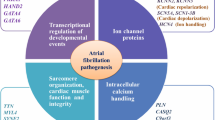
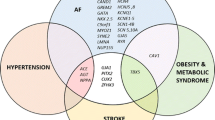
Abstract
As the most common cardiac arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation (AF) is a major risk factor for stroke, heart failure, and premature death with considerable associated costs. However, no available treatment options have optimal benefit-harm profiles currently, reflecting an incomplete understanding of the biological mechanisms underlying this complex arrhythmia. Recently, molecular epidemiological studies, especially genome-wide association studies, have emphasized the substantial genetic component of AF etiology. A comprehensive mapping of the genetic underpinnings for AF can expand our knowledge of AF mechanism and further facilitate the process of locating novel therapeutics for AF. Here we provide a state-of-the-art review of the molecular genetics of AF incorporating evidence from linkage analysis and candidate gene, as well as genome-wide association studies of common variations and rare copy number variations; potential epigenetic modifications (e.g., DNA methylation, histone modification, and non-coding RNAs) are also involved. We also outline the challenges in mechanism investigation and potential future directions in this article.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman MJ et al (2011) HRS/EHRA expert consensus statement on the state of genetic testing for the channelopathies and cardiomyopathies: this document was developed as a partnership between the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) and the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Europace 13:1077–1109. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eur245
Alkan C, Coe BP, Eichler EE (2011) Genome structural variation discovery and genotyping. Nat Rev Genet 12:363–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2958
Andersson R, Sandelin A (2020) Determinants of enhancer and promoter activities of regulatory elements. Nat Rev Genet 21:71–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0173-8
Arnar DO, Thorvaldsson S, Manolio TA, Thorgeirsson G, Kristjansson K, Hakonarson H, Stefansson K (2006) Familial aggregation of atrial fibrillation in Iceland. Eur Heart J 27:708–712. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehi727
Ball J, Carrington MJ, McMurray JJ, Stewart S (2013) Atrial fibrillation: profile and burden of an evolving epidemic in the 21st century. Int J Cardiol 167:1807–1824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.12.093
Bapat A, Anderson CD, Ellinor PT, Lubitz SA (2018) Genomic basis of atrial fibrillation. Heart (British Cardiac Society) 104:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2016-311027
Barrett JH, Teare MD (2011) Linkage analysis. In: Yu B, Hinchcliffe M (eds) In silico tools for gene discovery. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 19–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-176-5_2
Benaglio P et al (2019) Allele-specific NKX2-5 binding underlies multiple genetic associations with human electrocardiographic traits. Nat Genet 51:1506–1517. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0499-3
Benjamin EJ et al (2009) Variants in ZFHX3 are associated with atrial fibrillation in individuals of European ancestry. Nat Genet 41:879–881. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.416
Berry FB, Miura Y, Mihara K, Kaspar P, Sakata N, Hashimoto-Tamaoki T, Tamaoki T (2001) Positive and negative regulation of myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells by isoforms of the multiple homeodomain zinc finger transcription factor ATBF1. J Biol Chem 276:25057–25065. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M010378200
Brugada R et al (1997) Identification of a genetic locus for familial atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 336:905–911. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199703273361302
Calloe K et al (2007) Characterizations of a loss-of-function mutation in the Kir3.4 channel subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 364:889–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.10.106
Chang SH et al (2017) Association of a family history of atrial fibrillation with incidence and outcomes of atrial fibrillation: a population-based family cohort study. JAMA Cardiol 2:863–870. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2017.1855
Chen YH et al (2003) KCNQ1 gain-of-function mutation in familial atrial fibrillation. Science (New York, NY) 299:251–254. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1077771
Chen PS, Chen LS, Fishbein MC, Lin SF, Nattel S (2014) Role of the autonomic nervous system in atrial fibrillation: pathophysiology and therapy. Circ Res 114:1500–1515. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.114.303772
Chen Y, Hong T, Wang S, Mo J, Tian T, Zhou X (2017) Epigenetic modification of nucleic acids: from basic studies to medical applications. Chem Soc Rev 46:2844–2872. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00599c
Chinchilla A et al (2011) PITX2 insufficiency leads to atrial electrical and structural remodeling linked to arrhythmogenesis. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 4:269–279. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.110.958116
Christophersen IE, Ravn LS, Budtz-Joergensen E, Skytthe A, Haunsoe S, Svendsen JH, Christensen K (2009) Familial aggregation of atrial fibrillation: a study in Danish twins. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2:378–383. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.108.786665
Christophersen IE et al (2017) Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 49:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3843
