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09320
Ellegren H (2000) Microsatellite mutations in the germline: Implications for evolutionary inference. Trends Genet 16:551–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(00)02139-9
Ellisdon AM, Jani D, Köhler A et al (2010) Structural basis for the interaction between yeast Spt-Ada-Gcn5 acetyltransferase (SAGA) complex components Sgf11 and Sus1. J Biol Chem 285:3850–3856. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.070839
Evert BO, Araujo J, Vieira-Saecker AM et al (2006) Ataxin-3 represses transcription via chromatin binding, interaction with histone deacetylase 3, and histone deacetylation. J Neurosci 26:11474–11486. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2053-06.2006
Feng L, Guedes S, Wang T (2004) Atrophin-1-interacting protein 4/human Itch is a ubiquitin E3 ligase for human enhancer of filamentation 1 in transforming growth factor-β signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 279:29681–29690. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M403221200
Feng Q, Miao Y, Ge J et al (2018) ATXN3 positively regulates type I IFN antiviral response by deubiquitinating and stabilizing HDAC3. J Immunol 201:675–687. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1800285
Figueroa KP, Pulst SM (2003) Identification and expression of the gene for human ataxin-2-related protein on chromosome 16. Exp Neurol 184:669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-4886(03)00287-5
Fletcher CF, Tottene A, Lennon VA et al (2001) Dystonia and cerebellar atrophy in Cacna1a null mice lacking P/Q calcium channel activity. FASEB J 15:1288–1290. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.00-0562fje
Fotsing SF, Margoliash J, Wang C et al (2019) The impact of short tandem repeat variation on gene expression. Nat Genet 51:1652–1659. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0521-9
Fregeau B, Kim BJ, Hernández-García A et al (2016) De novo mutations of RERE cause a genetic syndrome with features that overlap those associated with proximal 1p36 deletions. Am J Hum Genet 98:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.03.002
Friedman MJ, Shah AG, Fang ZH et al (2007) Polyglutamine domain modulates the TBP-TFIIB interaction: Implications for its normal function and neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci 10:1519–1528. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2011
Friedman MJ, Wang CE, Li XJ, Li S (2008) Polyglutamine expansion reduces the association of TATA-binding protein with DNA and induces DNA binding-independent neurotoxicity. J Biol Chem 283:8283–8290. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M709674200
Fryer JD, Yu P, Kang H et al (2011) Exercise and genetic rescue of SCA1 via the transcriptional repressor capicua. Science 334:690–693. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1212673
Fukushima A, Okuda A, Nishimoto M et al (1998) Characterization of functional domains of an embryonic stem cell coactivator UTF1 which are conserved and essential for potentiation of ATF-2 activity. J Biol Chem 273:25840–25849. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.40.25840
Gazdag E, Rajkovic A, Torres-Padilla ME, Tora L (2007) Analysis of TATA-binding protein 2 (TBP2) and TBP expression suggests different roles for the two proteins in regulation of gene expression during oogenesis and early mouse development. Reproduction 134:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-06-0337
Gazdag E, Santenard A, Ziegler-Birling C et al (2009) TBP2 is essential for germ cell development by regulating transcription and chromatin condensation in the oocyte. Genes Dev 23:2210–2223. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.535209
Ge F, Chen W, Qin J et al (2015) Ataxin-3 like (ATXN3L), a member of the Josephin family of deubiquitinating enzymes, promotes breast cancer proliferation by deubiquitinating Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5). Oncotarget 6:21369–21378. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4128
Gehrking KM, Andresen JM, Duvick L et al (2011) Partial loss of Tip60 slows mid-stage neurodegeneration in a spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) mouse model. Hum Mol Genet 20:2204–2212. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr108
Gemayel R, Vinces MD, Legendre M, Verstrepen KJ (2010) Variable tandem repeats accelerate evolution of coding and regulatory sequences. Annu Rev Genet 44:445–477. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-072610-155046
Giunti P, Mantuano E, Frontali M, Veneziano L (2015) Molecular mechanism of Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 6: glutamine repeat disorder, channelopathy and transcriptional dysregulation. The multifaceted aspects of a single mutation. Front Cell Neurosci 9:5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00036
Gómez-Ramos A, Podlesniy P, Soriano E, Avila J (2015) Distinct X-chromosome SNVs from some sporadic AD samples. Sci Rep 5:18012. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18012
Gorman KM, Meyer E, Grozeva D et al (2019) Bi-allelic loss-of-function CACNA1B mutations in progressive epilepsy-dyskinesia. Am J Hum Genet 104:948–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.03.005
Goswami R, Bello AI, Bean J et al (2022) The molecular basis of spinocerebellar ataxia type 7. Front Neurosci 16:818757. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.818757
Gouge J, Satia K, Guthertz N et al (2015) Redox signaling by the RNA polymerase III TFIIB-related factor Brf2. Cell 163:1375–1387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.005
Govek EE, Hatten ME (2019) Tag-team genetics of spinocerebellar ataxia 6. Neuron 102:707–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.04.041
Groen JL, Andrade A, Ritz K et al (2015) CACNA1B mutation is linked to unique myoclonus-dystonia syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 24:987–993. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu513