Chugh SS et al (2014) Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a global burden of disease 2010 study. Circulation 129:837–847. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.113.005119
Colilla S, Crow A, Petkun W, Singer DE, Simon T, Liu X (2013) Estimates of current and future incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the U.S. adult population. Am J Cardiol 112:1142–1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.05.063
Collins MM et al (2019) Early sarcomere and metabolic defects in a zebrafish pitx2c cardiac arrhythmia model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:24115–24121. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913905116
Dai W et al (2019) A calcium transport mechanism for atrial fibrillation in Tbx5-mutant mice. eLife 8:e41814. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.41814
Darbar D, Motsinger AA, Ritchie MD, Gainer JV, Roden DM (2007) Polymorphism modulates symptomatic response to antiarrhythmic drug therapy in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 4:743–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2007.02.006
Darbar D, Hardy A, Haines JL, Roden DM (2008) Prolonged signal-averaged P-wave duration as an intermediate phenotype for familial atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 51:1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2007.11.058
de Wit E, de Laat W (2012) A decade of 3C technologies: insights into nuclear organization. Genes Dev 26:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.179804.111
Delaney JT, Muhammad R, Blair MA, Kor K, Fish FA, Roden DM, Darbar D (2012) A KCNJ8 mutation associated with early repolarization and atrial fibrillation. Europace 14:1428–1432. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eus150
Donate Puertas R et al (2017) Atrial fibrillation is associated with hypermethylation in human left atrium, and treatment with decitabine reduces atrial tachyarrhythmias in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Transl Res: J Lab Clin Med 184:57.e55–67.e55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2017.03.004
Drabkin M et al (2018) Nocturnal atrial fibrillation caused by mutation in KCND2, encoding pore-forming (α) subunit of the cardiac Kv4.2 potassium channel. Circ Genom Precis Med 11:e002293. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgen.118.002293
Ellinor PT, Shin JT, Moore RK, Yoerger DM, MacRae CA (2003) Locus for atrial fibrillation maps to chromosome 6q14-16. Circulation 107:2880–2883. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Cir.0000077910.80718.49
Ellinor PT et al (2010) Common variants in KCNN3 are associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 42:240–244. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.537
Ellinor PT et al (2012) Meta-analysis identifies six new susceptibility loci for atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 44:670–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2261
Feghaly J, Zakka P, London B, MacRae CA, Refaat MM (2018) Genetics of atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc 7:e009884. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.118.009884
Fox CS et al (2004) Parental atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation in offspring. JAMA 291:2851–2855. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.291.23.2851
Gollob MH et al (2006) Somatic mutations in the connexin 40 gene (GJA5) in atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 354:2677–2688. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa052800
Gudbjartsson DF et al (2007) Variants conferring risk of atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Nature 448:353–357. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06007
Gudbjartsson DF et al (2009) A sequence variant in ZFHX3 on 16q22 associates with atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke. Nat Genet 41:876–878. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.417
Hodgson-Zingman DM et al (2008) Atrial natriuretic peptide frameshift mutation in familial atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 359:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0706300
Hong K, Bjerregaard P, Gussak I, Brugada R (2005) Short QT syndrome and atrial fibrillation caused by mutation in KCNH2. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 16:394–396. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1540-8167.2005.40621.x
Hsieh CS, Huang PS, Chang SN, Wu CK, Hwang JJ, Chuang EY, Tsai CT (2019) Genome-wide copy number variation association study of atrial fibrillation related thromboembolic stroke. J Clin Med 8:332. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030332
Hundemer GL, Curhan GC, Yozamp N, Wang M, Vaidya A (2018) Incidence of atrial fibrillation and mineralocorticoid receptor activity in patients with medically and surgically treated primary aldosteronism. JAMA Cardiol 3:768–774. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2018.2003
Iwasaki YK, Nishida K, Kato T, Nattel S (2011) Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: implications for management. Circulation 124:2264–2274. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.111.019893
Jabbari J, Olesen MS, Holst AG, Nielsen JB, Haunso S, Svendsen JH (2011) Common polymorphisms in KCNJ5 [corrected] are associated with early-onset lone atrial fibrillation in Caucasians. Cardiology 118:116–120. https://doi.org/10.1159/000323840
Kannel WB, Benjamin EJ (2009) Current perceptions of the epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Cardiol Clin 27(13–24):vii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccl.2008.09.015
Kertai MD et al (2015) Genome-wide association study of new-onset atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. Am Heart J 170:580.e528–590.e528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2015.06.009