Ha I, Roberts S, Maldonado E et al (1993) Multiple functional domains of human transcription factor IIB: distinct interactions with two general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev 7:1021–1032. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.7.6.1021
Hannan AJ (2018) Tandem repeats mediating genetic plasticity in health and disease. Nat Rev Genet 19:286–298. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.115
Helbig KL, Lauerer RJ, Bahr JC et al (2018) De novo pathogenic variants in CACNA1E cause developmental and epileptic encephalopathy with contractures, macrocephaly, and dyskinesias. Am J Hum Genet 103:666–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.09.006
Heller H, Bengal E (1998) TFIID (TBP) stabilizes the binding of MyoD to its DNA site at the promoter and MyoD facilitates the association of TFIIB with the preinitiation complex. Nucleic Acids Res 26:2112–2119. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/26.9.2112
Helmlinger D, Tora L (2017) Sharing the SAGA. Trends Biochem Sci 42:850–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2017.09.001
Helmlinger D, Hardy S, Sasorith S et al (2004) Ataxin-7 is a subunit of GCN5 histone acetyltransferase-containing complexes. Hum Mol Genet 13:1257–1265. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddh139
Heyes S, Pratt WS, Rees E et al (2015) Genetic disruption of voltage-gated calcium channels in psychiatric and neurological disorders. Prog Neurobiol 134:36–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.09.002
Heyne HO, Singh T, Stamberger H et al (2018) De novo variants in neurodevelopmental disorders with epilepsy. Nat Genet 50:1048–1053. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0143-7
Hinkley CS, Hirsch HA, Gu L et al (2003) The small nuclear RNA-activating protein 190 Myb DNA binding domain stimulates TATA box-binding protein-TATA box recognition. J Biol Chem 278:18649–18657. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M204247200
Hochheimer A, Zhou S, Zheng S et al (2002) TRF2 associates with DREF and directs promoter-selective gene expression in Drosophila. Nature 420:439–445. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01167
Hong S, Kim SJ, Ka S et al (2002) USP7, a ubiquitin-specific protease, interacts with ataxin-1, the SCA1 gene product. Mol Cell Neurosci 20:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1006/mcne.2002.1103
Hong S, Ka S, Kim S et al (2003) p80 coilin, a coiled body-specific protein, interacts with ataxin-1, the SCA1 gene product. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1638:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4439(03)00038-3
Hou R, Sibinga NES (2009) Atrophin proteins interact with the Fat1 cadherin and regulate migration and orientation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 284:6955–6965. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M809333200
Hsiao TL, Vitkup D (2008) Role of duplicate genes in robustness against deleterious human mutations. PLoS Genet 4:e1000014. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000014
Hsu TC, Wang CK, Yang CY et al (2014) Deactivation of TBP contributes to SCA17 pathogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 23:6878–6893. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu410
Indelicato E, Boesch S (2021) From genotype to phenotype: expanding the clinical spectrum of CACNA1A variants in the era of next generation sequencing. Front Neurol 12:639994. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.639994
Innan H, Kondrashov F (2010) The evolution of gene duplications: classifying and distinguishing between models. Nat Rev Genet 11:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2689
Ino M, Yoshinaga T, Wakamori M et al (2001) Functional disorders of the sympathetic nervous system in mice lacking the α1B subunit (Cav 2.2) of N-type calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:5323–5328. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.081089398
Ishida Y, Kawakami H, Kitajima H et al (2016) Vulnerability of Purkinje cells generated from spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 patient-derived iPSCs. Cell Rep 17:1482–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.026
Isogai Y, Keles S, Prestel M et al (2007) Transcription of histone gene cluster by differential core-promoter factors. Genes Dev 21:2936–2949. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1608807
Iwasaki S, Momiyama A, Uchitel OD, Takahashi T (2000) Developmental changes in calcium channel types mediating central synaptic transmission. J Neurosci 20:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.20-01-00059.2000
Jacobi UG, Akkers RC, Pierson ES et al (2007) TBP paralogs accommodate metazoan- and vertebrate-specific developmental gene regulation. EMBO J 26:3900–3909. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601822
Jallow Z, Jacobi UG, Weeks DL et al (2004) Specialized and redundant roles of TBP and a vertebrate-specific TBP paralog in embryonic gene regulation in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:13525–13530. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405536101
Jiménez-López D, Guzmán P (2014) Insights into the evolution and domain structure of ataxin-2 proteins across eukaryotes. BMC Res Notes 7:453. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-7-453
Jordan VK, Fregeau B, Ge X et al (2018) Genotype–phenotype correlations in individuals with pathogenic RERE variants. Hum Mutat 39:666–675. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23400
Jun K, Piedras-Rentería ES, Smith SM et al (1999) Ablation of P/Q-type Ca2+ channel currents, altered synaptic transmission, and progressive ataxia in mice lacking the α(1A)-subunit. PNAS 96:15245–15250. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.26.15245
Kaehler C, Isensee J, Nonhoff U et al (2012) Ataxin-2-like is a regulator of stress granules and processing bodies. PLoS ONE 7:e50134. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050134
Kaehler C, Guenther A, Uhlich A, Krobitsch S (2015) PRMT1-mediated arginine methylation controls ATXN2L localization. Exp Cell Res 334:114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.02.022