Kim MH, Johnston SS, Chu BC, Dalal MR, Schulman KL (2011) Estimation of total incremental health care costs in patients with atrial fibrillation in the United States. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 4:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1161/circoutcomes.110.958165
Klein RJ et al (2005) Complement factor H polymorphism in age-related macular degeneration. Science (New York, NY) 308:385–389. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1109557
Lai LP et al (2002) Association of the human minK gene 38G allele with atrial fibrillation: evidence of possible genetic control on the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J 144:485–490. https://doi.org/10.1067/mhj.2002.123573
Laitinen-Forsblom PJ, Makynen P, Makynen H, Yli-Mayry S, Virtanen V, Kontula K, Aalto-Setala K (2006) SCN5A mutation associated with cardiac conduction defect and atrial arrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 17:480–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8167.2006.00411.x
Larson MG et al (2007) Framingham Heart Study 100 K project: genome-wide associations for cardiovascular disease outcomes. BMC Med Genet 8(Suppl 1):S5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-8-s1-s5
Lee JY et al (2017) Korean atrial fibrillation network genome-wide association study for early-onset atrial fibrillation identifies novel susceptibility loci. Eur Heart J 38:2586–2594. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx213
Li RG et al (2013) Mutations of the SCN4B-encoded sodium channel beta4 subunit in familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med 32:144–150. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1355
Lin H et al (2017) Methylome-wide association study of atrial fibrillation in framingham heart study. Sci Rep 7:40377. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40377
Lip GY et al (2016) Atrial fibrillation. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16016. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.16
Low SK et al (2017) Identification of six new genetic loci associated with atrial fibrillation in the Japanese population. Nat Genet 49:953–958. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3842
Lozano-Velasco E et al (2016) Pitx2 impairs calcium handling in a dose-dependent manner by modulating Wnt signalling. Cardiovasc Res 109:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvv207
Lubitz SA et al (2010) Association between familial atrial fibrillation and risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation. JAMA 304:2263–2269. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.1690
Lubitz SA et al (2016) Whole exome sequencing in atrial fibrillation. PLoS Genet 12:e1006284. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006284
Luo X, Yang B, Nattel S (2015) MicroRNAs and atrial fibrillation: mechanisms and translational potential. Nat Rev Cardiol 12:80–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2014.178
Mann SA et al (2012) Epistatic effects of potassium channel variation on cardiac repolarization and atrial fibrillation risk. J Am Coll Cardiol 59:1017–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2011.11.039
Moore LD, Le T, Fan G (2013) DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:23–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.112
Nadadur RD et al (2016) Pitx2 modulates a Tbx5-dependent gene regulatory network to maintain atrial rhythm. Sci Transl Med 8:354ra115. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf4891
Nattel S, Harada M (2014) Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: recent advances and translational perspectives. J Am Coll Cardiol 63:2335–2345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.555
Nelson MR et al (2015) The support of human genetic evidence for approved drug indications. Nat Genet 47:856–860. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3314
Ng SB et al (2009) Targeted capture and massively parallel sequencing of 12 human exomes. Nature 461:272–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08250
Nielsen JB et al (2018a) Genome-wide study of atrial fibrillation identifies seven risk loci and highlights biological pathways and regulatory elements involved in cardiac development. Am J Hum Genet 102:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.12.003
Nielsen JB et al (2018b) Biobank-driven genomic discovery yields new insight into atrial fibrillation biology. Nat Genet 50:1234–1239. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0171-3
Nishida K, Michael G, Dobrev D, Nattel S (2010) Animal models for atrial fibrillation: clinical insights and scientific opportunities. Europace 12:160–172. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eup328
Oberti C, Wang L, Li L, Dong J, Rao S, Du W, Wang Q (2004) Genome-wide linkage scan identifies a novel genetic locus on chromosome 5p13 for neonatal atrial fibrillation associated with sudden death and variable cardiomyopathy. Circulation 110:3753–3759. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Cir.0000150333.87176.C7
Ogimoto A, Hamada M, Nakura J, Miki T, Hiwada K (2002) Relation between angiotensin-converting enzyme II genotype and atrial fibrillation in Japanese patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Hum Genet 47:184–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100380200021
Olson TM et al (2005) Sodium channel mutations and susceptibility to heart failure and atrial fibrillation. JAMA 293:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.293.4.447
Olson TM et al (2006) Kv1.5 channelopathy due to KCNA5 loss-of-function mutation causes human atrial fibrillation. Hum Mol Genet 15:2185–2191. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddl143