Kaessmann H (2010) Origins, evolution, and phenotypic impact of new genes. Genome Res 20:1313–1326. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.101386.109
Kafri R, Levy M, Pilpel Y (2006) The regulatory utilization of genetics redundancy through responsive backup circuits. PNAS 103:11653–11658. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604883103
Kahle JJ, Souroullas GP, Yu P et al (2013) Ataxin1L is a regulator of HSC function highlighting the utility of cross-tissue comparisons for gene discovery. PLoS Genet 9:e1003359. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003359
Kaltenbach L, Horner MA, Rothman JH, Mango SE (2000) The TBP-like factor CeTLF is required to activate RNA polymerase II transcription during C. elegans embryogenesis. Mol Cell 6:705–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(00)00068-X
Kamada K, Shu F, Chen H et al (2001) Crystal structure of Negative Cofactor 2 recognizing the TBP-DNA transcription complex. Cell 106:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00417-2
Karres JS, Hilgers V, Carrera I et al (2007) The conserved microRNA MiR-8 tunes atrophin levels to prevent neurodegeneration in drosophila. Cell 131:136–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.020
Kedmi A, Zehavi Y, Glick Y et al (2014) Drosophila TRF2 is a preferential core promoter regulator. Genes Dev 28:2163–2174. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.245670.114
Key J, Harter PN, Sen N et al (2020) Mid-gestation lethality of Atxn2l-ablated Mice. Int J Mol Sci 21:5124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145124
Kieffer-Kwon P, Martianov I, Davidson I (2004) Cell-specific nucleolar localization of TBP-related factor 2. Mol Biol Cell 15:4356–4368. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e04-02-0138
Kim BJ, Scott DA (2014) Mouse model reveals the role of RERE in cerebellar foliation and the migration and maturation of Purkinje cells. PLoS ONE 9:e87518. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087518
Kim BJ, Zaveri HP, Shchelochkov OA et al (2013) An allelic series of mice reveals a role for RERE in the development of multiple organs affected in chromosome 1p36 deletions. PLoS ONE 8:e57460. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057460
Kim E, Lee Y, Choi S, Song JJ (2014) Structural basis of the phosphorylation dependent complex formation of neurodegenerative disease protein Ataxin-1 and RBM17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 449:399–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.063
Kim BJ, Zaveri HP, Kundert PN et al (2021) RERE deficiency contributes to the development of orofacial clefts in humans and mice. Hum Mol Genet 30:595–602. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddab084
Klockgether T, Mariotti C, Paulson HL (2019) Spinocerebellar ataxia. Nat Rev Dis Prim 5:24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0074-3
Köhler A, Zimmerman E, Schneider M et al (2010) Structural basis for assembly and activation of the heterotetrameric SAGA histone H2B deubiquitinase module. Cell 141:606–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.026
Koonin EV (2005) Orthologs, paralogs, and evolutionary genomics. Annu Rev Genet 39:309–338. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.39.073003.114725
Koshy B, Matilla T, Burright EN et al (1996) Spinocerebellar ataxia type-1 and spinobulbar muscular atrophy gene products interact with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Hum Mol Genet 5:1311–1318. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/5.9.1311
Kwan JZJ, Nguyen TF, Uzozie AC et al (2023) RNA Polymerase II transcription independent of TBP in murine embryonic stem cells. Elife 12:e83810. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.83810
Kwon H, Green MR (1994) The RNA polymerase I transcription factor, upstream binding factor, interacts directly with the TATA box-binding protein. J Biol Chem 269:30140–30146. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(18)43788-x
La Spada AR, Fu YH, Sopher BL et al (2001) Polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-7 antagonizes CRX function and indices cone-rod dystrophy in a mouse model of SCA7. Neuron 32:957–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00534-7
Lagman D, Ocampo Daza D, Widmark J et al (2013) The vertebrate ancestral repertoire of visual opsins, transducin alpha subunits and oxytocin/vasopressin receptors was established by duplication of their shared genomic region in the two rounds of early vertebrate genome duplications. BMC Evol Biol 13:238. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-13-238
Lam YC, Bowman AB, Jafar-Nejad P et al (2006) ATAXIN-1 interacts with the repressor capicua in its native complex to cause SCA1 neuropathology. Cell 127:1335–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.038
Lan X, Koutelou E, Schibler AC et al (2015) Poly(Q) expansions in ATXN7 affect solubility but not activity of the SAGA deubiquitinating module. Mol Cell Biol 35:1777–1787. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01454-14
Lang G, Bonnet J, Umlauf D et al (2011) The tightly controlled deubiquitination activity of the human SAGA complex differentially modifies distinct gene regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol 31:3734–3744. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.05231-11
Lasagna-Reeves CA, Rousseaux MWC, Guerrero-Munoz MJ et al (2015) A native interactor scaffolds and stabilizes toxic Ataxin-1 oligomers in SCA1. Elife 4:e07558. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.07558
Lastres-Becker I, Brodesser S, Lütjohann D et al (2008) Insulin receptor and lipid metabolism pathology in ataxin-2 knock-out mice. Hum Mol Genet 17:1465–1481. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddn035
Lebre AS, Jamot L, Takahashi J et al (2001) Ataxin-7 interacts with a Cbl-associated protein that it recruits into neuronal intranuclear inclusions. Hum Mol Genet 10:1201–1213. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/10.11.1201
Lee SK, Anzick SL, Choi JE et al (1999) A nuclear factor, ASC-2, as a cancer-amplified transcriptional coactivator essential for ligand-dependent transactivation by nuclear receptors in vivo. J Biol Chem 274:34283–34293. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.48.34283
Lee A, Westenbroek RE, Haeseleer F et al (2002) Differential modulation of Cav2.1 channels by calmodulin and Ca2+-binding protein 1. Nat Neurosci 5:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn805
Lee KK, Swanson SK, Florens L et al (2009) Yeast Sgf73/Ataxin-7 serves to anchor the deubiquitination module into both SAGA and Slik(SALSA) HAT complexes. Epigenetics Chromatin 2:6–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8935-2-2
Lee Y, Fryer JD, Kang H et al (2011) Atxn1 protein family and Cic regulate extracellular matrix remodeling and lung alveolarization. Dev Cell 21:746–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.017
Lee J, Kim M, Itoh TQ, Lim C (2018) Ataxin-2: a versatile posttranscriptional regulator and its implication in neural function. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 9:e1488. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1488
Lee DH, Park JH, Choi J et al (2020) Differential expression of DUB genes in ovarian cells treated with Di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate. Int J Mol Sci 21:1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051755
Li WH, Gu Z, Wang H, Nekrutenko A (2001) Evolutionary analyses of the human genome. Nature 409:847–849. https://doi.org/10.1038/35057039
Li F, Macfarlan T, Pittman RN, Chakravarti D (2002) Ataxin-3 is a histone-binding protein with two independent transcriptional corepressor activities. J Biol Chem 277:45004–45012. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M205259200
Li PP, Sun X, Xia G et al (2016a) ATXN2-AS, a gene antisense to ATXN2, is associated with spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 80:600–615. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24761
Li W, Atanassov BS, Lan X et al (2016b) Cytoplasmic ATXN7L3B interferes with nuclear functions of the SAGA deubiquitinase module. Mol Cell Biol 36:2855–2866. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00193-16
Lieberman AP, Shakkottai VG, Albin RL (2019) Polyglutamine repeats in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis 14:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012857
Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C et al (2006) A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration. Cell 125:801–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032
Lim J, Crespo-Barreto J, Jafar-Nejad P et al (2008) Opposing effects of polyglutamine expansion on native protein complexes contribute to SCA1. Nature 452:713–718. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06731
Lin L, Li X, Pan C et al (2019) ATXN2L upregulated by epidermal growth factor promotes gastric cancer cell invasiveness and oxaliplatin resistance. Cell Death Dis 10:173. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1362-2
Lu HC, Tan Q, Rousseaux MWC et al (2017) Disruption of the ATXN1-CIC complex causes a spectrum of neurobehavioral phenotypes in mice and humans. Nat Genet 49:527–536. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3808
Malecova B, Dall’Agnese A, Madaro L et al (2016) TBP/TFIID-dependent activation of myoD target genes in skeletal muscle cells. Elife 5:e12534. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.12534
Mark MD, Maejima T, Kuckelsberg D et al (2011) Delayed postnatal loss of P/Q-type calcium channels recapitulates the absence epilepsy, dyskinesia, and ataxia phenotypes of genomic Cacna1A mutations. J Neurosci 31:4311–4326. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5342-10.2011
Martianov I, Fimia GM, Dierich A et al (2001) Late arrest of spermiogenesis and germ cell apoptosis in mice lacking the TBP-like TLF/TRF2 gene. Mol Cell 7:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00198-8
Martianov I, Viville S, Davidson I (2002) RNA polymerase II transcription in murine cells lacking the TATA binding protein. Science 298:1036–1039. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1076327
Matilla A, Koshy BT, Cummings CJ et al (1997) The cerebellar leucine-rich acidic nuclear protein interacts with ataxin-1. Nature 389:974–978. https://doi.org/10.1038/40159
Matilla A, Gorbea C, Einum DD et al (2001) Association of ataxin-7 with the proteasome subunit S4 of the 19S regulatory complex. Hum Mol Genet 10:2821–2831. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/10.24.2821
McCampbell A, Taylor JP, Taye AA et al (2000) CREB-binding protein sequestration by expanded polyglutamine. Hum Mol Genet 9:2197–2202. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/9.14.2197
McIntosh CS, Li D, Wilton SD, Aung-Htut MT (2021) Polyglutamine ataxias: our current molecular understanding and what the future holds for antisense therapies. Biomedicines 9:1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111499
Meunier C, Bordereaux D, Porteu F et al (2002) Cloning and characterization of a family of proteins associated with Mpl. J Biol Chem 277:9139–9147. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M105970200
Mighell AJ, Smith NR, Robinson PA, Markham AF (2000) Vertebrate pseudogenes. FEBS Lett 468:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01199-6
Mishal R, Luna-Arias JP (2022) Role of the TATA-box binding protein (TBP) and associated family members in transcription regulation. Gene 833:146581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2022.146581
Mizutani A, Wang L, Rajan H et al (2005) Boat, an AXH domain protein, suppresses the cytotoxicity of mutant ataxin-1. EMBO J 24:3339–3351. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600785
Mohan RD, Dialynas G, Weake VM et al (2014) Loss of Drosophila Ataxin-7, a SAGA subunit, reduces H2B ubiquitination and leads to neural and retinal degeneration. Genes Dev 28:259–272. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.225151.113