Orr N et al (2016) A mutation in the atrial-specific myosin light chain gene (MYL4) causes familial atrial fibrillation. Nat Commun 7:11303. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11303
Pan H, Richards AA, Zhu X, Joglar JA, Yin HL, Garg V (2009) A novel mutation in LAMIN A/C is associated with isolated early-onset atrial fibrillation and progressive atrioventricular block followed by cardiomyopathy and sudden cardiac death. Heart Rhythm 6:707–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.01.037
Park JK et al (2017) Good responders to catheter ablation for long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: clinical and genetic characteristics. J Cardiol 69:584–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjcc.2016.04.017
Parvez B et al (2012) Symptomatic response to antiarrhythmic drug therapy is modulated by a common single nucleotide polymorphism in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 60:539–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.01.070
Parvez B et al (2013) Common genetic polymorphism at 4q25 locus predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence after successful cardioversion. Heart Rhythm 10:849–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.02.018
Posch MG et al (2010) Mutations in the cardiac transcription factor GATA4 in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Eur J Med Genet 53:201–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2010.03.008
Ravn LS et al (2008) Gain of function in IKs secondary to a mutation in KCNE5 associated with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 5:427–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2007.12.019
Ren X et al (2010) Identification of NPPA variants associated with atrial fibrillation in a Chinese GeneID population. Int J Clin Chem 411:481–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2009.12.019
Rickels R, Shilatifard A (2018) Enhancer logic and mechanics in development and disease. Trends Cell Biol 28:608–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2018.04.003
Ritchie MD et al (2012) Chromosome 4q25 variants are genetic modifiers of rare ion channel mutations associated with familial atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 60:1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.04.030
Roselli C et al (2018) Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study for atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 50:1225–1233. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0133-9
Sati S, Cavalli G (2017) Chromosome conformation capture technologies and their impact in understanding genome function. Chromosoma 126:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-016-0593-6
Savio-Galimberti E et al (2014) SCN10A/Nav1.8 modulation of peak and late sodium currents in patients with early onset atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 104:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvu170
Shen K et al (2017) DNA methylation dysregulations in valvular atrial fibrillation. Clin Cardiol 40:686–691. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.22715
Shoemaker MB et al (2015) Common genetic variants and response to atrial fibrillation ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 8:296–302. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.114.001909
Sinner MF et al (2014) Integrating genetic, transcriptional, and functional analyses to identify 5 novel genes for atrial fibrillation. Circulation 130:1225–1235. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.114.009892
Syeda F, Kirchhof P, Fabritz L (2017) PITX2-dependent gene regulation in atrial fibrillation and rhythm control. J Physiol 595:4019–4026. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp273123
Tao Y et al (2014) Pitx2, an atrial fibrillation predisposition gene, directly regulates ion transport and intercalated disc genes. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 7:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.113.000259
Tao H, Shi KH, Yang JJ, Li J (2016) Epigenetic mechanisms in atrial fibrillation: new insights and future directions. Trends Cardiovasc Med 26:306–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2015.08.006
Thorolfsdottir RB et al (2017) A missense variant in PLEC increases risk of atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 70:2157–2168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.09.005
Tsai CT et al (2004) Renin-angiotensin system gene polymorphisms and atrial fibrillation. Circulation 109:1640–1646. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Cir.0000124487.36586.26
Tsai CT, Lai LP, Hwang JJ, Lin JL, Chiang FT (2008) Molecular genetics of atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2008.02.072
Tsai CT et al (2016) Genome-wide screening identifies a KCNIP1 copy number variant as a genetic predictor for atrial fibrillation. Nat Commun 7:10190. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10190
Tucker NR, Ellinor PT (2014) Emerging directions in the genetics of atrial fibrillation. Circ Res 114:1469–1482. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.114.302225
Tucker NR, Clauss S, Ellinor PT (2016) Common variation in atrial fibrillation: navigating the path from genetic association to mechanism. Cardiovasc Res 109:493–501. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvv283
van den Berg NWE, Kawasaki M, Berger WR, Neefs J, Meulendijks E, Tijsen AJ, de Groot JR (2017) MicroRNAs in atrial fibrillation: from expression signatures to functional implications. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 31:345–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-017-6736-z