Monies D, Abouelhoda M, AlSayed M et al (2017) The landscape of genetic diseases in Saudi Arabia based on the first 1000 diagnostic panels and exomes. Hum Genet 136:921–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-017-1821-8
Moore PA, Ozer J, Salunek M et al (1999) A human TATA binding protein-related protein with altered DNA binding specificity inhibits transcription from multiple promoters and activators. Mol Cell Biol 19:7610–7620. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.19.11.7610
Morello G, Gentile G, Spataro R et al (2020) Genomic portrait of a sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis case in a large spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 family. J Pers Med 10:262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040262
Moseley ML, Zu T, Ikeda Y et al (2006) Bidirectional expression of CUG and CAG expansion transcripts and intranuclear polyglutamine inclusions in spinocerebellar ataxia type 8. Nat Genet 38:758–769. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1827
Müller F, Lakatos L, Dantonel JC et al (2001) TBP is not universally required for zygotic RNA polymerase II transcription in zebrafish. Curr Biol 11:282–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00076-8
Nakagawasai O, Onogi H, Mitazaki S et al (2010) Behavioral and neurochemical characterization of mice deficient in the N-type Ca 2+ channel α 1B subunit. Behav Brain Res 208:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.11.042
Nakamura Y, Tagawa K, Oka T et al (2012) Ataxin-7 associates with microtubules and stabilizes the cytoskeletal network. Hum Mol Genet 21:1099–1110. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr539
Nicastro G, Menon RP, Masino L et al (2005) The solution structure of the Josephin domain of ataxin-3: structural determinants for molecular recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10493–10498. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0501732102
Nonhoff U, Ralser M, Welzel F et al (2007) Ataxin-2 interacts with the DEAD/H-Box RNA helicase DDX6 and interferes with P-bodies and stress granules. Mol Biol Cell 18:1385–1396. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E06
Nonis D, Schmidt MHH, van de Loo S et al (2008) Ataxin-2 associates with the endocytosis complex and affects EGF receptor trafficking. Cell Signal 20:1725–1739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.05.018
Nowak B, Kozlowska E, Pawlik W, Fiszer A (2023) Atrophin-1 function and dysfunction in dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy. Mov Disord 38:526–536. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.29355
Nucifora J, Sasaki M, Peters MF et al (2001) Interference by huntingtin and atrophin-1 with CBP-mediated transcription leading to cellular toxicity. Science 291:2423–2428. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1056784
Ohbayashi T, Kishimoto T, Makino Y et al (1999a) Isolation of cDNA, chromosome mapping, and expression of the human TBP-like protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 255:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1999.0159
Ohbayashi T, Makino Y, Tamura TA (1999b) Identification of a mouse TBP-like protein (TLP) distantly related to the Drosophila TBP-related factor. Nucleic Acids Res 27:750–755. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/27.3.750
Okamura-Oho Y, Miyashita T, Ohmi K, Yamada M (1999) Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy protein interacts through a proline-rich region near polyglutamine with the SH3 domain of an insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate. Hum Mol Genet 8:947–957. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/8.6.947
Okamura-Oho Y, Miyashita T, Nagao K et al (2003) Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy protein is phosphorylated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. Hum Mol Genet 12:1535–1542. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddg168
Okazawa H, Rich T, Chang A et al (2002) Interaction between mutant ataxin-1 and PQBP-1 affects transcription and cell death. Neuron 34:701–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00697-9
Onodera O, Oyake M, Takano H et al (1995) Molecular cloning of a full-length cDNA for dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy and regional expressions of the expanded alleles in the CNS. Am J Hum Genet 57:1050–1060
Ophoff RA, Terwindt GM, Vergouwe MN et al (1996) Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4. Cell 87:543–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81373-2
Palmer EE, Hong S, Al Zahrani F et al (2019) De novo variants disrupting the HX repeat motif of ATN1 cause a recognizable non-progressive neurocognitive syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 104:542–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.01.013
Papadopoulos P, Gutiérrez L, Demmers J et al (2015) TAF10 Interacts with the GATA1 Transcription Factor and Controls Mouse Erythropoiesis. Mol Cell Biol 35:2103–2118. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01370-14
Papai G, Frechard A, Kolesnikova O et al (2020) Structure of SAGA and mechanism of TBP deposition on gene promoters. Nature 577:711–716. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-1944-2
Parajuli LK, Nakajima C, Kulik A et al (2012) Quantitative regional and ultra structural localization of the Ca v2.3 subunit of R-type calcium channel in mouse brain. J Neurosci 32:13555–13567. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1142-12.2012
Park KA, Tanaka Y, Suenaga Y, Tamura TA (2006) TATA-binding protein-related factor 2 is localized in the cytoplasm of mammalian cells and much of it migrates to the nucleus in response to genotoxic agents. Mol Cells 22:203–209
Paul S, Dansithong W, Figueroa KP et al (2018) Staufen1 links RNA stress granules and autophagy in a model of neurodegeneration. Nat Commun 9:3648. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06041-3
Paulson HL, Shakkottai VG, Clark HB, Orr HT (2017) Polyglutamine spinocerebellar ataxias—from genes to potential treatments. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:613–626. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.92
Paulson H (2018) Repeat expansion diseases. In: Handbook of Clinical Neurology, vol 147, pp 105–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63233-3.00009-9
Pellerin D, Danzi MC, Wilke C et al (2023) Deep intronic FGF14 GAA repeat expansion in late-onset cerebellar ataxia. N Engl J Med 388:128–141. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2207406
Pérez Ortiz JM, Mollema N, Toker N et al (2018) Reduction of protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of ATXN1-S776 in Purkinje cells delays onset of Ataxia in a SCA1 mouse model. Neurobiol Dis 116:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.05.002
Persengiev SP, Zhu X, Dixit BL et al (2003) TRF3, a TATA-box-binding protein-related factor, is vertebrate-specific and widely expressed. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:14887–14891. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2036440100
Pietrobon D (2002) Calcium channels and channelopathies of the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 25:31–50. https://doi.org/10.1385/mn:25:1:031
Pitt SJ, Reilly-O’Donnell B, Sitsapesan R (2016) Exploring the biophysical evidence that mammalian two-pore channels are NAADP-activated calcium-permeable channels. J Physiol 594:4171–4179. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP270936
Plaster N, Sonntag C, Schilling TF, Hammerschmidt M (2007) REREa/atrophin-2 interacts with histone deacetylase and Fgf8 signaling to regulate multiple processes of zebrafish development. Dev Dyn 236:1891–1904. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21196
Rabenstein MD, Zhou S, Lis JT, Tjian R (1999) TATA box-binding protein (TBP)-related factor 2 (TRF2), a third member of the TBP family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:4791–4796. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.9.4791
Rocha S, Vieira J, Vázquez N et al (2019) ATXN1 N-terminal region explains the binding differences of wild-type and expanded forms. BMC Med Genomics 12:145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-019-0594-4
Rodrigues A-J, Coppola G, Santos C et al (2007) Functional genomics and biochemical characterization of the C. elegans orthologue of the Machado-Joseph disease protein ataxin-3. FASEB J 21:1126–1136. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-7002com
Rousseaux MWC, Tschumperlin T, Lu H et al (2018) ATXN1-CIC complex is the primary driver of cerebellar pathology in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 through a gain-of- function mechanism. Neuron 97:1235–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.02.013
Royer-Bertrand B, Jequier Gygax M, Cisarova K et al (2021) De novo variants in CACNA1E found in patients with intellectual disability, developmental regression and social cognition deficit but no seizures. Mol Autism 12:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-021-00473-3
Sacco JJ, Yau TY, Darling S et al (2014) The deubiquitylase Ataxin-3 restricts PTEN transcription in lung cancer cells. Oncogene 33:4265–4272. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.512
Saegusa H, Kurihara T, Zong S et al (2000) Altered pain responses in mice lacking α1E subunit of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:6132–6137. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.100124197
Satterfield TF, Pallanck LJ (2006) Ataxin-2 and its Drosophila homolog, ATX2, physically assemble with polyribosomes. Hum Mol Genet 15:2523–2532. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddl173
Sawaya S, Bagshaw A, Buschiazzo E et al (2013) Microsatellite tandem repeats are abundant in human promoters and are associated with regulatory elements. PLoS ONE 8:e54710. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054710
Scheel H, Tomiuk S, Hofmann K (2003) Elucidation of ataxin-3 and ataxin-7 function by integrative bioinformatics. Hum Mol Genet 12:2845–2852. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddg297
Schmitt I, Linden M, Khazneh H et al (2007) Inactivation of the mouse Atxn3 (ataxin-3) gene increases protein ubiquitination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:734–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.08.062
Scholz KP, Miller RJ (1995) Developmental changes in presynaptic calcium channels coupled to glutamate release in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 15:4612–4617. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.15-06-04612.1995
Serra HG, Duvick L, Zu T et al (2006) RORα-mediated Purkinje cell development determines disease severity in adult SCA1 mice. Cell 127:697–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.036
Shah AG, Friedman MJ, Huang S et al (2009) Transcriptional dysregulation of TrkA associates with neurodegeneration in spinocerebellar ataxia type 17. Hum Mol Genet 18:4141–4152. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp363
Shen Y, Peterson AS (2009) Atrophins’ emerging roles in development and neurodegenerative disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:437–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8403-9
Shen Y, Lee G, Choe Y et al (2007) Functional architecture of atrophins. J Biol Chem 282:5037–5044. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M610274200
Shibata H, Huynh DP, Pulst SM (2000) A novel protein with RNA-binding motifs interacts with ataxin-2. Hum Mol Genet 9:1303–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/9.9.1303
Shimada M, Nakadai T, Tamura T (2003) TATA-binding protein-like protein (TLP/TRF2/TLF) negatively regulates cell cycle progression and is required for the stress-mediated G 2 checkpoint. Mol Cell Biol 23:4107–4120. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.23.12.4107-4120.2003
Shimohata T, Nakajima T, Yamada M et al (2000) Expanded polyglutamine stretches interact with TAF(II)130, interfering with CREB-dependent transcription. Nat Genet 26:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/79139