Volders PG et al (2007) Mapping a novel locus for familial atrial fibrillation on chromosome 10p11-q21. Heart Rhythm 4:469–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2006.12.023
Wagner AH et al (2016) DGIdb 2.0: mining clinically relevant drug-gene interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1036–D1044. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1165
Wang P et al (2010) Functional dominant-negative mutation of sodium channel subunit gene SCN3B associated with atrial fibrillation in a Chinese GeneID population. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 398:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.06.042
Wang J et al (2014a) Pitx2-microRNA pathway that delimits sinoatrial node development and inhibits predisposition to atrial fibrillation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:9181–9186. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1405411111
Wang J et al (2014b) NKX2-6 mutation predisposes to familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med 34:1581–1590. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.1971
Wang B et al (2020) Integrative omics approach to identifying genes associated with atrial fibrillation. Circ Res 126:350–360. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.119.315179
Watanabe H et al (2009) Mutations in sodium channel beta1- and beta2-subunits associated with atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2:268–275. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.108.779181
Weeke P et al (2014) Whole-exome sequencing in familial atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 35:2477–2483. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehu156
Weng LC et al (2017) Heritability of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 10:e001838. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.117.001838
Westphal S et al (2019) Genome-wide association study of myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, acute stroke, acute kidney injury and delirium after cardiac surgery—a sub-analysis of the RIPHeart-Study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 19:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-019-1002-x
Wijesurendra RS, Casadei B (2019) Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. Heart (British Cardiac Society) 105:1860–1867. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2018-314267
Wijffels MC, Kirchhof CJ, Dorland R, Allessie MA (1995) Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation. A study in awake chronically instrumented goats. Circulation 92:1954–1968. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.92.7.1954
Wu N et al (2019) Identification of long non-coding RNA and circular RNA expression profiles in atrial fibrillation. Heart Lung Circ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2019.10.018
Xia M et al (2005) A Kir2.1 gain-of-function mutation underlies familial atrial fibrillation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 332:1012–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.054
Xu S (2017) Relationship between angiotensin converting enzyme, apelin, mitochondrial DNA copy number and new-onset atrial fibrillation after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. The Forth Military Medical University, Shanxi Province
Yang Y et al (2004) Identification of a KCNE2 gain-of-function mutation in patients with familial atrial fibrillation. Am J Hum Genet 75:899–905. https://doi.org/10.1086/425342
Yang YQ et al (2011) GATA4 loss-of-function mutations in familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Clin Chem 412:1825–1830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2011.06.017
Yang YQ et al (2012) GATA6 loss-of-function mutation in atrial fibrillation. Eur J Med Genet 55:520–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2012.06.007
Ye J, Tucker NR, Weng LC, Clauss S, Lubitz SA, Ellinor PT (2016) A functional variant associated with atrial fibrillation regulates PITX2c expression through TFAP2a. Am J Hum Genet 99:1281–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.10.001
Yu W, Clyne M, Khoury MJ, Gwinn M (2010) Phenopedia and Genopedia: disease-centered and gene-centered views of the evolving knowledge of human genetic associations. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 26:145–146. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp618
Zhang DF, Liang B, Lin J, Liu B, Zhou QS, Yang YQ (2005) KCNE3 R53H substitution in familial atrial fibrillation. Chin Med J 118:1735–1738
Zhang M et al (2019) Long-range Pitx2c enhancer-promoter interactions prevent predisposition to atrial fibrillation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:22692–22698. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1907418116
Zhao G, Zhou J, Gao J, Liu Y, Gu S, Zhang X, Su P (2017) Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in permanent atrial fibrillation. Mol Med Rep 16:5505–5514. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7221
Funding
This work was supported by the research grant from the Science Foundation of Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital (grant number: YY2018-002), and Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (A2020453).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XH, YL and GL contributed towards the design and structure of the manuscript. XH and YL reviewed the literature, designed the figures and drafted the manuscript, GL, JZ, XW, and ZL contributed to the discussion, editing and revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Li, Y., Zhang, J. et al. The molecular genetic basis of atrial fibrillation. Hum Genet 139, 1485–1498 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-020-02203-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-020-02203-w