Shortt JA, Ruggiero RP, Cox C et al (2020) Finding and extending ancient simple sequence repeat-derived regions in the human genome. Mob DNA 11:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13100-020-00206-y
Shukla S, Tekwani BL (2020) Histone deacetylases inhibitors in neurodegenerative diseases, neuroprotection and neuronal differentiation. Front Pharmacol 11:537. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00537
Shukla KK, Mahdi AA, Rajender S (2012) Ion channels in sperm physiology and male fertility and infertility. J Androl 33:777–788. https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.111.015552
Sopher BL, Ladd PD, Pineda VV et al (2011) CTCF regulates ataxin-7 expression through promotion of a convergently transcribed, antisense noncoding RNA. Neuron 70:1071–1084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.027
Sousa e Silva R, Sousa AD, Vieira J, Vieira CP (2023) The Josephin domain (JD) containing proteins are predicted to bind to the same interactors: implications for spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA3) studies using Drosophila melanogaster mutants. Front Mol Neurosci 16:1140719. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2023.1140719
Stoyas CA, Bushart DD, Switonski PM et al (2017) Nicotinamide pathway dependent Sirt1 activation restores calcium homeostasis to achieve neuroprotection in spinocerebellar ataxia type 7. Neuron 105:630–644.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.019
Ström AL, Forsgren L, Holmberg M (2005) A role for both wild-type and expanded ataxin-7 in transcriptional regulation. Neurobiol Dis 20:646–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2005.04.018
Suter B, Fontaine JF, Yildirimman R et al (2013) Development and application of a DNA microarray-based yeast two-hybrid system. Nucleic Acids Res 41:1496–1507. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1329
Suzuki Y, Nakayama K, Hashimoto N, Yazawa I (2010) Proteolytic processing regulates pathological accumulation in dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy. FEBS J 277:4873–4887. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07893.x
Takata A, Nakashima M, Saitsu H et al (2019) Comprehensive analysis of coding variants highlights genetic complexity in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Nat Commun 10:2506. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10482-9
Tan JY, Vance KW, Varela MA et al (2014) Crosstalking noncoding RNAs contribute to cell-specific neurodegeneration in SCA7. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:955–961. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2902
Tan D, Wei C, Chen Z et al (2023) CAG repeat expansion in THAP11 is associated with a novel spinocerebellar ataxia. Mov Disord 38:1282–1293. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.29412
Tanaka Y, Nanba Y, Park K et al (2007) Transcriptional repression of the mouse wee1 gene by TBP-related factor 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.175
Teichmann M, Wang Z, Martinez E et al (1999) Human TATA-binding protein-related factor-2 (hTRF2) stably associates with HTFIIa in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13720–13725. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.24.13720
Tejwani L, Lim J, Program N et al (2021) Pathogenic mechanisms underlying spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Cell Mol Life Sci 77:4015–4029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03520-z
Tong X, Gui H, Jin F et al (2011) Ataxin-1 and Brother of ataxin-1 are components of the Notch signalling pathway. EMBO Rep 12:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2011.49
Tsai CC, Kao HY, Mitzutani A et al (2004) Ataxin 1, a SCA1 neurodegenerative disorder protein, is functionally linked to the silencing mediator of retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:4047–4052. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0400615101
Vauti F, Vögele V, Deppe I et al (2021) Structural analysis and spatiotemporal expression of atxn1 genes in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Int J Mol Sci 22:11348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111348
Veenstra GJC, Weeks DL, Wolffe AP (2000) Distinct roles for TBP and TBP-like factor in early embryonic gene transcription in xenopus. Science 290:2312–2315. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5500.2312
Venkatraman A, Hu YS, Didonna A et al (2014) The histone deacetylase HDAC3 is essential for Purkinje cell function, potentially complicating the use of HDAC inhibitors in SCA1. Hum Mol Genet 23:3733–3745. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu081
Vermeulen M, Eberl HC, Matarese F et al (2010) Quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling of epigenetic histone marks and their readers. Cell 142:967–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.08.020
Vlasschaert C, Cook D, Xia X, Gray DA (2017) The evolution and functional diversification of the deubiquitinating enzyme superfamily. Genome Biol Evol 9:558–573. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evx020
Waerner T, Gardellin P, Pfizenmaier K et al (2001) Human RERE is localized to nuclear promyelocytic leukemia oncogenic domains and enhances apoptosis. Cell Growth Differ 12:201–210
Wang L, Tsai CC (2008) Atrophin proteins: an overview of a new class of nuclear receptor corepressors. Nucl Recept Signal 6:e009. https://doi.org/10.1621/nrs.06009
Wang L, Rajan H, Pitman JL et al (2006) Histone deacetylase-associating Atrophin proteins are nuclear receptor corepressors. Genes Dev 20:525–530. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1393506
Wang L, Charroux B, Kerridge S, Tsai CC (2008) Atrophin recruits HDAC1/2 and G9a to modify histone H3K9 and to determine cell fates. EMBO Rep 9:555–562. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2008.67
Wang YL, Duttke SHC, Chen K et al (2014) TRF2, but not TBP, mediates the transcription of ribosomal protein genes. Genes Dev 28:1550–1555. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.245662.114
Wang B, Krall EB, Aguirre AJ et al (2017) ATXN1L, CIC, and ETS transcription factors modulate sensitivity to MAPK pathway inhibition. Cell Rep 18:1543–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.031
Weeks SD, Grasty KC, Hernandez-Cuebas L, Loll PJ (2011) Crystal structure of a Josephin-ubiquitin complex: evolutionary restraints on ataxin-3 deubiquitinating activity. J Biol Chem 286:4555–4565. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.177360
Weishäupl D, Schneider J, Pinheiro BP et al (2019) Physiological and pathophysiological characteristics of ataxin-3 isoforms. J Biol Chem 294:644–661. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.005801
Westenbroek RE, Hell JW, Warner C et al (1992) Biochemical properties and subcellular distribution of an N-type calcium channel α1 subunit. Neuron 9:1099–1115. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.15-10-06419.1995
Wheeler DB, Randall A, Tsien RW (1994) Roles of N-type and Q-type Ca2+ chnnels in supporting hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science 264:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7832825
Wong D, Lounsbury K, Lum A et al (2018) Transcriptomic analysis of CIC and ATXN1L reveal a functional relationship exploited by cancer. Oncogene 38:273–290. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0427-5
Wong D, Sogerer L, Lee SS et al (2020) TRIM25 promotes Capicua degradation independently of ERK in the absence of ATXN1L. BMC Biol 18:154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-020-00895-0
Wood JD, Yuan J, Margolis RL et al (1998) Atrophin-1, the DRPLA gene product, interacts with two families of WW domain-containing proteins. Mol Cell Neurosci 11:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1006/mcne.1998.0677
Wood JD, Nucifora FC, Duan K et al (2000) Atrophin-1, the dentato-rubral and pallido-luysian atrophy gene product, interacts with ETO / MTG8 in the nuclear matrix and represses transcription. Cell 150:939–948. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.150.5.939
Xu Y, Lv X, Cai R et al (2022) Possible implication of miR-142-3p in coronary microembolization induced myocardial injury via ATXN1L/HDAC3/NOL3 axis. J Mol Med 100:763–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-022-02198-z
Yanagisawa H, Bundo M, Miyashita T et al (2000) Protein binding of a DRPLA family through arginine-glutamic acid dipeptide repeats is enhanced by extended polyglutamine. Hum Mol Genet 9:1433–1442. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/9.9.1433
Yang S, Huang S, Gaertig MA et al (2014) Age-dependent decrease in chaperone activity impairs MANF expression, leading to Purkinje Cell degeneration in inducible SCA17 Mice. Neuron 81:349–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.002
Yang S, Li X-J, Li S (2016) Molecular mechanisms underlying Spinocerebellar Ataxia 17 (SCA17) pathogenesis. Rare Dis 4:e1223580. https://doi.org/10.1080/21675511.2016.1223580
Yazawa I, Nakase H, Kurisaki H (1999) Abnormal dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) protein complex is pathologically ubiquitinated in DRPLA brains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 260:133–138. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1999.0839
Yuan CX, Gurley WB (2000) Potential targets for HSF1 within the preinitiation complex. Cell Stress Chaperones 5:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1379/1466-1268(2000)005%3c0229:PTFHWT%3e2.0.CO;2
Zeng L, Zhang D, McLoughlin HS et al (2018) Loss of the Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 3 disease protein ATXN3 alters transcription of multiple signal transduction pathways. PLoS ONE 13:e0204438. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204438
Zhang D, Penttila TL, Morris PL et al (2001) Spermiogenesis deficiency in mice lacking the Trf2 gene. Science 292:1153–1155. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1059188
Zhang CL, Zou Y, Yu RT et al (2006) Nuclear receptor TLX prevents retinal dystrophy and recruits the corepressor atrophin1. Genes Dev 20:1308–1320. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1413606
Zhang F, Xu D, Yuan L et al (2014) Epigenetic regulation of Atrophin1 by lysine-specific demethylase 1 is required for cortical progenitor maintenance. Nat Commun 5:5815. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6815
Zhao Y, Lang G, Ito S et al (2008) A TFTC/STAGA module mediates histone H2A and H2B deubiquitination, coactivates nuclear receptors, and counteracts heterochromatin silencing. Mol Cell 29:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.011
Zoltewicz JS, Stewart NJ, Leung R, Peterson AS (2004) Atrophin 2 recruits histone deacetylase and is required for the function of multiple signaling centers during mouse embryogenesis. Development 131:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.00908
Zu T, Gibbens B, Doty NS et al (2011) Non-ATG-initiated translation directed by microsatellite expansions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:260–265. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1013343108
Funding
Open access funding provided by FCT|FCCN (b-on). This work was partly supported by FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia in the framework of the project “Evolution and functional activity of gene paralogues in spinocerebellar ataxias” (2022.04896.PTDC). Sandra Martins (CEECIND/00684/2017) and Daniela Felício (PhD fellowship, UI/BD/154402/2023) are also funded by FCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM designed the study and obtained funding. DF and TRM performed the literature search and drafted the manuscript. SM and AA critically revised the manuscript. The final draft has been read and approved for publication by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Felício, D., du Mérac, T.R., Amorim, A. et al. Functional implications of paralog genes in polyglutamine spinocerebellar ataxias. Hum. Genet. 142, 1651–1676 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-023-02607-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-023-02607-4